Abstract
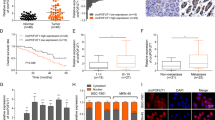
Autophagy-related gene 7 (ATG7) and miR-106a play an important role in cancer cell autophagy and apoptosis, but the outcome of ATG7 and miR-106a in colorectal cancer (CRC) still remains not clear. In this study, we found that ATG7 and miR-106a expression were mutually related with cell death and prognosis in CRC patients. In addition, we also showed that ATG7 and miR-106a expression were changeable in colorectal cancer cell lines when compared with normal cell lines, but ATG7 and miR-106a mRNA level was negatively correlated. Furthermore, ATG7 protein and mRNA levels decreased after over-expression of miR-106a, whereas the suppression of ATG7 had the opposite effect. We confirmed that miR-106a down-regulated ATG7 mRNA level by binding the specific sequence of ATG7 mRNA 3′UTR region. Moreover, the over-expression of ATG7 induced CRC cells death both in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, our study data demonstrated that ATG7 aggravated the cell death of CRC, which was inhibited by miR-106a.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2016) Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut
Baquero P, Karvela M, Mitchell R, Mukhopadhyay A, Pellicano F, Hopcroft L, Holyoake TL, Helgason G V (2015) The autophagy related protein ATG7 regulates differentiation and energy metabolism of CML cells. Br J Haematol 6
Bovell LC, Shanmugam C, Putcha BD, Katkoori VR, Zhang B, Bae S, Singh KP, Grizzle WE, Manne U (2013) The prognostic value of microRNAs varies with patient race/ethnicity and stage of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19:3955–3965
Brody H (2015) Colorectal cancer. Nature 521:S1
Catela IT, Aralica G, Cacev T, Loncar B, Kapitanovic S (2013) miR-106a overexpression and pRB downregulation in sporadic colorectal cancer. Exp Mol Pathol 94:148–154
Chang TK, Shravage BV, Hayes SD, Powers CM, Simin RT, Wade HJ, Baehrecke EH (2013) Uba1 functions in Atg7- and Atg3-independent autophagy. Nat Cell Biol 15:1067–1078
Chen WY, Zhao XJ, Yu ZF, Hu FL, Liu YP, Cui BB, Dong XS, Zhao YS (2015) The potential of plasma miRNAs for diagnosis and risk estimation of colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:7092–7101
Comincini S, Allavena G, Palumbo S, Morini M, Durando F, Angeletti F, Pirtoli L, Miracco C (2013) microRNA-17 regulates the expression of ATG7 and modulates the autophagy process, improving the sensitivity to temozolomide and low-dose ionizing radiation treatments in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther 14:574–586
Ergun M, Eyigor S, Karaca B, Kisim A, Uslu R (2013) Effects of exercise on angiogenesis and apoptosis-related molecules, quality of life, fatigue and depression in breast cancer patients. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 22:626–637
Gómez-Puerto MC, Folkerts H, Wierenga ATJ, Schepers K, Schuringa JJ, Coffer PJ, Vellenga E (2016) Autophagy proteins ATG5 and ATG7 are essential for the maintenance of human CD34+ hematopoietic stem-progenitor cells. Stem Cells
Hao H, Liu L, Zhang D, Wang C, Xia G, Zhong F, Hu X (2016) Diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-106a in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.13766
Hofius D, Schultz-Larsen T, Joensen J, Tsitsigiannis DI, Petersen NH, Mattsson O, Jorgensen LB, Jones JD, Mundy J, Petersen M (2009) Autophagic components contribute to hypersensitive cell death in Arabidopsis. Cell 137:773–783
Hsieh YY, Lo HL, Yang PM (2016) EZH2 inhibitors transcriptionally upregulate cytotoxic autophagy and cytoprotective unfolded protein response in human colorectal cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res 6:1661–1680
