Abstract
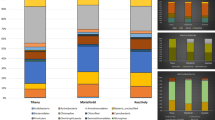
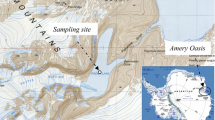
The potentially metabolically active components within the prokaryotic assemblages inhabiting the Antarctic Lake Limnopolar (Byers Peninsula, Maritime Antarctica) were investigated by a polyphasic approach which included culture-dependent and culture-independent methods (based on RNA molecules). Results support previous observations on the Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes dominance, followed by Actinobacteria, in Antarctic lakes. In particular, Alpha-, Betaproteobacteria and Bacteroidetes were mainly detected by CARD-FISH and cDNA cloning, whereas Gammaproteobacteria and Actinobacteria dominated within the cultivable fraction. Overall, this study demonstrates the survival potential and physiological heterogeneity of the prokaryotic community in the Lake Limnopolar. The microbial community composition in the lake is affected by external influences (such as marine environment by sea spray and seabird dropping, and microbial mats and mosses of the catchment). However, most external bacteria would be inactive, whereas typical polar taxa dominate the potentially active fraction and are subsidized by external nutrient sources, thus assuming the main biogeochemical roles within the lake.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amann RI, Binder BJ, Olson RJ, Chisholm SW, Devereux R, Stahl DA (1990) Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1919–1925
Barberán A, Casamayor EO (2010) Global phylogenetic community structure and betadiversity patterns of surface bacterioplankton metacommunities. Aquat Microb Ecol 59:1–10
Blazewicz SJ, Barnard RL, Daly RA, Firestone MK (2013) Evaluating rRNA as an indicator of microbial activity in environmental communities: limitations and uses. ISME J 7:2061–2068
Camacho A (2006) Planktonic microbial assemblages and the potential effect of metazooplankton predation on the food web of lakes from the maritime Antarctica and sub-Antarctic islands. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 5:176–185
Daims H, Brühl A, Amann R, Schleifer KH, Wagner M (1999) The domain-specific probe EUB338 is insufficient for the detection of all Bacteria: development and evaluation of a more comprehensive probe set. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:434–444
Darcy JL, Lynch RC, King AJ, Robeson MS, Schmidt SK (2011) Global distribution of Polaromonas phylotypes—evidence for a highly successful dispersal capacity. PLoS One 6(8):e23742
Fernández-Valiente E, Camacho A, Rochera C, Rico E, Vincent WF, Quesada A (2007) Community structure and physiological characterization of microbial mats in Byers Peninsula. Livingston Island (South Shetland Islands, Antarctica). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:377–385
Franzmann PD, Springer N, Ludwig W, Conway De Macario E, Rohde M (1993) A methanogenic archaeon from Ace Lake, Antarctica: Methanococcoides burtonii sp. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:573–581
Franzmann PD, Liu Y, Balkwill DL, Aldrich HC, Conway de Macario E, Boone DR (1997) Methanogenium frigidum sp. nov., a psychrophilic H2-utilizing methanogen from Ace Lake, Antarctica. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:1068–1072
García-Jurado F, Jiménez-Gómez F, Guerrero F (2011) Effects of a dry period on the limnological characteristics of a Mediterranean high mountain lake. Limnetica 30:5–16
Gentile G, Giuliano L, D’Auria G, Smedile F, Azzaro M, De Domenico M, Yakimov MM (2006) Study of bacterial communities in Antarctic coastal waters by a combination of 16S rRNA and 16S rDNA sequencing. Environ Microbiol 8:2150–2161
Gugliandolo C, Michaud L, Lo Giudice A, Lentini V, Rochera C, Camacho A, Maugeri TL (2016) Prokaryotic community in lacustrine sediments of Byers Peninsula (Livingston Island, Maritime Antarctica). Microb Ecol 71:387–400
Izaguirre I, Allende L, Marinone MC (2003) Comparative study of the planktonic communities of three lakes of contrasting trophic status at Hope Bay (Antarctic Peninsula). J Plankton Res 25:1079–1097
Karr EA, Ng JM, Belchik SM, Sattley WM, Madigan MT, Achenbach LA (2006) Biodiversity of methanogenic and other Archaea in the permanently frozen Lake Fryxell, Antarctica. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1663–1666
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2003) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 2:150–163
Laferla R, Logiudice A, Maimone G (2004) Morphology and LPS content for the estimation of the bacterial biomass in the Ionian Sea. Sci Mar 68:23–31
Laybourn-Parry J, Bayliss P, Ellis-Evans JC (1995) The dynamics of heterotrophic nanoflagellates and bacterioplankton in a large ultra-oligotrophic Antarctic lake. J Plankton Res 17:1834–1850
