Abstract
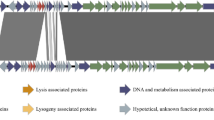
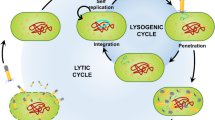
Toxin–antitoxin (TA) system is bacterial or archaeal genetic module consisting of toxin and antitoxin gene that be organized as a bicistronic operon. TA system could elicit programmed cell death, which is supposed to play important roles for the survival of prokaryotic population under various physiological stress conditions. The phage abortive infection system (AbiE family) belongs to bacterial type IV TA system. However, no archaeal AbiE family TA system has been reported so far. In this study, a putative AbiE TA system (PygAT), which is located in a genomic island PYG1 in the chromosome of Pyrococcus yayanosii CH1, was identified and characterized. In Escherichia coli, overexpression of the toxin gene pygT inhibited its growth while the toxic effect can be suppressed by introducing the antitoxin gene pygA in the same cell. PygAT also enhances the stability of shuttle plasmids with archaeal plasmid replication protein Rep75 in E. coli. In P. yayanosii, disruption of antitoxin gene pygA cause a significantly growth delayed under high hydrostatic pressure (HHP). The antitoxin protein PygA can specifically bind to the PygAT promoter region and regulate the transcription of pygT gene in vivo. These results show that PygAT is a functional TA system in P. yayanosii, and also may play a role in the adaptation to HHP environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravind L, Anantharaman V, Balaji S, Babu MM, Iyer LM (2005) The many faces of the helix-turn-helix domain: transcription regulation and beyond. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:231–262
Birrien JL, Zeng X, Jebbar M, Cambon-Bonavita MA, Querellou J, Oger P, Bienvenu N, Xiao X, Prieur D (2011) Pyrococcus yayanosii sp. nov., an obligate piezophilic hyperthermophilic archaeon isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2827–2831
Bustamante P, Tello M, Orellana O (2014) Toxin–antitoxin systems in the mobile genome of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. PLoS One 9:e112226
Cooper CR, Daugherty AJ, Tachdjian S, Blum PH, Kelly RM (2009) Role of vapBC toxin–antitoxin loci in the thermal stress response of Sulfolobus solfataricus. Biochem Soc Trans 37:123–126
Dy RL, Przybilski R, Semeijn K, Salmond GP, Fineran PC (2014) A widespread bacteriophage abortive infection system functions through a type IV toxin–antitoxin mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res 42:4590–4605
Fineran PC, Blower TR, Foulds IJ, Humphreys DP, Lilley KS, Salmond GP (2009) The phage abortive infection system, ToxIN, functions as a protein-RNA toxin–antitoxin pair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:894–899
Garvey P, Fitzgerald GF, Hill C (1995) Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of two abortive infection phage resistance determinants from the lactococcal plasmid pNP40. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4321–4328
Gerdes K, Rasmussen PB, Molin S (1986) Unique type of plasmid maintenance function: postsegregational killing of plasmid-free cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3116–3120
Goeders N, Van Melderen L (2014) Toxin–antitoxin systems as multilevel interaction systems. Toxins (Basel) 6:304–324
Hazan R, Engelberg-Kulka H (2004) Escherichia coli mazEF-mediated cell death as a defense mechanism that inhibits the spread of phage P1. Mol Genet Genom 272:227–234
He W, Huang T, Tang Y, Liu YH, Wu XL, Chen S, Chan W, Wang YJ, Liu XY, Chen S, Wang LR (2015) Regulation of DNA phosphorothioate modification in Salmonella enterica by DndB. Sci Rep 5:12368. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12368
Jun X, Lupeng L, Minjuan X, Oger P, Fengping W, Jebbar M, Xiang X (2011) Complete genome sequence of the obligate piezophilic hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus yayanosii CH1. J Bacteriol 193:4297–4298
Krupovic M, Gonnet M, Hania WB, Forterre P, Erauso G (2013) Insights into dynamics of mobile genetic elements in hyperthermophilic environments from five new Thermococcus plasmids. PLoS One 8:e49044
Landini P, Egli T, Wolf J, Lacour S (2014) SigmaS, a major player in the response to environmental stresses in Escherichia coli: role, regulation and mechanisms of promoter recognition. Environ Microbiol Rep 6:1–13
Li X, Fu L, Li Z, Ma X, Xiao X, Xu J (2015) Genetic tools for the piezophilic hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus yayanosii. Extremophiles 19:59–67
Li P, Tai C, Deng ZX, Gan JH, Oggioni MR, Ou HY (2016a) Identification and characterization of chromosomal relBE toxin–antitoxin locus in Streptomyces cattleya DSM46488. Sci Rep 6:32047
Li Z, Li X, Xiao X, Xu J (2016b) An integrative genomic island affects the adaptations of the piezophilic hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus yayanosii to high temperature and high hydrostatic pressure. Front Microbiol 7:1927
