Abstract
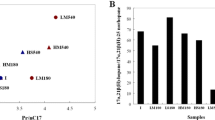
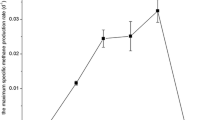
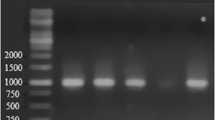
The ability of a psychrotolerant microbial consortium to degrade crude oil at low temperatures was investigated. The enriched arctic microbial community was also tested for its ability to utilize various hydrocarbons, such as long-chain alkanes (n-C24 to n-C34), pristane, (methyl-)naphthalenes, and xylenes, as sole carbon and energy sources. Except for o-xylene and methylnaphthalenes, all tested compounds were metabolized under conditions that are typical for contaminated marine liquid sites, namely at pH 6–9 and at 4–27°C. By applying molecular biological techniques (16S rDNA sequencing, DGGE) nine strains could be identified in the consortium. Five of these strains could be isolated in pure cultures. The involved strains were closely related to the following genera: Pseudoalteromonas (two species), Pseudomonas (two species), Shewanella (two species), Marinobacter (one species), Psychrobacter (one species), and Agreia (one species). Interestingly, the five isolated strains in different combinations were unable to degrade crude oil or its components significantly, indicating the importance of the four unculturable microorganisms in the degradation of single or of complex mixtures of hydrocarbons. The obtained mixed culture showed obvious advantages including stability of the consortium, wide range adaptability for crude oil degradation, and strong degradation ability of crude oil.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mallah M, Gout M, Mille G, Bertrand JC (1990) Production of emulsifying agents during growth of a marine Alteromonas in sea water with eicosane as carbon source, a solid hydrocarbon. Oil Chem Pollut 6:289–305
Annweiler E, Richnow HH, Antranikian G, Hebenbrock S, Harms C, Franke S, Franke W, Michaelis W (2000) Naphthalene degradation and incorporation of naphthalene-derived carbon into biomass by the thermophile Bacillus thermoleovorans. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:518–523
Atlas MA, Bartha R (1992) Hydrocarbon biodegradation and oil spill bioremediation. In: Marshall KC (ed) Advances in microbial ecology, vol 12. Plenum Press, New York, pp 287–338
Bartlett DH, Wright ME, Silverman M (1988) Variable expression of extracellular polysaccharide in the marine bacterium Pseudomonas atlantica is controlled by genome rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:3923–3927
Bastiens L, Springael D, Wattiau P, Harms H, de Wachter R, Verachtert H, Diels L (2000) Isolation of new polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) degrading bacteria using PAH sorbing carriers. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1834–1843
Belas DH, Silverman M (1989) Nucleotide sequence of IS492, a novel insertion sequence causing variation in extracellular polysaccharide production in the marine bacterium Pseudomonas atlantica. J Bacteriol 171:1763–1766
Bowman JP, McCammon SA, Nichols DS, Skerratt JH, Rea SM, Nichols PD, McMeekin TA (1997) Shewanella gelidimarina sp. nov. and S. frigidimarina sp. nov., novel antarctic species with the ability to produce eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5ω3) and grow anaerobically by dissimilatory Fe (III) reduction. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:1040–1047
Buchholz-Cleven BE, Rattunde EB, Straub KL (1997) Screening of genetic diversity of isolates of anaerobic Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria using DGGE and whole-cell hybridization. Syst Appl Microbiol 20:301–309
Corpe WA (1970) Adhesion of marine bacteria to solid surfaces. In: Manley RS (ed) Adhesion in biological systems. Academic Press, New York, pp 73–87
Ferris MJ, Muyzer G, Ward DM (1996) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles of 16S rRNA-defined population inhabiting a hot spring microbial mat community. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:340–346
Friedrich M, Grosser RJ, Kern A, Inskeep WP, Ward DM (2000) Effect of model sorptive phases on phenanthrene degradation: molecular analysis of enrichments and isolates suggests selection based on bioavailability. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:2703–2710
Gauthier MJ, Lafay B, Christen R, Fernandez L, Acquaviva M, Bonin P, Bertrand JC (1992) Marinobacter hydrocarbonocalsticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new, extremely halotolerant, hydrocarbon-degrading marine bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:568–576
Geerdink MJ, van Loosdrecht MCM, Luyben KChAM (1996) Biodegradability of diesel oil. Biodegradation 7:73–81
Gillan DC, Speksnijder AGCL, Zwart G, De Ridder C (1998) Genetic diversity of the biofilm covering Montacuta ferruginose (Mollusca, bivalvia) as evaluated by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis and cloning of PCR-amplified gene fragments coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3464–3472
Grosser RJ, Friedrich M, Ward DM, Inskeep WP (2000) Influence of different chemical treatments on transport of Alcaligenes paradoxus in porous media. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1750–1756
Guerin WF, Boyd SA (1992) Differential bioavailability of soil-sorbed naphthalene to two bacterial species. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1141–1152
Hamme van JD, Odumeru JA, Ward OP (2000) Community dynamics of a mixed-bacterial culture growing on petroleum hydrocarbons in batch culture. Can J Microbiol 46:441–450
