Abstract
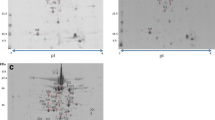
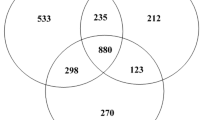
The North-Western part of Argentina is particularly rich in wetlands located in the Puna in an altitude between 3,600 and 4,600 m above sea level. Most of these high-altitude Andean lakes are inhospitable areas due to extreme habitat conditions such as high contents of toxic elements, particularly arsenic. Exiguobacterium sp. S17, isolated from stromatolites in Laguna Socompa, exhibited remarkable tolerance to high arsenic concentration, i.e., it tolerated arsenic concentration such as 10 mM of As(III) and 150 mM of As(V). A proteomics approach was conducted to reveal the mechanisms that provide the observed outstanding resistance of Exiguobacterium sp. S17 against arsenic. A comparative analysis of S17, exposed and unexposed to arsenic revealed 25 differentially expressed proteins. Identification of these proteins was performed by MALDI-TOF/MS revealing upregulation of proteins involved in energy metabolism, stress, transport, and in protein synthesis being expressed under arsenic stress. To our knowledge, this work represents the first proteomic study of arsenic tolerance in an Exiguobacterium strain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achour AR, Bauda P, Billard P (2007) Diversity of arsenite transporter genes from arsenic-resistant soil bacteria. Res Microbiol 158:128–137
Anderson CR, Cook GM (2004) Isolation and characterization of arsenate-reducing bacteria from arsenic contaminated sites in New Zealand. Curr Microbiol 48:341–347
ATSDR—Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2000) Toxicological profile for arsenic september prepared for the US department of health and human services by syracuse research corporation
Baker-Austin G, Dopson M, Wexler M, Sawers RG, Stemmler A, Rosen BP, Bond PL (2007) Extreme arsenic resistance by the acidophilic archaeon ‘Ferroplasma acidarmanus’ Fer1. Extremophiles 11:425–434
Borja Sánchez B, Champomier-Vergès MC, Anglade P, Baraige F, de los Reyes-Gavilán CG, Margolles A, Zagorec M (2005) Proteomic analysis of global changes in protein expression during bile salt exposure of bifidobacterium longum NCIMB 8809. J Bacteriol 187(16):5799–5808
Cai L, Lui G, Rensing C, Wang G (2009) Genes involved in arsenic transformation and resistance associated with different levels of arsenic-contaminated soils. BMC Microbiol 9:4
Caldas TD, Yaagaubia AE, Richarme G (1998) Chaperone properties of bacterial elongation factor EF-Tu. J Biol Chem 273:11478–11482
Castro de Esparza ML (2006) Remocion del arsenico en el agua para bebida y bioremediacion de suelos from http://www.bvsde.paho.org/bvsacd/cd51/remocion-agua.pdf International Congress Mexico City, Natural arsenic in groundwater of Latin America
Champomier-Vergés MC, Zagorec M, Fadda S (2010) Bacteria adaptation to streeful environments. In: Mozzi F, Raya R, Vignolo G (eds) Biotecnology of lactic acid bacteria. Novel applications. Wiley, USA, pp 57–71
Ciprandi A, Azevedo Barauna R, Valadares Santos A, Costa Goncalves E, Peixe Carepo MS, Cruz Schneider MP, Silva A (2012) Proteomic response to arsenic stress in chromobacterium violaceum. J I Omics 2:69–73
Cleiss-Arnold J, Koechler S, Proux C, Fardeau ML, Dillies MA, Coppee JY, Arsène-Ploetze F, Bertin PN (2010) Temporal transcriptomic response during arsenic stress in Herminiimonas arsenicoxydans. BMC Genomics 11:709
Couoh Uicab YL, Canto Canche BB, Islas Flores I (2010) Review of characteristics of ABC transporters involved in fungal pathogenesis. Tecnociencia Chihuahua 4(2):87–96
Duché O, Trémoulet F, Glaser P, Labadie J (2002) Salt stress proteins induced in Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1491–1498
