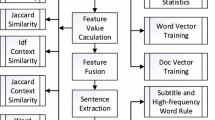
Abstract
The rapid growth of scientific literature has made it difficult for the researchers to quickly learn about the developments in their respective fields. Scientific summarization addresses this challenge by providing summaries of the important contributions of scientific papers. We present a framework for scientific summarization which takes advantage of the citations and the scientific discourse structure. Citation texts often lack the evidence and context to support the content of the cited paper and are even sometimes inaccurate. We first address the problem of inaccuracy of the citation texts by finding the relevant context from the cited paper. We propose three approaches for contextualizing citations which are based on query reformulation, word embeddings, and supervised learning. We then train a model to identify the discourse facets for each citation. We finally propose a method for summarizing scientific papers by leveraging the faceted citations and their corresponding contexts. We evaluate our proposed method on two scientific summarization datasets in the biomedical and computational linguistics domains. Extensive evaluation results show that our methods can improve over the state of the art by large margins.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Text Analysis Conference, http://tac.nist.gov/2014/BiomedSumm/.
Term Frequency - Inverted Document Frequency.
we indexed up to 3 consecutive sentences in our experiments.
We empirically set this threshold to 1.9 and 2.2 for the TAC and CL-SciSum datasets, respectively.
MEdical Subject Headings.
National Institute of Standards and Technology.
We do not report results of supervised model on TAC dataset because the TAC data do not have separate train and test sets.
The cut-off point has similar effect on all the models.
References
Abu-Jbara, A., Ezra, J., Radev, D.R.: Purpose and polarity of citation: towards nlp-based bibliometrics. In: NAACL-HLT, pp. 596–606 (2013)
Abu-Jbara, A., Radev, D.: Coherent citation-based summarization of scientific papers. In: Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, vol. 1, pp. 500–509. Association for Computational Linguistics (2011)
Abu-Jbara, A., Radev, D.: Reference scope identification in citing sentences. In: NAACL-HLT, pp. 80–90. ACL (2012)
Atanassova, I., Bertin, M., Larivière, V.: On the composition of scientific abstracts. J. Doc. 72(4), 636–647 (2016). doi:10.1108/JDOC-09-2015-0111
Bendersky, M., Croft, W.B.: Discovering key concepts in verbose queries. In: Proceedings of the 31st Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 491–498. ACM (2008)
Bengio, Y., Courville, A., Vincent, P.: Representation learning: a review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(8), 1798–1828 (2013). doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2013.50
Bengio, Y., Ducharme, R., Vincent, P., Janvin, C.: A neural probabilistic language model. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 3, 1137–1155 (2003)
Berg-Kirkpatrick, T., Gillick, D., Klein, D.: Jointly learning to extract and compress. In: Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, vol. 1, pp. 481–490. Association for Computational Linguistics (2011)
Bertin, M., Atanassova, I., Gingras, Y., Larivière, V.: The invariant distribution of references in scientific articles. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 67(1), 164–177 (2016). doi:10.1002/asi.23367
Bodenreider, O.: The unified medical language system (umls): integrating biomedical terminology. Nucl. Acids Res. 32(suppl 1), D267–D270 (2004)
Bornmann, L., Mutz, R.: Growth rates of modern science: a bibliometric analysis based on the number of publications and cited references. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 66(11), 2215–2222 (2015)
Cao, G., Nie, J.Y., Gao, J., Robertson, S.: Selecting good expansion terms for pseudo-relevance feedback. In: Proceedings of the 31st Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 243–250. ACM (2008)
Cao, Z., Li, W., Wu, D.: Polyu at cl-scisumm 2016. In: BIRNDL 2016 Joint Workshop on Bibliometric-enhanced Information Retrieval and NLP for Digital Libraries (2016)
Carbonell, J., Goldstein, J.: The use of mmr, diversity-based reranking for reordering documents and producing summaries. In: SIGIR, pp. 335–336. ACM (1998)