Harayama S, Kishira H, Kasai Y, Shutsubo K (1999) Petroleum biodegradation in marine environments. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 1:63–70
Jobson A, Cook FD, Westlake DWS (1972) Microbial utilization of crude oil. Appl Microbiol 23:1082–1089
Kasai Y, Kishira H, Syutsubo K, Harayama S (2001) Molecular detection of marine bacterial populations on beaches contaminated by the Nakhodka tanker oil-spill accident. Environ Microbiol 3:246–255
Ko SH, Lebault JM (1999) Effect of a mixed culture on co-oxidation during the degradation of saturated hydrocarbon mixture. J Appl Microbiol 87:72–79
Lane DJ (1993) In: Goodfellow M, O’Donnell AG (eds) Handbook of new bacterial systematics. Academic Press, London, pp 115–194
Leahy JG, Colwell RR (1990) Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:305–315
Margesin R, Schinner F (1997a) Bioremediation of diesel-oil-contaminated alpine soils at low temperatures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47:462–468
Margesin R, Schinner F (1997b) Efficiency of indigenous and inoculated Cold-adapted soil microorganisms for biodegradation of diesel oil in saline soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2660–2664
Mohn WW, Westerberg K, Cullen WR, Reimer KJ (1997) Aerobic biodegradation of biphenyl and polychlorinated biphenyls by arctic soil microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3378–3384
Morita RY (1975) Psychrophilic Bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 39:144–167
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Muyzer G, Hottenträger S, Teske A, Wawer C (1996) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of PCR-amplified 16 S rDNA—a new molecular approach to analyze the genetic diversity of mixed microbial communities. Mol Microbial Ecol Man 3.4.4(1):1–23
Pelz O, Tesar M, Wittich RM, Moore ERB, Timmis KN, Abraham WR (1999) Towards elucidation of microbial community metabolic pathways: unrevealing the network of carbon sharing in a pollutant-degrading bacterial consortium by immunocapture and isotopic ratio mass spectrometry. Environ Microbiol 1:167–174
Peters KE, Moldowan JM (1993) The biomarker guide. Interpreting molecular fossils in petroleum and ancient sediments. Prentice Hall Inc., Englewood cliffs
Polz MF, Cavanaugh CM (1998) Bias in template-to-product ratios in multitemplate PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:33724–33730
Raghukumar C, Vipparty V, David JJ, Chandramohan D (2001) Degradation of crude oil by marine cyanobacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:433–436
Rosenberg E, Legmann R, Kushmaro A, Taube R, Adler E, Ron EZ (1992) Petroleum bioremediation—a multiphase problem. Biodegradation 3:337–350
Sahm K, Knoblauch C, Amann R (1999) Phylogenetic affiliation and quantification of psychrophilic sulfate-reducing isolates in marine arctic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3976–3981
Syutsubo K, Kishira H, Harayama S (2001) Development of specific oligonucleotide probes for the identification and in situ detection of hydrocarbon degrading Alcanivorax strains. Environ Microbiol 3:371–379
Thomas JM, Yordy JR, Amador JA, Alexander M (1986) Rates of dissolution and biodegradation of water-insoluble organic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 52:290–296
Von Witzingerode F, Göbel UB, Stackebrandt E (1997) Determination of microbial diversity in environmental samples: pitfalls of PCR-based rRNA analysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21:213–229
Westlake DWS, Jobson A, Philippe R, Cook FD (1974) Biodegradability and crude oil composition. Can J Microbiol 20:915–928
Whyte LG, Hwari J, Zhou E, Bourbonnière L, Inniss WE, Greer CW (1998) Biodegradation of variable-chain-length alkanes at low temperatures by a psychrotrophic Rhodoccoccus sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2578–2584
Whyte LG, Slagmann SJ, Pietrantonio F, Bourbonniére L, Koval SF, Lawrence JR, Inniss WE, Greer CW (1999) Physiological adaptations involved in alkane assimilation at a low temperature by Rhodococcus sp. strain Q15. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2961–2968
Wick LY, Springdael D, Harms H (2001) Bacterial strategies to improve the bioavailability of hydrophobic organic pollutants. In: Stegmann R, Brunner G, Calmano W, Matz G (eds) Treatment of contaminated soil. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 203–217
Wick LY, de Munain AR, Springael D, Harms H (2002a) Responses of Mycobacterium sp. LB501T to the low bioavailability of solid anthracene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:378–385
Wick LY, Wattiau P, Harms H (2002b) Influence of the growth substrate on the mycolic acid profiles of mycobacteria. Environ Microbiol 4:612–616
Yakimov MM, Guiliano L, Crisafi E, Chemikova TN, Timmis KN, Golyshin PN (2002) Microbial community of a saline mud volcano at San Biagio-Belpasso, Mt. Etna (Italy). Environ Microbiol 4:249–256
Ziemke F, Höfle MG, Lalucat J, Roselló-Mora R (1998) Reclassification of Shewanella putrefaciens Owen‘s genomic group II as Shewanella baltica sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:769–774
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to Hauke Trinks from Hamburg University of Technology for supplying the samples from Spitzbergen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Horikoshi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deppe, U., Richnow, HH., Michaelis, W. et al. Degradation of crude oil by an arctic microbial consortium. Extremophiles 9, 461–470 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-005-0463-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-005-0463-2