Farías ME, Revale S, Mancini E, Ordoñez O, Turjanski A, Cortez N, Vazquez MP (2011) Genome sequence of Sphingomonas sp. S17, isolated from an alkaline, hiperarsenic, and hypersaline volcano-associated lake at high altitud in the Argentinean Puna. J Bacteriol 193:3686–3687
Farías ME, Rascovan N, Toneatti DM, Albarracín VH, Flores MR, Poire DG, Collavino MM, Aguilar OM, Vazquez MP, Polerecky L (2012) The discovery of stromatolites developing at 3570 m above sea level in a high-altitude volcanic lake Socompa, Argentinean Andes. PLOS ONE (accepted to publish)
Ferguson JF, Gavis J (1972) A review of arsenic cycle in natural waters. Water Res 6(11):1259–1274
Fernández Zenoff V, Siñeriz F, Faria ME (2006) Diverse responses to UV-B radiation and repair mechanisms of bacteria isolated from high-altitude aquatic environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(12):7857–7863
Gorbach ZV, Maglysh SS, Kubyshin VL, Ostrovskii IM (1981) Purification and properties of rat liver transketolase. Biokhimiia 46:1963–1969
Hartl FU (1996) Molecular chaperones in cellular protein folding. Nature 381:571–580
Kaiser W (1979) Reversible inhibition of the Calvin cycle and activation of oxidative pentose phosphate cycle in isolated intact chloroplasts by hydrogen peroxide. Planta 145:377–382
Kiriyama MT, Oka M, Takehana M, Kobayashi S (2001) Expression of a small heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) in mouse skin tumors induced by UVB-irradiation. Biol Pharm Bull 24:197–200
Kramer GF, Ames BM (1988) Isolation and characterization of a selenium metabolism mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol 170:736–743
Kvint K, Nachin L, Diez A, Nystrom T (2003) The bacterial universal stress protein: function and regulation. Curr Opin Microbiol 6(2):140–145
Lakshmi Sunita MS, Prashant S, Bramha Chari PV, Nageswara Rao S, Padma Balaravi PB, Kishor K (2012) Molecular identification of arsenic-resistant estuarine bacteria and characterization of their ars genotype. Ecotoxicology 21(1):202–212
Lopez L, Pozo C, Rodelas B, Calvo C, Juarez B, Martinez-Toledo MV, Gonzalez-Lopez J (2005) Identification of bacteria isolated from an oligotrophic lake with pesticide removal capacities. Ecotoxicology 14(3):299–312
Middelhoven WJ, Hoogkramer-Te Niet MC, Kreger-Van Rij NJW (1984) Trichosporon adeninivorans sp. nov., a yeast species utilizing adenine, xanthine, uric acid, putrescine and primary n-alkalymines as the sole source of carbon, nitrogen and energy. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 50:369–378
Mogk A, Deurling E, Voderwulbecke S, Vierling E, Bukau B (2003) Small heat shock proteins, ClpB and the DnaL system from a functional triade in reversing protein aggregation. Mol Bio 50(2):585–595
Moore LE, Pfeiffer R, Warner M, Clark M, Skibola C, Steinmous C, Alguacil J, Rothman N, Smith MT, Smith AH (2005) Identification of biomarkers of arsenic exposure and metabolism in urine using SELDI technology. J Biochem Mol Tox 19:176
Mukhopadhyay R, Rosen BP, Phung LT, Silver S (2002) Microbial arsenic: from geocycles to genes to enzymes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:311–325
Nguyen TTA, Michaud D, Cloutier C (2009) A proteomic analysis of the aphid Macrosiphum euphorbiae under heat and radiation stress. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39:20–30
Okeke BC, Laymon J, Oji C, Crenshaw S (2007) Rapid bioreduction of hexavalent chromium in water by Exiguobacterium sp. GS1. In: ASM general 107th meeting, ASM Press, Toronto, pp Q-199
Ordoñez OF (2012) Factores ambientales extremos en ecosistemas microbianos de humedales altoandinos: mecanismos de adaptacion. PhD thesis from Universidad Nacional de Tucumán, Tucumán, Argentina