Celikyilmaz, A., Hakkani-Tur, D.: A hybrid hierarchical model for multi-document summarization. In: ACL, pp. 815–824. Association for Computational Linguistics (2010)
Chakraborty, T., Krishna, A., Singh, M., Ganguly, N., Goyal, P., Mukherjee, A.: Ferosa: A faceted recommendation system for scientific articles. In: Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 528–541. Springer (2016)
Chakraborty, T., Narayanam, R.: All fingers are not equal: intensity of references in scientific articles. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 1348–1358. Association for Computational Linguistics, Austin, Texas (2016). https://aclweb.org/anthology/D16-1142
Chali, Y.: Hasan, S.a.: Query-focused multi-document summarization: Automatic data annotations and supervised learning approaches. Nat. Lang. Eng. 18(1), 109–145 (2012). doi:10.1017/S1351324911000167
Chopra, S., Auli, M., Rush, A.M.: Abstractive sentence summarization with attentive recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pp. 93–98. Association for Computational Linguistics, San Diego, California (2016). http://www.aclweb.org/anthology/N16-1012
Clarke, J., Lapata, M.: Global inference for sentence compression an integer linear programming approach. J. Artif. Int. Res. 31(1), 399–429 (2008). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1622655.1622667
Cohan, A., Goharian, N.: Scientific article summarization using citation-context and article’s discourse structure. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 390–400. Association for Computational Linguistics, Lisbon, Portugal (2015). https://aclweb.org/anthology/D/D15/D15-1045
Cohan, A., Goharian, N.: Contextualizing citations for scientific summarization using word embeddings and domain knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 40th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, SIGIR ’17. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2017). http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/3077136.3080740
Cohan, A., Soldaini, L., Goharian, N.: Matching citation text and cited spans in biomedical literature: a search-oriented approach. In: Proceedings of the 2015 NAACL-HLT, pp. 1042–1048. Association for Computational Linguistics (2015). http://aclweb.org/anthology/N15-1110
Conroy, J.M., Davis, S.T.: Vector space and language models for scientific document summarization. In: Proceedings of NAACL-HLT, pp. 186–191 (2015)
Conroy, J.M., Schlesinger, J.D., Kubina, J., Rankel, P.A., OLeary, D.P.: Classy 2011 at tac: Guided and multi-lingual summaries and evaluation metrics. In: Proceedings of the Text Analysis Conference (2011)
De Waard, A., Maat, H.P.: Epistemic modality and knowledge attribution in scientific discourse: a taxonomy of types and overview of features. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Detecting Structure in Scholarly Discourse, pp. 47–55. Association for Computational Linguistics (2012)
Durrett, G., Berg-Kirkpatrick, T., Klein, D.: Learning-based single-document summarization with compression and anaphoricity constraints. In: Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, vol. 1, Long Papers. Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin, Germany (2016)
Elkiss, A., Shen, S., Fader, A., Erkan, G., States, D., Radev, D.: Blind men and elephants: what do citation summaries tell us about a research article? J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 59(1), 51–62 (2008)
Erkan, G., Radev, D.R.: Lexrank: graph-based lexical centrality as salience in text summarization. J. Artif. Intell. Res. (JAIR) 22(1), 457–479 (2004)
Erkan, G., Radev, D.R.: Lexrank: graph-based lexical centrality as salience in text summarization. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 22, 457–479 (2004)
Faruqui, M., Dodge, J., Jauhar, K.S., Dyer, C., Hovy, E., Smith, A.N.: Retrofitting word vectors to semantic lexicons. In: NAACL-HLT, pp. 1606–1615. Association for Computational Linguistics (2015). http://aclweb.org/anthology/N15-1184
Garzone, M., Mercer, R.E.: Towards an automated citation classifier. In: Conference of the Canadian Society for Computational Studies of Intelligence, pp. 337–346. Springer (2000)
Gong, Y., Liu, X.: Generic text summarization using relevance measure and latent semantic analysis. In: Proceedings of the 24th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 19–25. ACM (2001)
Guo, S., Sanner, S.: Probabilistic latent maximal marginal relevance. In: SIGIR, pp. 833–834. ACM (2010)
