Abstract
The double-histone fold is a rare protein fold in which two consecutive regions characterized by the typical structure of histones assemble together, thus giving a histone pseudodimer. Previously, this fold was found in a few prokaryotic histones and in the regulatory region of guanine–nucleotide exchange factors of the Sos family. Standard methods of sequence comparison did not allow us to find new proteins containing a histone pseudodimer, as previously reported (Sondermann et al. 2003). However, a deeper investigation of protein sequences showed that the two histone folds included in Sos proteins share significant sequence similarity with nucleosomal histones. On the basis of this observation, we applied a specific strategy of sequence-homology search, which led to the identification of a new group of histone pseudodimers in Cca3 and proteins similar to Cca3 (Cca3S). A homology model of the histone pseudodimer included in rat Cca3 was constructed. A subsequent structure–function relationship study revealed that the histone pseudodimers included in Cca3 and Cca3S proteins, but not those present in Sos proteins, could retain the ability of mediating protein–DNA interactions, and could consequently act as DNA-binding modules.

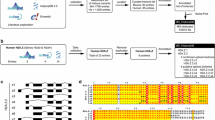
a and b Graphical representation of the statistical parameters (Pscore and Parea, see [20]) on which the prediction of DNA-binding site is based. Black crosses indicate the Pscore and Parea values calculated for 63 representative dsDNA-binding proteins, while the red asterisks refer to the values of the same parameters for Cca3 histone pseudodimer model (a), and for the amino-terminal domain of hSos1 (b). Only the proteins with Pscore > 0.12 and Parea > 250 (thus included in the upper right region of the graph) are considered dsDNA-binding proteins. c Localization of the predicted DNA-binding surface (in blue) on the rat Cca3 model







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cca3:
-
Confluent
- 3Y1:
-
Cell-associated
- hSos1:
-
Human Son of Sevenless 1
- Hs:
-
Homo sapiens
- Mm:
-
Mus musculus
- Rn:
-
Rattus norvegicus
- Tn:
-
Tetraodon nigroviridis
- Fr:
-
Fugu rubripes
- Xt:
-
Xenopus tropicalis
- Xl:
-
Xenopus laevis
- Dm:
-
Drosophila melanogaster
- Ag:
-
Anopheles gambiae
- Ce:
-
Caenorhabditis elegans
- Nr:
-
Non-redundant
References
Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ (1997) Nature 389:251–260
Fahrner RL, Cascio D, Lake JA, Slesarev A (2001) Protein Sci 10:2002–2007
Sondermann H, Soisson SM, Bar-Sagi D, Kuriyan J (2003) Structure 11:1583–1593
Baxevanis AD, Arents G, Moudrianakis EN, Landsman D (1995) Nucleic Acids Res 23:2685–2691
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Higgins D, Thompson J, Gibson T, Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Jones DT (1992) J Mol Biol 292:195–202
Cuff JA, Clamp ME, Siddiqui AS, Finlay M, Barton GJ (1998) Bioinformatics 14:892–893
Rost B, Sander C, Schneider R (1994) Comput Appl Biosci 1:53–60
Ginalski K, Elofsson A, Fischer D, Rychlewski L (2003) Bioinformatics 19:1015–1018
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) J Appl Cryst 26:283–291
DeLano LW, DeLano Scientific LLC, San Carlos, CA, USA
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) Electrophoresis 18:2714–2723
Bork P (1993) Proteins 17:363–374
Ahmad KF, Engel CK, Prive GG (1998) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12123–12128
Werten S, Mitschler A, Romier C, Gangloff YG, Thuault S, Davidson I, Moras D (2002) J Biol Chem 277:45502–45509
Schlessinger J (2000) Cell 103:211–215
Collins T, Stone JR, Williams AJ (2001) Mol Cell Biol 21:3609–3615
Tsuchiya Y, Kinoshita K, Nakamura H (2004) Proteins 55:885–894
Hayashi Y, Kiyono T, Fujita M, Ishibashi M (1997) Biochim Biophys Acta 1352:145–50
Hayashi Y, Ichinose M, Yuasa H, Tatematsu M, Ishibashi M (1997) FEBS Lett 406:147–150
Slesarev AI, Belova GI, Kozyavkin SA, Lake JA (1998) Nucleic Acids Res 26:427–430
Jorge R, Zarich N, Oliva JL, Azañedo M, Martínez N, de la Cruz X, Rojas JM (2002) J Biol Chem 277:44171–44179
Acknowledgements
M.V. thanks MIUR-FAR for financial support. E.S. was supported by a FIRC fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greco, C., Sacco, E., Vanoni, M. et al. Identification and in silico analysis of a new group of double-histone fold-containing proteins. J Mol Model 12, 76–84 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-005-0008-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-005-0008-8