Abstract
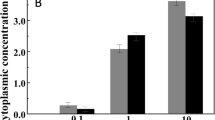
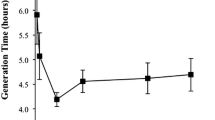
Halobacillus halophilus is a strictly chloride-dependent, moderately halophilic bacterium that synthesizes glutamate and glutamine as the major compatible solutes at intermediate NaCl concentrations. The key enzyme in production of the compatible solutes glutamine and glutamate, glutamine synthetase, is dependent on chloride on a transcriptional and activity level. This led us to ask whether exogenous supply of glutamate may relief the chloride dependence of growth of H. halophilus. Growth of H. halophilus in minimal medium at 1 M NaCl was stimulated by exogenous glutamate and transport experiments revealed a chloride-independent glutamate uptake by whole cells. Growth was largely impaired in the absence of chloride and, at the same time, glutamate and glutamine pools were reduced by 90%. Exogenous glutamate fully restored growth, and cellular glutamate and glutamine pools were refilled. Although glutamate could restore growth in the absence of chloride, another chloride-dependent process, flagellum synthesis and motility, was not restored by glutamate. The differential effect of glutamate on the two chloride-dependent processes, growth and motility, indicates that glutamate can not substitute chloride in general but apparently bypasses one function of the chloride regulon, the adjustment of pool sizes of compatible solutes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
da Costa MS, Santos H, Galinski EA (1998) An overview of the role and diversity of compatible solutes in Bacteria and Archaea. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 61:117–153
Dohrmann AB, Müller V (1999) Chloride dependence of endospore germination in Halobacillus halophilus. Arch Microbiol 172:264–267
Galinski EA, Trüper HG (1994) Microbial behaviour in salt-stressed ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol Rev 15:95–108
Grant WD (2004) Life at low water activity. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 359:1249–1266
Krämer R, Morbach S (2004) BetP of Corynebacterium glutamicum, a transporter with three different functions: betaine transport, osmosensing, and osmoregulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1658:31–36
Kunte HJ, Galinski EA, Trüper HG (1993) A modified FMOC-method for the detection of amino acid-type osmolytes and tetrahydropyrimidines (ectoines). J Microbiol Meth 17:129–136
Müller V, Saum SH (2005) The chloride regulon of Halobacillus halophilus: a novel regulatory network for salt perception and signal transduction in bacteria. In: Gunde-Cimerman N, Oren A, Plemenitas A (eds) Adaption to life at hight salt concentrations in Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 303–310
Poolman B, Glaasker E (1998) Regulation of compatible solute accumulation in bacteria. Mol Microbiol 29:397–407
Roeßler M, Müller V (1998) Quantitative and physiological analyses of chloride dependence of growth of Halobacillus halophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3813–3817
Roeßler M, Müller V (2001) Chloride dependence of glycine betaine transport in Halobacillus halophilus. FEBS Lett 489:125–128
Roeßler M, Müller V (2002) Chloride, a new environmental signal molecule involved in gene regulation in a moderately halophilic bacterium, Halobacillus halophilus. J Bacteriol 184:6207–6215
Roeßler M, Pflüger K, Flach H, Lienard T, Gottschalk G, Müller V (2002) Identification of a salt-induced primary transporter for glycine betaine in the methanogen Methanosarcina mazei Gö1. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2133–2139
Roeßler M, Wanner G, Müller V (2000) Motility and flagellum synthesis in Halobacillus halophilus are chloride dependent. J Bacteriol 182:532–535
Saum SH, Sydow JF, Palm P, Pfeiffer F, Oesterhelt D, Müller V (2006) Biochemical and molecular characterization of the biosynthesis of glutamine and glutamate, two major compatible solutes in the moderately halophilic bacterium Halobacillus halophilus. J Bacteriol 188:6808–6815
Schägger H, von Jagow G (1987) Tricine-sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem 166:369–379
Schmidt K, Liaanen-Jensen S, Schlegel HG (1963) Die Carotinoide der Thiorodaceae. Arch Mikrobiol 46:117–126
Severin J (1993) Kompatible Solute und Wachstumskinetik bei halophilen aeroben heterotrophen Eubakterien. University of Bonn, Germany
Sewald X, Saum SH, Palm P, Pfeiffer F, Oesterhelt D, Müller V (2007) Autoinducer-2-producing protein LuxS, a novel salt- and chloride-induced protein in the moderately halophilic bacterium Halobacillus halophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:371–379
Sleator RD, Hill C (2002) Bacterial osmoadaptation: the role of osmolytes in bacterial stress and virulence. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:49–71
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:504–544
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the German Israeli Foundation (GIF). We are indebted to Gerhard Wanner for providing the excellent electron micrographs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Antranikian.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saum, S.H., Roeßler, M., Koller, C. et al. Glutamate restores growth but not motility in the absence of chloride in the moderate halophile Halobacillus halophilus . Extremophiles 11, 711–717 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-007-0090-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-007-0090-1