Lo Giudice A, Caruso C, Mangano S, Bruni V, De Domenico M, Michaud L (2012) Marine bacterioplankton diversity and community composition in an Antarctic coastal environment. Microb Ecol 63:210–223
Loy A, Lehner A, Lee N, Adamczyk J, Meier H, Ernst J, Schleifer KH, Wagner M (2002) Oligonucleotide microarray for 16S rRNA gene based detection of all recognized lineages of sulfate reducing prokaryotes in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5064–5081
Loy A, Maixner F, Wagner M, Horn M (2007) ProbeBase: an online resource for rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:800–804
Lyons WB, Quesada A, Camacho A (2013) Long-term studies: lessons from Byers Peninsula. Antarct Sci 25:121
Manz W, Amann R, Ludwig W, Wagner M, Schleifer K-H (1992) Phylogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide probes for the major subclasses of proteobacteria: problems and solutions. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:593–600
Manz W, Amann R, Ludwig W, Vancanneyt M, Schleifer KH (1996) Application of a suite of 16S rRNA specific oligonucleotide probes designed to investigate bacteria of the phylum Cytophaga–Flavobacter–Bacteroides in the natural environment. Microbiology 142:1097–1106
Massana R, Murray AE, Preston CM, DeLong EF (1997) Vertical distribution and phylogenetic characterization of marine planktonic Archaea in the Santa Barbara channel. Appl Environ Microbiol 3:50–56
McDonald JE, de Menezes AB, Allison HE, McCarthy AJ (2009) Molecular biological detection and quantification of novel Fibrobacter populations in freshwater lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5148–5152
Meier H, Amann R, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1999) Specific oligonucleotide probes for in situ detection of a major group of Gram-positive bacteria with low DNA G + C content. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:186–196
Michaud L, Caruso C, Mangano S, Interdonato F, Bruni V, Lo Giudice A (2012) Predominance of Flavobacterium, Pseudomonas, and Polaromonas within the prokaryotic community of freshwater shallow lakes in the northern Victoria Land, East Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 82:391–404
Neef A (1997) Application of in situ identification of bacteria to population analysis in complex microbial communities. PhD Dissertation, Munich
Pearce DA (2003) Bacterioplankton community structure in a maritime Antarctic oligotrophic lake during a period of holomixis, as determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH). Microb Ecol 46:92–105
Pearce DA, Van Der Gast CJ, Lawley B, Ellis-Evans JC (2003) Bacterioplankton community diversity in a Maritime Antarctic lake, determined by culture-dependent and culture-independent techniques. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45:59–70
Pearce DA, van der Gast CJ, Woodward K, Newsham KK (2005) Significant changes in the bacterioplankton community structure of a maritime Antarctic freshwater lake following nutrient enrichment. Microbiology 151:3237–3248
Peeters K, Hodgson DA, Convey P, Willems A (2011) Culturable diversity of heterotrophic bacteria in Forlidas Pond (Pensacola Mountains) and Lundström Lake (Shackleton Range), Antarctica. Microb Ecol 62:399–413
Pernthaler A, Pernthaler J, Amann R (2004) Sensitive multi-color fluorescence in situ hybridization for the identification of environmental microorganisms. In: Kowalchuk G et al (eds) Molecular microbial ecology manual, 2nd edn. vol 11. Kluwer Academic Press, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 711–726
Porter KG, Feig YS (1980) The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol Oceanogr 25:943–948
Purdy KJ, Nedwell DB, Embley TM (2003) Analysis of the sulfate-reducing bacterial and methanogenic archaeal populations in contrasting Antarctic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3181–3191
Quayle WC, Peck LS, Peat H, Ellis-Evans JC, Harrigan PR (2002) Extreme responses to climate change in Antarctic lakes. Science 295:645
Quesada A, Camacho A, Lyons WB (2013) Multidisciplinary research on Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island: a future benchmark for change in Maritime Antarctica. Antarct Sci 25:123–127
Rochera C, Justel A, Fernández-Valiente E, Bañón M, Rico E, Toro M, Camacho A, Quesada A (2010) Interannual meteorological variability and its effects on a lake from maritime Antarctica. Polar Biol 33:1615–1628
Rochera C, Toro M, Rico E, Fernández-Valiente E, Villaescusa JA, Picazo A, Quesada A, Camacho A (2013) Structure of planktonic microbial communities along a trophic gradient in lakes of Byers Peninsula, South Shetland Islands. Antarct Sci 25:277–287
Roller C, Wagner M, Amann R, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1994) In situ probing of Gram-positive bacteria with high DNA G + C content using 23S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotides. Microbiology 140:2849–2858