Oremland RS, Stolz JF (2003) The ecology of arsenic. Science 300:939–944
Paez-Espino D, Tamames J, de Lorenzo V, Canovas D (2009) Microbial responses to environmental arsenic. Biometals 22:117–130
Pandey S, Rai R, Lal Chand Rai (2011) Proteomics combines morphological, physiological and biochemical attributes to unravel the survival strategy of Anabaena sp. PGG7120 under arsenic stress. J Proteomics 75:921–937
Parsell DA, Lindquist S (1993) The function of heat-shock proteins in stress tolerance: degradation and reactivation of damaged proteins. Annu Rev Genet 27:437–496
Parvatiyar K, Alsabbagh EM, Ochsner UA, Stegemeyer MA, Smulian AG, Hei Hwang S, Jackson CR, McDermott T, Hassett DJ (2005) Global analysis of cellular factors and responses involved in Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance to arsenite. J Bacteriol 187(14):4853–4864
Pattanapipitpaisal P, Mabbett AN, Finlay JA, Beswick AJ, Paterson-Beedle M, Essa A, Wright J, Tolley MR, Badar U, Ahmed N, Hobman JL, Brown NL, MAcaskie LE (2002) Reduction of Cr(VI) and bioaccumulation of chromium by gram positive and gram negative microorganisms not previously exposed to CR-stress. Environ Technol 23:731–745
Rodrigues FD, Ivanova N, He Z, Huebner M, Zhou J, Tiedje JM (2008) Architecture of thermal adaptation in an Exiguobaterium sibiricum strain isolated from 3 million year old permafrost: a genome and transcriptome approach. BMC Genomics 9:547
Rodriguez-Gabriel MA, Russell P (2005) Distinct signaling pathways respond to arsenite and reactive oxygen species in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Eukaryot Cell 4(8):1396–1402
Ron EZ (2006) Bacterial stress response. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Resenberg E, Schleifer KH, Stackebrandt E (eds) The Prokaryotes. Springer, Singapore, pp 1012–1027
Rosen BP (2002) Biochemistry of arsenic detoxification. FEBS Lett 529:86–92
Rosen BP, Lui Z (2009) Transport pathways for arsenic and selenium: a miniriew. Environ Int 35(3):512–515
Siegele D (2005) Universal stress proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187(18):6253–6254
Silver S, Phung LT (2005) Genes and enzymes involved in bacterial oxidation and reduction of inorganic arsenic. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:599–608
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of source, behavior and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Tedengren M, Olsson B, Bradley B, Zhou LZ (1999) Heavy metal uptake, physiological response and survival of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) from marine and brackish waters in relation to the induction of heat-shock protein 70. Hydrobiologia 393:261–269
Tkáčová J, Angelovičová M (2012) Heat shock proteins (Hsps): a review. Anim Sci Biotechnol 45(1):349–353
Zhang Y, Ma YF, Qi SW, Meng B, Tausif Chaudhry M, Liu SQ and Liu SJ (2007) Responses to arsenate stress by Comamonas sp. strain CNB-1 at genetic and proteomic levels. Microbiology 153:3713–372
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Préstamo BID PICT 2010 N°1788-Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica. Carolina Belfiore and Omar F. Ordoñez are recipients of a CONICET fellowship. We thank Dra. Silvia de Moreno for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Atomi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belfiore, C., Ordoñez, O.F. & Farías, M.E. Proteomic approach of adaptive response to arsenic stress in Exiguobacterium sp. S17, an extremophile strain isolated from a high-altitude Andean Lake stromatolite. Extremophiles 17, 421–431 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-013-0523-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-013-0523-y