Abstract
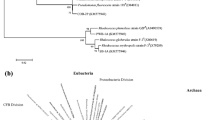
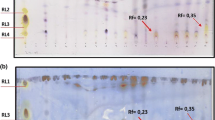
We aimed to isolate biosurfactant-producing bacteria in high salt conditions from uncontaminated soils on the Brazilian oceanic island, Trindade. Blood agar medium was used for the isolation of presumptive biosurfactant-producing bacteria. Confirmation and measurements of biosurfactant production were made using an oil-spreading method. The isolates were identified by fatty acid profiles and partial 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. A total of 14 isolates obtained from the 12 soil samples were found to produce biosurfactants. Among them, two isolates stood out as being able to produce biosurfactant that is increasingly active in solutions containing up to 175 g L−1 NaCl. These high salt tolerant biosurfactant producers are affiliated to different species of the genus Bacillus. Soil organic matter showed positive correlation with the number of biosurfactant-producing bacteria isolated from our different sampling sites. The applied approach successfully recovered and identified biosurfactant-producing bacteria from non-contaminated soils. Due to the elevated salt tolerance, as well as their capacity to produce biosurfactants, these isolates are promising for environmental biotechnological applications, especially in the oil production chain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi H, Hamedi MM, Lotfabad TB, Zahiri HS, Sharafi H, Masoomi F, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Ortiz A, Amanlou M, Noghabi KA (2012) Biosurfactant-producing bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MA01 isolated from spoiled apples: physicochemical and structural characteristics of isolated biosurfactant. J Biosci Bioeng 113(2):211–219. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.10.002
Abdou M, Carnegie A, Mathews SG, McCarthy K, O’Keefe M, Raghuramen B, Wei W, Xian CG (2011) Finding value in formation water. Oilfield Rev Spring 23(1):24–35
Aislabie JM, Jordan S, Barker GM (2008) Relation between soil classification and bacterial diversity in soils of the Ross Sea region, Antarctica. Geoderma 144:9–20. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.10.006
Antón J, Rosselló-Mora R, Rodríguez-Valera F, Amann R (2000) Extremely halophilic Bacteria in crystallizer ponds from solar salterns. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3052–3057
Banat IM (1995) Biosurfactants production and possible uses in microbial enhanced oil recovery and oil pollution remediation. Bioresour Technol 51(1):1–12. doi:10.1016/0960-8524(94)00101-6
Banat IM, Franzetti A, Gandolfi I, Bestetti G, Martinotti MG, Fracchia L, Smyth TJ, Marchant R (2010) Microbial biosurfactants production, applications and future potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87(2):427–444. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2589-0
Bharali P, Das S, Konwar BK, Thakur AJ (2011) Crude biosurfactant from thermophilic Alcaligenes faecalis: feasibility in petro-spill bioremediation. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 65:682–690. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.04.001
Bodour AA, Drees KP, Maier RM (2003) Distribution of biosurfactant-producing bacteria in undisturbed and contaminated arid southwestern soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(6):3280–3287. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.6.3280-3287.2003
Boniek D, Figueiredo D, Pylro VS, Duarte GF (2010) Characterization of bacterial strains capable of desulphurisation in soil and sediment samples from Antarctica. Extremophiles 14(5):475–481. doi:10.1007/s00792-010-0326-3
Clemente EP, Schaefer CEGR, Oliveira FS, Albuquerque FMR, Alves RV, Sá MMF, Melo VF, Corrêa GR (2009) Topossequência de solos na ilha da Trindade, Atlântico Sul. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 33:1357–1371. doi:10.1590/S0100-06832009000500028
Das K, Mukherjee AK (2007) Crude petroleum-oil bio-degradation efficiency of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a petroleum oil contaminated soil from North-East India. Bioresour Technol 98:1339–1345. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2006.05.032
Desai JD, Banat IM (1997) Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61(1):47–64
Farias ME, Revale S, Mancini E, Ordonez O, Turjanski A, Cortez N, Vazquez MP (2011) Genome sequence of Sphingomonas sp. S17, isolated from an alkaline, hyperarsenic, and hypersaline volcano-associated lake at high altitude in the Argentinean Puna. J Bacteriol 193:3686–3687
Fox SL, Bala GA (2000) Production of surfactant from Bacillus subtilis ATCC 21332 using potato substrates. Bioresour Technol 75:235–240. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00059-6
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17(8):754–755. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754
James SR, Burton HR, McMeekin TA, Mancuso CA (1994) Seasonal abundance of Halomonas meridian, Halomonas suglaciescola, Flavobacterium gondowanense and Flavobacterium salegens in four Antarctic lakes. Antarct Sci 6:325–332
Kunitsky C, Osterhout G, Sasser M (2006) Identification of microorganisms using fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) analysis and the MIDI Sherlock® microbial identification system. In: Miller MJ (ed) Encyclopedia of rapid microbiological methods, vol 3. Hardcover, pp 480
Kunte HJ (2012) Osmoregulation in halophilic bacteria. Extremophiles. Encyclopedia of Life Support (EOLSS) 2:263–277
Lima TMS, Procópio LC, Brandão FD, Leão BA, Tótola MR, Borges AC (2011a) Evaluation of bacterial surfactant toxicity towards petroleum degrading microorganisms. Bioresour Technol 102(3):2957–2964. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.109
Lima TMS, Procópio LC, Brandão FD, Carvalho AMX, Tótola MR, Borges AC (2011b) Biodegradability of bacterial surfactants. Biodegradation 22(3):585–592. doi:10.1007/s10532-010-9431-3
