Abstract
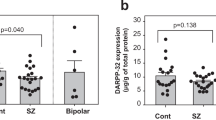
The prevalence of dopamine and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein 32kD (DARPP-32) is associated with the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. To date, the findings on DARPP-32 cellular expression and distribution in postmortem brains from patients with schizophrenia have been inconsistent. To clarify the detailed cellular expression of DARPP-32 in patients with schizophrenia, we immunohistochemically stained sections from postmortem brains using specific antibodies. We measured the density of immunopositive cells in various brain regions including the prefrontal cortex and compared the data from nine schizophrenia subjects with those of nine age- and sex-matched control subjects. The density of DARPP-32-immunoreactive (IR) neurons was significantly lower in layers II-V of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) from subjects with schizophrenia. In contrast, there were no marked differences in DARPP-32 expression in other brain regions. In addition, the density of threonine (Thr34)-phosphorylated DARPP-32-IR neurons was significantly higher in layer V of DLPFC from subjects with schizophrenia. These results suggest that the decrease in DARPP-32 in schizophrenia was more marked in neurons of DLPFC than in other cells or other brain regions, and that this decrease might be partly compensated for by an increase in expression of Thr34-phosphorylated DARPP-32 in DLPFC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Del Arco A, Mora F (2008) Prefrontal cortex-nucleus accumbens interaction: in vivo modulation by dopamine and glutamate in the prefrontal cortex. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 90:226–235
Berger B, Febvret A, Greengard P, Goldman-Rakic PS (1990) DARPP-32, a phosphoprotein enriched in dopaminoceptive neurons bearing D1 receptors: distribution in the cerebral cortex of newborn and adult rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 229:327–348
Brene S, Hall H, Lindefors N, Karlson P, Halldin C, Sedvall G (1995) Distribution of messenger RNAs for D1 dopamine receptors and DARPP-32 in striatum and cerebral cortex of the cynomolgus monkey: relationship to D1 dopamine receptors. Neuroscience 67:37–48
Ouimet C, Miller PE, Hemmings HC Jr, Walaas SI, Greengard P (1984) DARPP-32, a dopamine-and adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. III: Immunocytochemical localization. J Neurosci 4:111–124
Ouimet C, Lamantia AS, Goldman-Rakic P, Rakic P, Greengard P (1992) Immunocytochemical localization of DARPP-32, a dopamine and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein, in the primate brain. J Comp Neurol 323:209–218
Walaas SI, Greengard P (1984) DARPP-32, a dopamine-and adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. I: Regional and cellular distribution in the rat brain. J Neurosci 4:84–98
Hemmings HC Jr, Nairn AC, Bibb JA, Greengard P (1995) Signal transduction in the striatum: DARPP-32, a molecular integrator of multiple signaling pathways. In: Ariano MA, Surmeier DJ (eds) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of neostriatal function. Landes, Austin, pp 283–297
Greengard P, Allen PB, Nairn AC (1999) Beyond the dopamine receptor: the DARPP-32/protein phosphatase-1 cascade. Neuron 23:435–447
Albert KA, Hemmings HC Jr, Adamo AIB, Potkin SG, Akbarian S, Sandman CA, Cotman CW, Bunney WE, Greengard P (2002) Evidence for decreased DARPP-32 in the prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:705–712
Ishikawa M, Mizukami K, Iwakiri M, Asada T (2007) Immunohistochemical and immunoblot analysis of dopamine and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein, relative molecular mass 32,000 (DARPP-32) in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:1177–1181
Baracskay KL, Haroutunian V, Meador-Woodruff JH (2006) Dopamine receptor signaling molecules are altered in elderly schizophrenic cortex. Synapse 60:271–279
Li CH, Liao HM, Hung TW, Chen CH (2006) Mutation analysis of DARPP-32 as a candidate gene for schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 87:1–5
Hu JX, Yu L, Shi YY, Zhao XZ, Meng JW, He G, Xu YF, Feng GY, He L (2007) An association study between PPP1R1B gene and schizophrenia in the Chinese population. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:1303–1306
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Straub RE, Lipska BK, Verchinski BA, Goldberg T, Callicott JH, Egan MF, Huffaker SS, Mattay VS, Kolachana B, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR (2007) Genetic evidence implicating DARPP-32 in human frontostriatal structure, function, and cognition. J Clin Invest 117:672–682
