Abstract
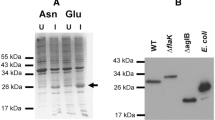
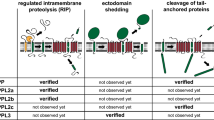
In Archaea, type IV prepilins and prearchaellins are processed by designated signal peptidase III (SPaseIII) prior to their incorporation into pili and the archaellum, respectively. These peptidases belong to the family of integral membrane aspartic acid proteases that contain two essential aspartate residues of which the second aspartate is located in a conserved GxGD motif. To this group also bacterial type IV prepilin peptidases, Alzheimer disease-related secretases, signal peptide peptidases and signal peptide peptidase-like proteases in humans belong. Here we have performed detailed in vivo analyses to understand the cleavage activity of PibD, SPaseIII from the thermoacidophilic crenarchaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Using an already established in vivo heterologous system cleavage assay, we could successfully identify the key amino acid residues essential for catalysis of PibD. Furthermore, in trans complementation of a pibD S. acidocaldarius deletion mutant with PibD variants having substituted key amino acids has consolidated our observations of the importance of these residues in catalysis. Based on our data, we propose to re-define class III peptidases/type IV prepilin/prearchaellin peptidases as GxHyD group (rather than GxGD) of proteases [Hy-hydrophobic amino acid].




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers SV, Pohlschroder M (2009) Diversity of archaeal type IV pilin-like structures. Extremophiles 13(3):403–410
Albers SV, Szabo Z, Driessen AJ (2003) Archaeal homolog of bacterial type IV prepilin signal peptidases with broad substrate specificity. J Bacteriol 185(13):3918–3925
Bardy SL, Jarrell KF (2002) FlaK of the archaeon Methanococcus maripaludis possesses preflagellin peptidase activity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 208(1):53–59
Bardy SL, Jarrell KF (2003) Cleavage of preflagellins by an aspartic acid signal peptidase is essential for flagellation in the archaeon Methanococcus voltae. Mol Microbiol 50(4):1339–1347
Berkner S, Grogan D, Albers SV, Lipps G (2007) Small multicopy, non-integrative shuttle vectors based on the plasmid pRN1 for Sulfolobus acidocaldarius and Sulfolobus solfataricus, model organisms of the (cren-)archaea. Nucleic Acids Res 35(12):e88
Brock TD, Brock KM, Belly RT, Weiss RL (1972) Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol 84(1):54–68
Craig L, Li J (2008) Type IV pili: paradoxes in form and function. Curr Opin Struc Biol 18(2):267–277
de Bentzmann S, Aurouze M, Ball G, Filloux A (2006) FppA, a novel Pseudomonas aeruginosa prepilin peptidase involved in assembly of type IVb pili. J Bacteriol 188(13):4851–4860
Fluhrer R, Steiner H, Haass C (2009) Intramembrane proteolysis by signal peptide peptidases: a comparative discussion of GXGD-type aspartyl proteases. J Biol Chem 284(21):13975–13979
Frols S, Ajon M, Wagner M, Teichmann D, Zolghadr B, Folea M, Boekema EJ, Driessen AJ, Schleper C, Albers SV (2008) UV-inducible cellular aggregation of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus is mediated by pili formation. Mol Microbiol 70(4):938–952
Golde TE, Wolfe MS, Greenbaum DC (2009) Signal peptide peptidases: a family of intramembrane-cleaving proteases that cleave type 2 transmembrane proteins. Sem Cell Dev Biol 20(2):225–230
Hansen JK, Forest KT (2006) Type IV pilin structures: insights on shared architecture, fiber assembly, receptor binding and type II secretion. J Mol Microbiol Biotech 11((3–5)):192–207
Henche AL, Ghosh A, Yu X, Jeske T, Egelman E, Albers SV (2012) Structure and function of the adhesive type IV pilus of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Environ Microbiol 14(12):3188–3202
Hu J, Xue Y, Lee S, Ha Y (2011) The crystal structure of GXGD membrane protease FlaK. Nature 475(7357):528–531