Harris, Z.S.: Distributional structure. Word 10(23), 146–162 (1954)
Hernández-alvarez, M., Gomez, J.M.: Survey about citation context analysis: tasks, techniques, and resources. Nat. Lang. Eng. 22(03), 327–349 (2016)
Hersh, W., Voorhees, E.: Trec genomics special issue overview. Inf. Retr. 12(1), 1–15 (2009). doi:10.1007/s10791-008-9076-6
Hill, F., Reichart, R., Korhonen, A.: Simlex-999: evaluating semantic models with genuine similarity estimation. Comput. Linguist. 41(4), 665–695 (2015). doi:10.1162/COLI_a_00237
Hulth, A.: Improved automatic keyword extraction given more linguistic knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 2003 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 216–223. Association for Computational Linguistics (2003)
Huston, S., Croft, W.B.: Evaluating verbose query processing techniques. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 291–298. ACM (2010)
Jaidka, K., Chandrasekaran, M.K., Rustagi, S., Kan, M.Y.: Overview of the 2nd computational linguistics scientific document summarization shared task (cl-scisumm 2016). In: Proceedings of the Joint Workshop on Bibliometric-Enhanced Information Retrieval and Natural Language Processing for Digital Libraries (BIRNDL 2016) (2016)
Jha, R., Coke, R., Radev, D.: Surveyor: a system for generating coherent survey articles for scientific topics. Ann. Arbor. 1001, 48109 (2015)
Jian, F., Huang, J.X., Zhao, J., He, T., Hu, P.: A simple enhancement for ad-hoc information retrieval via topic modelling. In: SIGIR, pp. 733–736. ACM (2016)
Jones, K.S., Walker, S., Robertson, S.E.: A probabilistic model of information retrieval: development and comparative experiments: part 2. Inf. Process. Manag. 36(6), 809–840 (2000)
Jurgens, D., Kumar, S., Hoover, R., McFarland, D., Jurafsky, D.: Citation classification for behavioral analysis of a scientific field. CoRR (2016)
Kataria, S., Mitra, P., Bhatia, S.: Utilizing context in generative bayesian models for linked corpus. In: AAAI, vol. 10, p. 1 (2010)
Klampfl, S., Rexha, A., Kern, R.: Identifying referenced text in scientific publications by summarisation and classification techniques. In: BIRNDL@ JCDL, pp. 122–131 (2016)
Le, Q., Mikolov, T.: Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In: ICML, pp. 1188–1196 (2014)
Li, L., Mao, L., Zhang, Y., Chi, J., Huang, T., Cong, X., Peng, H.: Cist system for cl-scisumm 2016 shared task. In: BIRNDL 2016 Joint Workshop on Bibliometric-Enhanced Information Retrieval and NLP for Digital Libraries (2016)
Lin, C.Y.: Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: Text Summarization Branches Out, Proceedings of the ACL-04 Workshop, pp. 74–81 (2004)
Lin, J., Madnani, N., Dorr, B.J.: Putting the user in the loop: interactive maximal marginal relevance for query-focused summarization. In: NAACL-HLT, pp. 305–308. Association for Computational Linguistics (2010)
Lipscomb, C.E.: Medical subject headings (mesh). Bull. Med. Libr. Assoc. 88(3), 265 (2000)
Mihalcea, R.: Graph-based ranking algorithms for sentence extraction, applied to text summarization. In: The Companion Volume to the Proceedings of 42nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 170–173. Association for Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain (2004)
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G.S., Dean, J.: Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: NIPS, pp. 3111–3119 (2013)
Miller, G.A.: Wordnet: a lexical database for english. Commun. ACM 38(11), 39–41 (1995)
Moraes, L., Baki, S., Verma, R., Lee, D.: University of houston at cl-scisumm 2016: Svms with tree kernels and sentence similarity. In: BIRNDL@ JCDL, pp. 113–121 (2016)
Mrkšić, N., Séaghdha, D.Ó., Thomson, B., Gašić, M., Rojas-Barahona, L., Su, P.H., Vandyke, D., Wen, T.H., Young, S.: Counter-fitting word vectors to linguistic constraints. In: NAACL-HLT (2016)
Nakov, P.I., Schwartz, A.S., Hearst, M.: Citances: Citation sentences for semantic analysis of bioscience text. In: Proceedings of the SIGIR’04 Workshop on Search and Discovery in Bioinformatics, pp. 81–88 (2004)
Nomoto, T.: Neal: A neurally enhanced approach to linking citation and reference. In: BIRNDL 2016 Joint Workshop on Bibliometric-Enhanced Information Retrieval and NLP for Digital Libraries (2016)
Osborne, M.: Using maximum entropy for sentence extraction. In: Proceedings of the ACL-02 Workshop on Automatic Summarization, vol. 4, pp. 1–8. Association for Computational Linguistics (2002)