Makarova KS, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (2013) Comparative genomics of defense systems in archaea and bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 41:4360–4377
Masuda H, Tan Q, Awano N, Wu KP, Inouye M (2012a) YeeU enhances the bundling of cytoskeletal polymers of MreB and FtsZ, antagonizing the CbtA (YeeV) toxicity in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 84:979–989
Masuda H, Tan Q, Awano N, Yamaguchi Y, Inouye M (2012b) A novel membrane-bound toxin for cell division, CptA (YgfX), inhibits polymerization of cytoskeleton proteins, FtsZ and MreB, in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 328:174–181
Michoud G, Jebbar M (2016) High hydrostatic pressure adaptive strategies in an obligate piezophile Pyrococcus yayanosii. Sci Rep 6:27289
O’Connor L, Tangney M, Fitzgerald GF (1999) Expression, regulation, and mode of action of the AbiG abortive infection system of Lactococcus lactis sub sp. cremoris UC653. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:330–335
Otsuka Y, Yonesaki T (2012) Dmd of bacteriophage T4 functions as an antitoxin against Escherichia coli LsoA and RnlA toxins. Mol Microbiol 83:669–681
Page R, Peti W (2016) Toxin–antitoxin systems in bacterial growth arrest and persistence. Nat Chem Biol 12:208–214
Pecota DC, Wood TK (1996) Exclusion of T4 phage by the hok/sok killer locus from plasmid R1. J Bacteriol 178:2044–2050
Ramisetty BCM, Santhosh RS (2017) Endoribonuclease type II toxin–antitoxin systems: functional or selfish? Microbiology 163:931–939
Rolfe MD, Rice CJ, Lucchini S, Pin C, Thompson A, Cameron ADS, Alston M, Stringer MF, Betts RP, Baranyi J, Peck MW, Hinton JCD (2012) Lag phase is a distinct growth phase that prepares bacteria for exponential growth and involves transient metal accumulation. J Bacteriol 194:686–701
Schuster CF, Bertram R (2013) Toxin–antitoxin systems are ubiquitous and versatile modulators of prokaryotic cell fate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 340:73–85
Shao YC, Harrison EM, Bi DX, Tai C, He XY, Ou HY, Rajakumar K, Deng ZX (2011) TADB: a web-based resource for Type 2 toxin–antitoxin loci in bacteria and archaea. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D606–D611
Simonato F, Campanaro S, Lauro FM, Vezzi A, D’Angelo M, Vitulo N, Valle G, Bartlett DH (2006) Piezophilic adaptation: a genomic point of view. J Biotechnol 126:11–25
Tachdjian S, Kelly RM (2006) Dynamic metabolic adjustments and genome plasticity are implicated in the heat shock response of the extremely thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. J Bacteriol 188:4553–4559
Tan Q, Awano N, Inouye M (2011) YeeV is an Escherichia coli toxin that inhibits cell division by targeting the cytoskeleton proteins, FtsZ and MreB. Mol Microbiol 79:109–118
Tangney M, Fitzgerald GF (2002) AbiA, a lactococcal abortive infection mechanism functioning in Streptococcus thermophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6388–6391
Unterholzner SJ, Poppenberger B, Rozhon W (2013) Toxin–antitoxin systems: biology, identification, and application. Mob Genet Elem 3:e26219
Wang XX, Wood TK (2011) Toxin–antitoxin systems influence biofilm and persister cell formation and the general stress response. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:5577–5583
Wang X, Kim Y, Hong SH, Ma Q, Brown BL, Pu M, Tarone AM, Benedik MJ, Peti W, Page R, Wood TK (2011) Antitoxin MqsA helps mediate the bacterial general stress response. Nat Chem Biol 7:359–366
Winther KS, Gerdes K (2011) Enteric virulence associated protein VapC inhibits translation by cleavage of initiator tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:7403–7407
Wozniak RA, Waldor MK (2009) A toxin–antitoxin system promotes the maintenance of an integrative conjugative element. PLoS Genet 5:e1000439
Yamaguchi Y, Park JH, Inouye M (2011) Toxin–antitoxin systems in bacteria and archaea. Annu Rev Genet 45:61–79
Zeng X, Birrien JL, Fouquet Y, Cherkashov G, Jebbar M, Querellou J, Oger P, Cambon-Bonavita MA, Xiao X, Prieur D (2009) Pyrococcus CH1, an obligate piezophilic hyperthermophile: extending the upper pressure-temperature limits for life. ISME J 3:873–876
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41676121, 41376137) and the National Basic Research Program of China (“973” Program 2014CB441503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZL XX and JX designed the experiments; ZL and QHS performed the experiments; ZL, YZW and JX drafted the manuscript. All authors discussed and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by L. Huang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Song, Q., Wang, Y. et al. Identification of a functional toxin–antitoxin system located in the genomic island PYG1 of piezophilic hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus yayanosii. Extremophiles 22, 347–357 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-018-1002-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-018-1002-2