Clinton SM, Ibrahim HM, Frey KA, Davis KL, Haroutunian V, Meador-Woodruff JH (2005) Dopaminergic abnormalities in select thalamic nucleiin schizophrenia: involvement of the intracellular signal integrating proteins calcyon and spinophilin. Am J Psychiatry 162:1859–1871
Fienberg AA, Greengard P (2000) The DARPP-32 knockout mouse. Brain Res Rev 31:313–319
Grebb JA, Girault JA, Ehrlich M, Greengard P (1990) Chronic treatment of rats with SCH-23390 or raclopride does not affect the concentrations of DARPP-32 or its mRNA in dopamine-innervated brain regions. J Neurochem 55:204–207
Souza BR, Motta BS, Rosa DV, Torres KC, Castro AA, Comim CM, Sampaio AM, Lima FF, Jeromin A, Quevedo J, Romano-Silva MA (2008) DARPP-32 and NCS-1 expression is not altered in brains of rats treated with typical or atypical antipsychotics. Neurochem Res 33:533–538
Rajkowska G, Goldman-Rakic PS (1995a) Cytoarchitectonic definition of prefrontal areas in the normal human cortex: I. Remapping of areas 9 and 46 using quantitative criteria. Cereb Cortex 5:307–322
Rajkowska G, Goldman-Rakic PS (1995) Cytoarchitectonic definition of prefrontal areas in the normal human cortex: II. Variability in locations of areas 9 and 46 and relationship to the Talairach Coordinate System. Cereb Cortex 5:323–337
Selemon LD, Rajkowska G, Goldman-Rakic PS (1995) Abnormally high neuronal density in the schizophrenic cortex. A morphometric analysis of prefrontal area 9 and occipital area 17. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:805–818
Ito M, Depaz I, Wilce P, Suzuki T, Niwa S, Matsumoto I (2005) Expression of human neuronal protein 22, a novel cytoskeletonassociated protein, was decreased in the anterior cingulate cortex of schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 378:125–130
Iwazaki T, Shibata I, Niwa S, Matsumoto I (2004) Selective reduction of chromogranin A-like immunoreactivities in the prefrontal cortex of schizophrenic subjects: a post-mortem study. Neurosci Lett 367:293–297
Tamagaki C, Sedvall GC, Jönsson EG, Okugawa G, Hall H, Pauli S, Agartz I (2005) Altered white matter/gray matter proportions in the striatum of patients with schizophrenia: a volumetric MRI study. Am J Psychiatry 162:2315–2321
Lara DR, Gama CS, Belmonte-de-Abreu P, Portela LV, Gonçalves CA, Fonseca M, Hauck S, Souza DO (2001) Increased serum S100B protein in schizophrenia: a study in medication-free patients. J Psychiatr Res 35(6):347–350
Rothermundt M, Falkai P, Ponath G, Abel S, Bürkle H, Diedrich M, Hetzel G, Peters M, Siegmund A, Pedersen A, Maier W, Schramm J, Suslow T, Ohrmann P, Arolt V (2004) Glial cell dysfunction in schizophrenia indicated by increased S100B in the CSF. Mol Psychiatry 9:897–899
Coyle JT, Schwarcz R (2000) Mind glue: implications of glial cell biology for psychiatry. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:90–93
Rajkowska G, Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, Makkos Z, Meltzer H, Overholser J, Stockmeier C (2002) Layer-specific reductions in GFAPreactive astroglia in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 57:127–138
Webster MJ, O’Grady J, Kleinman JE, Weickert CS (2005) Glial fibrillary acidic protein mRNA levels in the cingulate cortex of individuals with depression, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Neuroscience 133:453–461
Johnston-Wilson NL, Sims CD, Hofmann JP, Anderson L, Shore AD, Torrey EF, Yolken RH (2000) Disease-specific alterations in frontal cortex brain proteins in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. The Stanley Neuropathology Consortium. Mol Psychiatry 5:142–149
Hakak Y, Walker JR, Li C, Wong WH, Davis KL, Buxbaum JD, Haroutunian V, Fienberg AA (2001) Genome-wide expression analysis reveals dysregulation of myelination-related genes in chronic schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:4746–4751
Park SK, Miller R, Krane I, Vartanian T (2001) The erbB2 gene is required for the development of terminally differentiated spinal cord oligodendrocytes. J Cell Biol 154:1245–1258
Fellin T, Sul JY, D’Ascenzo M, Takano H, Pascual O, Haydon PG (2006) Bidirectional astrocyte-neuron communication: the many roles of glutamate and ATP. Novartis Found Symp 276:208–217
D’Antoni S, Berretta A, Bonaccorso CM, Bruno V, Aronica E, Nicoletti F, Catania MV (2008) Metabotropic glutamate receptors in glial cells. Neurochem Res 33:2436–2443
Haydon PG (2001) Glia: listening and talking to the synapse. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:185–193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunii, Y., Ikemoto, K., Wada, A. et al. Detailed DARPP-32 expression profiles in postmortem brains from patients with schizophrenia: an immunohistochemical study. Med Mol Morphol 44, 190–199 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-010-0524-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-010-0524-1