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Ueno T, Iwata J, Murata S, Tanida I, Ezaki J, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Uchiyama Y (2005) Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7. J Cell Biol 169:425–434
Ma HL, Wen XP, Zhang XZ, Wang XL, Zhao DL, Che SM, Dang CX (2015) miR-106a* inhibits the proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cells by targeting CDK2-associated Cullin 1 (CACUL1). Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 61:56–62
Masui A, Hamada M, Kameyama H, Wakabayashi K, Takasu A, Imai T, Iwai S, Yura Y (2016) Autophagy as a survival mechanism for squamous cell carcinoma cells in endonuclease G-mediated apoptosis. PLoS One 11:e162786
Mccoy F, Hurwitz J, Mctavish N, Paul I, Barnes C, O’Hagan B, Odrzywol K, Murray J, Longley D, Mckerr G (2009) Obatoclax induces Atg7-dependent autophagy independent of beclin-1 and BAX/BAK. Cell Death Dis 1:e108
Moscat J, Diaz-Meco MT (2009) p62 at the crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell 137:1001–1004
Qi L, Bart J, Tan LP, Platteel I, Sluis TVD, Huitema S, Harms G, Fu L, Hollema H, Berg AVD (2009) Expression of miR-21 and its targets (PTEN, PDCD4, TM1) in flat epithelial atypia of the breast in relation to ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive carcinoma. BMC Cancer 9:163
Qiu Y, Yuan R, Zhang S, Chen L, Huang D, Hao H, Shao J (2015) Rock2 stabilizes beta-catenin to promote tumor invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 467:629–637
Wang R, Li Y, Hou Y, Yang Q, Chen S, Wang X, Wang Z, Yang Y, Chen C, Wang Z et al (2015) The PDGF-D/miR-106a/Twist1 pathway orchestrates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine resistance hepatoma cells. Oncotarget 6:7000–7010
Wang Z, Liu M, Zhu H, Zhang W, He S, Hu C, Quan L, Bai J, Xu N (2013) miR-106a is frequently upregulated in gastric cancer and inhibits the extrinsic apoptotic pathway by targeting FAS. Mol Carcinog 52:634–646
Yang G, Zhang R, Chen X, Mu Y, Ai J, Shi C, Liu Y, Shi C, Sun L, Rainov N G et al (2011) MiR-106a inhibits glioma cell growth by targeting E2F1 independent of p53 status. J Mol Med (Berl) 89:1037–1050
Yang G, Zhang R, Chen X, Mu Y, Ai J, Shi C, Liu Y, Shi C, Sun L, Rainov NG et al (2011) MiR-106a inhibits glioma cell growth by targeting E2F1 independent of p53 status. J Mol Med (Berl) 89:1037–1050
Yu L, Alva A, Su H, Dutt P, Freundt E, Welsh S, Baehrecke EH, Lenardo MJ (2004) Regulation of an ATG7-beclin 1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science 304:1500–1502
Yuan R, Zhi Q, Zhao H, Han Y, Gao L, Wang B, Kou Z, Guo Z, He S, Xue X et al (2015) Upregulated expression of miR-106a by DNA hypomethylation plays an oncogenic role in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol 36:3093–3100
Zeng Y, Gang H, Mo Y, Wang W, Hong C (2015) MIR137 regulates starvation-induced autophagy by targeting ATG7. J Mol Neurosci 56:815–821
Zhang Y, Lu Q, Cai X (2013) MicroRNA-106a induces multidrug resistance in gastric cancer by targeting RUNX3. FEBS Lett 587:3069–3075
Zhu M, Zhang N, He S, Yan R, Zhang J (2016) MicroRNA-106a functions as an oncogene in human gastric cancer and contributes to proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Clin Exp Metastasis 33:509–519
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Ethics statement
The study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of our institution that conforming to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Haibin Hao, Guangfeng Xia, and Chao Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, H., Xia, G., Wang, C. et al. miR-106a suppresses tumor cells death in colorectal cancer through targeting ATG7. Med Mol Morphol 50, 76–85 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-016-0150-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-016-0150-7