Lozupone CA, Knight R (2007) Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11436–11440. doi:10.1073/pnas.0611525104
Maneerat S, Nitoda T, Kanzak H, Kawai F (2005) Bile acids are new products of a marine bacterium, Myroides sp. strain SM1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67(5):679–683. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1777-1
Moore E, Arnscheidt A, Krüger A, Strömpl C, Mau M (2004) Simplified protocols for the preparation of genomic DNA from bacterial cultures. Mol Microb Ecol Man Second Edit 1(01):3–18
Morikawa M, Hirata Y, Imanaka T (2000) A study on the structure-function relationship of lipopeptide biosurfactants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1488(3):211–218
Mukherjee S, Das P, Sen R (2006) Towards commercial production of microbial surfactants. Trends Biotechnol 24:509–515. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2006.09.005
Muthusamy K, Gopalakrishnan S, Kochupappy T, Sivachidambaram P (2008) Biosurfactants: properties, commercial production and application. Curr Sci 94:736–774
Nitschke M, Pastore GM (2002) Biossurfactantes: propriedades e Aplicações. Quim Nova 25(5):772–776. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422002000500013
Nylander JAA (2004) MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author, Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University, Sweden
Pacwa-Płociniczak M, Płaza GA, Piotrowska-Seget Z, Cameotra SS (2011) Environmental applications of biosurfactants: recent advances. Int J Mol Sci 12:633–654. doi:10.3390/ijms12010633
Paulay G (1994) Biodiversity on oceanic islands—Its origin and extinction. Am Zool 34(1):134–144. doi:10.1093/icb/34.1.134
Peters W (1991) Peritrophic membranes. Springer, New York
Pylro VS, Roesch LF, Ortega JM, doAmaral AM, Tótola MR, Hirsch PR, Rosado AS, Góes-Neto A, daCostadaSilva AL, Rosa CA, Morais DK, Andreote FD, Duarte GF, de Melo IS, Seldin L, Lambais MR, Hungria M, Peixoto RS, Kruger RH, Tsai SM, Azevedo V, Brazilian Microbiome Project Organization Committee (2014) Brazilian microbiome project: revealing the unexplored microbial diversity—challenges and prospects. Microb Ecol 67(2):237–241. doi:10.1007/s00248-013-0302-4
Reasoner DJ, Geldreich EE (1985) A new medium for the enumeration and subculture of bacteria from potable water. Appl Environ Microbiol 49(1):1–7
Saimmai A, Tani A, Sobhon V, Maneerat S (2012) Mangrove sediment, a new source of potential biosurfactant-producing bacteria. Ann Microbiol 62(4):1669–1679. doi:10.1007/s13213-012-0424-9
Sharma MK, Shah DO (1989) Use of surfactants in oil recovery. In Donaldson EC, Chilingarian GV Enhanced oil recovery II process and operations. The Fu Yen (ed), Elsevier, New York, pp 253-315
Sharma S, Singh P, Raj M, Chadha BS, Saini HS (2009) Aqueus phase partitioning of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) isomers by biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa WH-2. J Hazard Mater 171(1–3):1178–1182. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.116
Shavandi M, Mohebali G, Haddadi A, Shakarami H, Nuhi A (2011) Emulsification potential of a newly isolated biosurfactant––producing bacterium, Rhodococcus sp. strain TA6. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 82(2):477–482. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.10.005
Singh A, Van Hamme JD, Ward OP (2007) Surfactants in microbiology and biotechnology: part 2. Application Aspects Biotechnol Adv 25:99–121. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.10.004
Soberón-Chávez G, Maier RM (2011) Biosurfactants: a General Overview. In: Soberón-Chávez G (ed) Biosurfactants. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–11
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Teixeira LC, Peixoto RS, Cury JC, Sul WJ, Pellizari VH, Tiedje J, Rosado AS (2010) Bacterial diversity in rhizosphere soil from Antarctic vascular plants of Admiralty Bay, maritime Antarctica. ISME J 4(8):989–1001. doi:10.1038/ismej.2010.35
Vater J, Kablitz B, Wilde C, Franke P, Mehta N, Cameotra SS (2002) Matrix assisted laser desortion ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry of lipopeptide biosurfactants in whole cells and culture filtrates of Bacillus subtilis C-1 isolated from petroleum sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(12):6210–6219. doi:10.1128/AEM.68.12.6210-6219.2002
Wilde JE, Linton SM, Greenaway P (2004) Dietary assimilation and the digestive strategy of the omnivorous anomuran land crab Birgus latro (Coenobitidae). J Comp Physiol B 174:299–308. doi:10.1007/s00360-004-0415-7
Youssef NH, Duncan KE, Nagle DP, Savage KN, Knapp RM, Mcinerney MJ (2004) Comparison of methods to detect biosurfactant production by diverse microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 56:339–347. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2003.11.001
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Brazilian Navy and Captain Rodrigo Otoch Chaves for the logistic support while collecting samples, and providing the essential structure to sample transportation and storage, and Dr. Marc Redmile-Gordon (Centre for Sustainable Soils and Grassland Systems, Rothamsted Research, UK) for critical comments and review of the written English in the manuscript. CNPq grant 405544/2012-0 (PROTRINDADE), FAPEMIG and CAPES (PROEX) funded this work. This work is also supported by the Brazilian Microbiome Project (http://brmicrobiome.org).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. da Costa.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, F.S.P., Pylro, V.S., Fernandes, P.L. et al. Unexplored Brazilian oceanic island host high salt tolerant biosurfactant-producing bacterial strains. Extremophiles 19, 561–572 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-015-0740-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-015-0740-7