LaPointe CF, Taylor RK (2000) The type 4 prepilin peptidases comprise a novel family of aspartic acid proteases. J Biol Chem 275(2):1502–1510
Lassak K, Ghosh A, Albers SV (2012) Diversity, assembly and regulation of archaeal type IV pili-like and non-type-IV pili-like surface structures. Res Microbiol 163(9–10):630–644
Ng SY, VanDyke DJ, Chaban B, Wu J, Nosaka Y, Aizawa S, Jarrell KF (2009) Different minimal signal peptide lengths recognized by the archaeal prepilin-like peptidases FlaK and PibD. J Bacteriol 191(21):6732–6740
Pearl L, Blundell T (1984) The active site of aspartic proteinases. FEBS Lett 174(1):96–101
Pepe JC, Lory S (1998) Amino acid substitutions in PilD, a bifunctional enzyme of Pseusomonas aeruginosa. Effect on leader peptidase and N-methyltransferase activities in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 273(30):19120–19129
Pohlschroder M, Ghosh A, Tripepi M, Albers SV (2011) Archaeal type IV pilus-like structures–evolutionarily conserved prokaryotic surface organelles. Curr Opin Microbiol 14(3):357–363
Strom MS, Bergman P, Lory S (1993) Identification of active-site cysteines in the conserved domain of PilD, the bifunctional type IV pilin leader peptidase/N-methyltransferase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 268(21):15788–15794
Szabo Z, Albers SV, Driessen AJ (2006) Active-site residues in the type IV prepilin peptidase homologue PibD from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. J Bacterio 188(4):1437–1443
Szabo Z, Stahl AO, Albers SV, Kissinger JC, Driessen AJ, Pohlschroder M (2007) Identification of diverse archaeal proteins with class III signal peptides cleaved by distinct archaeal prepilin peptidases. J Bacteriol 189(3):772–778
Tomita T, Iwatsubo T (2013) Structural biology of presenilins and signal peptide peptidases. J Biol Chem 288(21):14673–14680
Tripepi M, Imam S, Pohlschroder M (2010) Haloferax volcanii flagella are required for motility but are not involved in PibD-dependent surface adhesion. J Bacteriol 192(12):3093–3102
Voss M, Schroder B, Fluhrer R (2013) Mechanism, specificity, and physiology of signal peptide peptidase (SPP) and SPP-like proteases. Biochim Biophysica Acta 1828(12):2828–2839
Wagner M, van Wolferen M, Wagner A, Lassak K, Meyer BH, Reimann J, Albers SV (2012) Versatile Genetic Tool Box for the Crenarchaeote Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Frontiers Microbiology 3:214
Wolfe MS (2010) Structure, mechanism and inhibition of gamma-secretase and presenilin-like proteases. Biological chemistry 391(8):839–847
Wolfe MS (2013) Toward the structure of presenilin/gamma-secretase and presenilin homologs. Biochim Biophys Acta 1828(12):2886–2897
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Andreas Klingl for assistance in electron microscopy and Prof. Uwe-G. Maier for allocation of the electron microscopic facilities. A.K. was supported by the LOEWE Research Centre for Synthetic Microbiology (Synmikro). A. L. H. was supported by the German Research Council within the framework of the Collaborative Research Center 987 “Microbial Diversity in Environmental Signal Response”. M. v. W. was supported by a grant from the German Research Council AL1206/3-1 and SVA received intramural funds from the Max Planck Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by M. W. W. Adams.
This article is part of a special issue based on the 10th International Congress on Extremophiles held in Saint Petersburg, Russia, September 7–11, 2014.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henche, AL., van Wolferen, M., Ghosh, A. et al. Dissection of key determinants of cleavage activity in signal peptidase III (SPaseIII) PibD. Extremophiles 18, 905–913 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-014-0675-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-014-0675-4