Saitou M, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Saul DJ, Aislabie J-M, Brown CE, Harris L, Foght JM (2005) Hydrocarbon contamination changes the bacterial diversity of soil from around Scott Base, Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 53:141–155
Stahl DA, Amann R (1991) Development and application of nucleic acid probes. In: Stackebrand E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 205–248
Takacs CD, Priscu JC (1998) Bacterioplankton dynamics in the McMurdo Dry Valley lakes, Antarctica: production and biomass loss over four seasons. Microb Ecol 36:239–250
Tamames J, Abellan JJ, Pignatelli M, Camacho A, Moya A (2010) Environmental distribution of prokaryotic taxa. BMC Microbiol 10:85
Tang C, Michael TM, Lanoila B (2013) Bacterial and Archaeal diversity in sediments of West Lake Bonney, McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:1034–1038
Teira E, Reinthaler T, Pernthaler A (2004) Combining catalyzed reporter deposition-fluorescence in situ hybridization and microautoradiography to detect substrate utilization by bacteria and archaea in the deep ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4411–4414
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Toro M, Camacho A, Rochera C, Rico E, Bañón M, Fernández-Valiente E, Marco E, Justel A, Avendaño MC, Ariosa Y, Vincent WF, Quesada A (2007) Limnological characteristics of the freshwater ecosystems of Byers Peninsula, Livingston Island, in maritime Antarctica. Polar Biol 30:635–649
Tytgat B, Verleyen E, Obbels D, Peeters K, De Wever A, D’hondt S, De Meyer T, Van Criekinge W, Vyverman W, Willems A (2014) Bacterial diversity assessment in Antarctic terrestrial and aquatic microbial mats: a comparison between bidirectional pyrosequencing and cultivation. PLoS One 9(6):e97564
Van Trappen S, Mergaert J, Van Eygen S, Dawyndt P, Cnockaert MC, Swings J (2002) Diversity of 746 heterotrophic bacteria isolated from microbial mats from ten Antarctic lakes. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:603–610
Velázquez D, Rochera C, Camacho A, Quesada A (2011) Temperature effects on Antarctic non-marine phototrophic communities. Polar Biol 34:1045–1055
Velázquez D, López-Bueno A, de Cárcer DA, de los Ríos A, Alcamí A, Quesada A (2016) Ecosystem function decays by fungal outbreaks in Antarctic microbial mats. Sci Rep 6:22954
Villaescusa JA, Casamayor EO, Rochera C, Velázquez D, Chicote A, Quesada A, Camacho A (2010) A close link between bacterial community composition and environmental heterogeneity in maritime Antarctic lakes. Int Microbiol 13:67–77
Villaescusa JA, Rochera C, Velázquez D, Rico E, Quesada A, Camacho A (2013a) Bacterioplankton summer dynamics in a maritime Antarctic Lake. Limnetica 32:253–268
Villaescusa JA, Casamayor EO, Rochera C, Quesada A, Michaud L, Camacho A (2013b) Heterogeneous vertical structure of the bacterioplankton community in a non-stratified Antarctic lake. Antarct Sci 25:229–238
Villaescusa JA, Jørgensen SE, Rochera C, Velázquez D, Quesada A, Camacho A (2016) Carbon dynamics modelization and biological community sensitivity to temperature in an oligotrophic freshwater Antarctic lake. Ecol Model 219:21–30
Wallner G, Amann R, Beisker W (1993) Optimizing fluorescent in situ hybridization of suspended cells with rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes for the flow cytometric identification of microorganisms. Cytometry 14:136–143
Zeng Y, Zou Y, Grebmeier JM, He J, Zheng T (2012) Culture-independent and -dependent methods to investigate the diversity of planktonic bacteria in the northern Bering Sea. Polar Biol 35:117–129
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all the members of the LIMNOPOLAR Team for their support, as well as to the crew of the ship Las Palmas (Spanish Navy) and the Marine Technology Unit (UTM-CSIC) for logistic support. L. Michaud is particularly indebted to Mr. Hilo Moreno for his professional and enthusiastic help and support, which made sampling possible. The authors thank the reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants from PNRA (Programma Nazionale di Ricerche in Antartide), Italian Ministry of Education and Research (PEA 2004, Research Project PNRA 2004/1.6); MNA (Museo Nazionale dell’Antartide); Spanish Ministry of Education and Science, with one of them co-financed by the European FEDER funds (POL2006-06635 and CGL2005-06549-C02-02/ANT).
Additional information
Communicated by A. Oren.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papale, M., Rizzo, C., Villescusa, J.A. et al. Prokaryotic assemblages in the maritime Antarctic Lake Limnopolar (Byers Peninsula, South Shetland Islands). Extremophiles 21, 947–961 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-017-0955-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-017-0955-x