Abstract
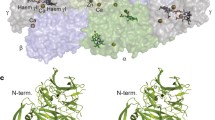
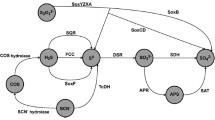
Sulfur oxygenase reductase (SOR) enzyme is responsible for the initial oxidation step of elemental sulfur in archaea. Curiously, Aquifex aeolicus, a hyperthermophilic, chemolithoautotrophic and microaerophilic bacterium, has the SOR-encoding gene in its genome. We showed, for the first time the presence of the SOR enzyme in A. aeolicus, its gene was cloned and recombinantly expressed in Escherichia coli and the protein was purified and characterised. It is a 16 homo-oligomer of approximately 600 kDa that contains iron atoms indispensable for the enzyme activity. The optimal temperature of SOR activity is 80°C and it is inactive at 20°C. Studies of the factors involved in getting the fully active molecule at high temperature show clearly that (1) incubation at high temperature induces more homogeneous form of the enzyme, (2) conformational changes observed at high temperature are required to get the fully active molecule and (3) acquisition of an active conformation induced by the temperature seems to be more important than the subunit number. Differences between A. aeolicus SOR and the archaea SORs are described.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A. aeolicus :
-
Aquifex aeolicus
- A. ambivalens :
-
Acidianus ambivalens
- S°:
-
Elemental sulfur
- SOR:
-
Sulfur oxygenase reductase
- SOX:
-
Sulfur oxidising enzyme system
- TOMES:
-
Thiosulfate oxidising multienzyme system
- TQOR:
-
Thiosulfate quinone oxidoreductase
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- CMC:
-
Carboxymethyl cellulose
- MALDI-TOF:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight
- E. coli :
-
Escherichia coli
References
Andrade MA, Chacon P, Merelo JJ, Mora NF (1993) Evaluation of secondary structure of proteins from UV circular dichroism spectra using an unsupervised learning neural network. Prot eng 6:383–390
Brugna-Guiral M, Tron P, Nitschke W, Stetter KO, Burlat B, Guigliarelli B, Bruschi M, Giudici-Orticoni MT (2003) [NiFe] hydrogenases from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Aquifex aeolicus: properties, function, and phylogenetics. Extremophiles 7:145–157
Chen ZW, Jiang CY, She Q, Liu SJ, Zhou PJ (2005) Key role of cysteine residues in catalysis and subcellular localization of sulfur oxygenase-reductase of Acidianus tengchongensis. Appl Env Microbiol 71:621–628
Chen ZW, Liu YY, Wu JF, She Q, Jiang CY, Liu SJ (2007) Novel bacterial sulfur oxygenase reductases from bioreactors treating gold-bearing concentrates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:688–698
Deckert et al (1998) The complete genome of the hyperthermophilic bacterium Aquifex aeolicus. Nature 392:353–358
Dopson M, Barker-Austin C, Hind A, Bowman JP, Bond PL (2004) Characterization of Ferroplasma isolates and Ferroplasma acidarmanus sp. nov., extreme acidophiles from acid mine drainage and industrial bioleaching environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2079–2088
Enori-Eta J, Gigot D, Thia-Toong TL, Glansdorff N, Charlier D (2000) Purification and characterization of Sa-lrp, a DNA-binding protein from the extreme thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius homologous to the bacterial global transcriptional regulator Lrp. J bacteriol 182:3661–3672
Friedrich CG, Rother D, Bardischewsky F, Quentmeier A, Fischer J (2001) Oxidation of reduced inorganic sulfur compounds by bacteria: Emergence of a common mechanism? Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2873–2882
Friedrich CG, Bardischewsky F, Rother D, Quentmeier A, Fischer J (2005) Prokaryotic sulfur oxidation. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:253–259
Guermeur Y, Geourjon C, Gallinari P, Deleage G (1999) Improved performance in protein secondary structure prediction by inhomogeneous score combination. Bioinformatics 15:413–421
Guiral M, Tron P, Aubert C, Gloter A, Iobbi-Nivol C, Giudici-Orticoni M-T (2005) A membrane-bound multienzyme, hydrogen-oxidizing, and sulfur-reducing complex from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Aquifex aeolicus. J Biol Chem 280:42004–42015
Hedderich R, Klimmek O, Kröger A, Dirmeier R, Keller M, Stetter KO (1998) Anaerobic respiration with elemental sulfur and with disulfides. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:353–381
Huber R, Stetter KO (2002) Aquificales. In: Encyclopedia of life sciences. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp 1–6
Huber R, Wilharm T, Huber D, Trincone A, Burggraf S, König H, Rachel R, Rockinger I, Fricke H, Stetter KO (1992) Aquifex pyrophilus ge.nov.sp.nov. represents a novel group of marine hyperthermopilic hydrogen bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:340–351
Kletzin A (1989) Coupled enzymatic production of sulfite, thiosulfate, and hydrogen sulfide from sulfur: purification and properties of a sulfur oxygenase reductase from the facultatively anaerobic archaebacterium Desulfurolobus ambivalens. J Bacteriol 171:1638–1643
Kletzin A (1992) Molecular characterization of the sor gene, which encodes the sulfur oxygenase/reductase of the thermoacidophilic Archaeum Desulfurolobus ambivalens. J Bacteriol 174:5854–5859