Page, L., Brin, S., Motwani, R., Winograd, T.: The pagerank citation ranking: Bringing order to the web. (1999)
Paul, M., Zhai, C., Girju, R.: Summarizing contrastive viewpoints in opinionated text. In: EMNLP, pp. 66–76. Association for Computational Linguistics (2010). http://aclweb.org/anthology/D10-1007
Pennington, J., Socher, R., Manning, C.D.: Glove: global vectors for word representation. EMNLP 12, 1532–1543 (2014)
Ponte, J.M., Croft, W.B.: A language modeling approach to information retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 21st Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 275–281. ACM (1998)
Qazvinian, V., Radev, D., Mohammad, S.: Generating extractive summaries of scientific paradigms. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 46, 165–201 (2013)
Qazvinian, V., Radev, D.R.: Scientific paper summarization using citation summary networks. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Computational Linguistics, vol. 1, pp. 689–696. Association for Computational Linguistics (2008)
Qazvinian, V., Radev, D.R.: Identifying non-explicit citing sentences for citation-based summarization. In: Proceedings of the 48th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 555–564. Association for Computational Linguistics (2010)
Qazvinian, V., Radev, D.R., Mohammad, S.M., Dorr, B., Zajic, D., Whidby, M., Moon, T.: Generating extractive summaries of scientific paradigms. J. Artif. Int. Res. 46(1), 165–201 (2013). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2512538.2512543
Robertson, S., Zaragoza, H.: The Probabilistic Relevance Framework: BM25 and Beyond. Now Publishers Inc, Hanover (2009)
Rush, A.M., Chopra, S., Weston, J.: A neural attention model for abstractive sentence summarization. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 379–389. Association for Computational Linguistics, Lisbon, Portugal (2015). http://aclweb.org/anthology/D15-1044
Saggion, H., AbuRaed, A., Ronzano, F.: Trainable citation-enhanced summarization of scientific articles. In: Cabanac G, Chandrasekaran MK, Frommholz I, Jaidka K, Kan M, Mayr P, Wolfram D, editors. Proceedings of the Joint Workshop on Bibliometric-enhanced Information Retrieval and Natural Language Processing for Digital Libraries (BIRNDL); 2016 June 23; Newark, United States. CEUR Workshop Proceedings:[Sl]; 2016. p. 175-86. CEUR Workshop Proceedings (2016)
Snomed, C.: Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine-Clinical Terms. International Health Terminology Standards Development Organisation, Copenhagen (2011)
Sparck Jones, K.: A statistical interpretation of term specificity and its application in retrieval. J. Doc. 28(1), 11–21 (1972)
Steinberger, J., Jezek, K.: Using latent semantic analysis in text summarization and summary evaluation. In: Proceedings of ISIM04, pp. 93–100 (2004)
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., Le, Q.V.: Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In: Welling, M. et al. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 3104–3112. Curran Associates, Inc. (2014)
Teufel, S., Moens, M.: Summarizing scientific articles: experiments with relevance and rhetorical status. Comput. Linguist. 28(4), 409–445 (2002). doi:10.1162/089120102762671936
Teufel, S., Siddharthan, A., Tidhar, D.: Automatic classification of citation function. In: EMNLP ’06, p. 103 (2006)
Vanderwende, L., Suzuki, H., Brockett, C., Nenkova, A.: Beyond sumbasic: task-focused summarization with sentence simplification and lexical expansion. Inf. Process. Manag. 43(6), 1606–1618 (2007)
Wang, S., Manning, C.D.: Baselines and bigrams: simple, good sentiment and topic classification. In: Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Short Papers, vol. 2, pp. 90–94. Association for Computational Linguistics (2012)
Zhai, C., Lafferty, J.: A study of smoothing methods for language models applied to information retrieval. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. (TOIS) 22(2), 179–214 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohan, A., Goharian, N. Scientific document summarization via citation contextualization and scientific discourse. Int J Digit Libr 19, 287–303 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00799-017-0216-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00799-017-0216-8