Abstract
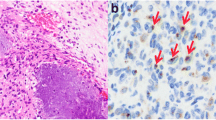
Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors (PMT) are the most common cause of tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO) related to mesenchymal neoplasms. The lineage of differentiation of PMTs has not been elucidated in existing literature. Fourteen cases of PMT were analyzed for this study to elucidate its lineage. We used vascular and/or lymphatic endothelial markers for the immunohistochemical analysis, which included CD31, CD34, factor VIII-related antigen, podoplanin, Freund’s leukemia integration site 1 (FLI1), and avian v-ets erythroblastosis virus E26 oncogene homolog (ERG). FLI1 and ERG were stained in all cases with proportion of immunopositive tumor cells largely more than 50 %; staining intensity was moderate or strong for both FLI1 and ERG. The tumor cells were stained with CD31 and/or CD34, with significantly less staining than observed for FLI1 and ERG. The tumor cells were completely immunonegative for factor VIII-related antigen and podoplanin. FLI1 and ERG are known to have considerable specificity to endothelial cells; ERG is more widely equipped in surgical pathology laboratories than FLI1. We concluded that ERG (or FLI1 if available) is useful marker for the diagnosis of PMT, and that PMTs may have an endothelial cell lineage.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chong WH, Molinolo AA, Chen CC, Collins MT (2011) Tumor-induced osteomalacia. Endocr Relat Cancer 18(3):R53–R77. doi:10.1530/ERC-11-0006
Nakahama H, Nakanishi T, Uno H, Takaoka T, Taji N, Uyama O, Kitada O, Sugita M, Miyauchi A, Sugishita T et al (1995) Prostate cancer-induced oncogenic hypophosphatemic osteomalacia. Urol Int 55(1):38–40
Folpe AL, Fanburg-Smith JC, Billings SD, Bisceglia M, Bertoni F, Cho JY, Econs MJ, Inwards CY, Jan de Beur SM, Mentzel T, Montgomery E, Michal M, Miettinen M, Mills SE, Reith JD, O’Connell JX, Rosenberg AE, Rubin BP, Sweet DE, Vinh TN, Wold LE, Wehrli BM, White KE, Zaino RJ, Weiss SW (2004) Most osteomalacia-associated mesenchymal tumors are a single histopathologic entity: an analysis of 32 cases and a comprehensive review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol 28(1):1–30
Folpe AL (2013) phosphaturic mesenchymal tumour. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone. IARC, Lyon
Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2007) FGF23 is a hormone-regulating phosphate metabolism–unique biological characteristics of FGF23. Bone 40(5):1190–1195. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2006.12.062
Bhattacharyya N, Chong WH, Gafni RI, Collins MT (2012) Fibroblast growth factor 23: state of the field and future directions. Trends Endocrinol Metab 23(12):610–618. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2012.07.002
Westra WH, Gerald WL, Rosai J (1994) Solitary fibrous tumor. consistent CD34 immunoreactivity and occurrence in the orbit. Am J Surg Pathol 18(10):992–998
Miettinen M, Lindenmayer AE, Chaubal A (1994) Endothelial cell markers CD31, CD34, and BNH9 antibody to H- and Y-antigens–evaluation of their specificity and sensitivity in the diagnosis of vascular tumors and comparison with von Willebrand factor. Mod Pathol 7(1):82–90
Breiteneder-Geleff S, Soleiman A, Kowalski H, Horvat R, Amann G, Kriehuber E, Diem K, Weninger W, Tschachler E, Alitalo K, Kerjaschki D (1999) Angiosarcomas express mixed endothelial phenotypes of blood and lymphatic capillaries: podoplanin as a specific marker for lymphatic endothelium. Am J Pathol 154(2):385–394. doi:10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65285-6
Folpe AL, Chand EM, Goldblum JR, Weiss SW (2001) Expression of Fli-1, a nuclear transcription factor, distinguishes vascular neoplasms from potential mimics. Am J Surg Pathol 25(8):1061–1066
Miettinen M, Wang ZF, Paetau A, Tan SH, Dobi A, Srivastava S, Sesterhenn I (2011) ERG transcription factor as an immunohistochemical marker for vascular endothelial tumors and prostatic carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 35(3):432–441. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318206b67b
Sato Y (2001) Role of ETS family transcription factors in vascular development and angiogenesis. Cell Struct Funct 26(1):19–24
Williams K, Flanagan A, Folpe A, Thakker R, Athanasou NA (2007) Lymphatic vessels are present in phosphaturic mesenchymal tumours. Virchows Arch 451(5):871–875. doi:10.1007/s00428-007-0471-y
Yaskiv O, Rubin BP, He H, Falzarano S, Magi-Galluzzi C, Zhou M (2012) ERG protein expression in human tumors detected with a rabbit monoclonal antibody. Am J Clin Pathol 138(6):803–810. doi:10.1309/ajcp3k5vufalztkc
Morais CL, Han JS, Gordetsky J, Nagar MS, Anderson AE, Lee S, Hicks JL, Zhou M, Magi-Galluzzi C, Shah RB, Epstein JI, De Marzo AM, Lotan TL (2015) Utility of PTEN and ERG immunostaining for distinguishing high-grade PIN from intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy. Am J Surg Pathol 39(2):169–178. doi:10.1097/pas.0000000000000348
Schneider TM, Osunkoya AO (2014) ERG expression in intraductal carcinoma of the prostate: comparison with adjacent invasive prostatic adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 27(8):1174–1178. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2013.248
Tomlins SA, Palanisamy N, Brenner JC, Stall JN, Siddiqui J, Thomas DG, Lucas DR, Chinnaiyan AM, Kunju LP (2013) Usefulness of a monoclonal ERG/FLI1 antibody for immunohistochemical discrimination of Ewing family tumors. Am J Clin Pathol 139(6):771–779. doi:10.1309/ajcpn4l1bmrqpeit
van de Rijn M, Lombard CM, Rouse RV (1994) Expression of CD34 by solitary fibrous tumors of the pleura, mediastinum, and lung. Am J Surg Pathol 18(8):814–820
Houang M, Clarkson A, Sioson L, Elston MS, Clifton-Bligh RJ, Dray M, Ranchere-Vince D, Decouvelaere AV, de la Fouchardiere A, Gill AJ (2013) Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors show positive staining for somatostatin receptor 2A (SSTR2A). Hum Pathol 44(12):2711–2718. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2013.07.016
Clugston E, Gill AC, Graf N, Bonar F, Gill AJ (2015) Use of immunohistochemistry for SSTR2A to support a diagnosis of phosphaturic mesenchymal tumour. Pathology 47(2):173–175. doi:10.1097/pat.0000000000000221
Portela-Gomes GM, Hacker GW, Weitgasser R (2004) Neuroendocrine cell markers for pancreatic islets and tumors. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 12(3):183–192
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Kei Sakuma for his excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tajima, S., Takashi, Y., Ito, N. et al. ERG and FLI1 are useful immunohistochemical markers in phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors. Med Mol Morphol 49, 203–209 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-015-0115-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-015-0115-2