Kletzin A, Urich T, Müller F, Bandeiras TM, Gomes CM (2004) Oxidation and reduction of elemental sulfur in themophilic bacteria. J Bioenerg Biomemb 36:77–91
Maniatis T, Fritsh E, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Cold Spring Harbor
Manning MC, Woody RW (1989) Theoretical study of the contribution of aromatic side chains to the circular dichroism of basic bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Biochemistry 28:8609–8613
McClure WR (1985) Mechanism and control of transcription initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem 54:11–204
Morris MC, Mery J, Heitz A, Heitz F, Divita G (1999) Design and synthesis of a peptide derived from positions 195–244 of human cdc25C phosphatase. J Pept Sci 5:63–271
Müller FH, Bandeiras TM, Urich T, Texeira M, Gomes CM, Kletzin A (2004) Coupling of the pathway of sulfur oxydation to dioxygen reduction: characterization of a novel membrane-bound thiosulfate:quinone oxidoreductase. Mol Microbiol 53:1147–1160
Nübel T, Klughammer C, Huber R, Hauska G, Schütz M (2000) Sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase in membranes of the hyperthermophilic bacterium Aquifex aeolicus (VF5). Arch Microbiol 173:233–244
Reiter WD, Palm P, Zillig W (1988) Transcription termination in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus: signal structures and linkage to transcription initiation. Nucleic Acid Res 16:2445–2459
Rother D, Henrich HJ, Quentmeier A, Bardischewsky F, Friedrich CG (2001) Novel genes of the sox gene cluster, mutagenesis of the flavoprotein SoxF, and evidence for a general sulfur-oxidizing system in Paracoccus pantotrophus GB17. J Bacteriol 183:4499–4508
Schägger H, Von Jagow G (1991) Blue native electrophoresis for isolation of membrane protein complexes in enzymatically active form. Anal Biochem 199:223–231
Schägger H, Cramer A, Von Jagow G (1994) Analysis of molecular masses and oligomeric states of protein complexes by blue native electrophoresis and isolation of membrane protein complexes by two-dimensional native electrophoresis. Anal Biochem 217:220–230
Segel IK (1993) Wiley Classics Library Edition, New York
Stetter KO, König H, Stackebrandt E (1983) Pyrodictium gen. nov., a new genus of submarine disc-shaped sulpur reducing archaebacteria growing optimally at 105°C. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:535–551
Sun CW, Chen ZW, He ZG, Zhou PJ, Liu SJ (2003) Purification and properties of the sulfur oxygenase/reductase from the acidothermophilic archaeon, Acidianus strain S5. Extremophiles 7:131–134
Suzuki I (1999) Oxidation of inorganic sulfur compounds: chemicals and enzymatic reactions. Can J Microbiol 45:97–105
Tan YJ, Oliveberg M, Davis B, Fersht R (1995) Perturbed pKA-values in the denatured states of proteins. J Biol Chem 254:980–992
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Urich T, Bandeiras TM, Leal SS, Albrecht T, Zimmermann P, Scholz C, Teixeira M, Gomes CM, Kletzin A (2004) The sulphur oxygenase reductase from Acidianus ambivalens is a multimeric protein containing a low-potential mononuclear non haem iron center. Biochem J 381:137–146
Urich T, Kroke A, Bauer C, Seyfarth K, Reuff M, Kletzin A (2005) Identification of core active site residues of the sulfur oxygenase reductase from Acidianus ambivalens by site-directed mutagenesis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 248:171–176
Urich T, Gomes CM, Kletzin A, Frazao C (2006) X-ray structure of a self-compartmentalizing sulfur cycle metalloenzyme. Science 311:996–1000
Wakai S, Kikumoto M, Kanao T, Kamimura K (2004) Involvement of sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase in sulfur oxidation of an acidophilic iron-oxidizing bacterium, Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans NASF-1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:2519–2528
Washio T, Sasayama J, Tomita M (1998) Analysis of complete genomes suggests that many prokaryotes do not rely on hairpin formation in transcription termination. Nucleic Acid Res 26:5426–5463
Wich G, Hummel M, Jarsch M, Bar U, Böck A (1986) Transcription signals for stable RNA genes in Methanococcus. Nucleic Acid Res 14:2459–2479
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the contribution of Marielle Bauzan (Institute of Microbiology and Structural Biology, CNRS, Marseilles, France) for growing bacteria; Bruno Gugliarelli for EPR experiments; and Danielle Moinier and Sabrina Lignon (Proteomic Analysis Center, Marseilles, France) for mass spectroscopy analysis. We also thank Alain Dolla, Wolfgang Nitschke, Mari Luz Cardenas and Athel Cornish-Bowden for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Horikoshi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelletier, N., Leroy, G., Guiral, M. et al. First characterisation of the active oligomer form of sulfur oxygenase reductase from the bacterium Aquifex aeolicus . Extremophiles 12, 205–215 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-007-0119-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-007-0119-5