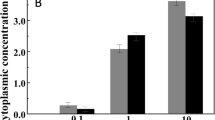
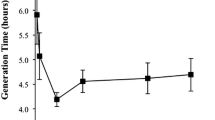
Abstract
While much understanding has been achieved on the intracellular sodium and potassium concentrations of halophilic and halotolerant microorganisms and on their regulation, we know little on the metabolism of anions. Archaea of the family Halobacteriaceae contain molar concentrations of chloride, which is pumped into the cells by cotransport with sodium ions and/or using the light-driven primary chloride pump halorhodopsin. Most halophilic and halotolerant representatives of the bacterial domain contain low intracellular ion concentrations, with organic osmotic solutes providing osmotic balance. However, some species show a specific requirement for chloride. In Halobacillus halophilus certain functions, such as growth, endospore germination, motility and flagellar synthesis, and glycine betaine transport are chloride dependent. In this organism the expression of a large number of proteins is chloride regulated. Other moderately halophilic Bacteria such as Halomonas elongata do not show a specific demand for chloride. A very high requirement for chloride was demonstrated in two groups of Bacteria that accumulate inorganic salts intracellularly rather than using organic osmotic solutes: the anaerobic Halanaerobiales and the aerobic extremely halophilic Salinibacter ruber. It is thus becoming increasingly clear that chloride has specific functions in haloadaptation in different groups of halophilic microorganisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antón J, Oren A, Benlloch S, Rodríguez-Valera F, Amann R, Rosselló-Mora R (2002) Salinibacter ruber gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel extreme halophilic Bacterium from saltern crystallizer ponds. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:485–491
Bamberg E, Hegemann P, Oesterhelt D (1984) The chromoprotein of halorhodopsin is the light-driven electrogenic chloride pump in Halobacterium halobium. Biochemistry 23:6216–6221
Bivin DB, Stoeckenius W (1986) Photoactive retinal pigments in haloalkaliphilic archaebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 132:2167–2177
Christian JHB, Waltho JA (1962) Solute concentrations within cells of halophilic and non-halophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 65:506–508
Claus D, Fahmy F, Rolf HJ, Tosunoglu N (1983) Sporosarcina halophila sp. nov., an obligate, slightly halophilic bacterium from salt marsh soils. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:496–506
Dohrmann A-B, Müller V (1999) Chloride dependence of endospore germination in Halobacillus halophilus. Arch Microbiol 172:264–267
Duschl A, Wagner G (1986) Primary and secondary chloride transport in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol 168:548–552
Ginzburg M, Sachs L, Ginzburg BZ (1970) Ion metabolism in a Halobacterium. I. Influence of age of culture on intracellular concentrations. J Gen Physiol 55:187–207
Incharoensakdi A, Takabe T (1988) Determination of intracellular chloride ion concentration in a halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica. Plant Cell Physiol 29:1073–1075
Kamekura M, Kushner DJ (1984) Effect of chloride and glutamate ions on in vitro protein synthesis by the moderate halophile Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol 160:385–390
Kolbe M, Besir H, Essen L-O, Oesterhelt D (2000) Structure of the light-driven chloride pump halorhodopsin at 1.8 Å resolution. Science 288:1391–1396
Kunji ERS, Gronau S von, Oesterhelt D, Henderson R (2000) The three-dimensional structure of halorhodopsin to 5 Å by electron crystallography: a new unbending procedure for two-dimensional crystals by using a global reference structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4637–4642
Kushner DJ (1989) Halophilic bacteria: life in and out of salt. In: Hattori T, Ishida Y, Maruyama Y, Morita RY, Uchida A (eds) Recent advances in microbial ecology. Japan Scientific, Tokyo, pp 60–64
Lanyi JK (1984) Light-dependent trans to cis isomerization of the retinal in halorhodopsin. FEBS Lett 175:337–342
Lanyi JK (1986) Halorhodopsin: a light-driven chloride ion pump. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem 15:11–28
Lanyi JK (1990) Halorhodopsin, a light-driven electrogenic chloride-transport system. Physiol Rev 70:319–330
Lanyi JK, Duschl A, Hatfield GW, May K, Oesterhelt D (1990) The primary structure of a halorhodopsin from Natronobacterium pharaonis. Structural, functional and evolutionary implications for bacterial rhodopsins and halorhodopsins. J Biol Chem 265:1253–1260
Lindley EV, MacDonald RE (1979) A second mechanism for sodium extrusion in Halobacterium halobium: a light-driven sodium pump. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 88:491–499
MacLeod RA, Onofrey E (1956) Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. II. Observations on the relation of sea water to the growth of marine bacteria. J Bacteriol 71:661–667
MacLeod RA, Onofrey E (1957) Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. VI. Quantitative requirements for halides, magnesium, calcium, and iron. Can J Microbiol 3:753–757
Masui M, Wada S (1973) Intracellular concentrations of Na+, K+ and Cl− of a moderately halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol 19:1181–1186
Matsuno-Yagi A, Mukohata Y (1977) Two possible roles of bacteriorhodopsin; a comparative study of strains of Halobacterium halobium differing in pigmentation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 78:237–243
Matsuno-Yagi A, Mukohata Y (1980) ATP synthesis linked to light-dependent proton uptake in a red mutant strain of Halobacterium lacking bacteriorhodopsin. Arch Biochem Biophys 199:297–303
Oesterhelt D (1995) Structure and function of halorhodopsin. Isr J Chem 35:475–494
Oren A (1986) Intracellular salt concentration of the anaerobic halophilic eubacteria Haloanaerobium praevalens and Halobacteroides halobius. Can J Microbiol 32:4–9
Oren A (2002) Halophilic microorganisms and their environments. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht
Oren A, Heldal M, Norland S (1997) X-ray microanalysis of intracellular ions in the anaerobic halophilic eubacterium Haloanaerobium praevalens. Can J Microbiol 43:588–592
Oren A, Heldal M, Norland S, Galinski EA (2002) Intracellular ion and organic solute concentrations of the extremely halophilic Bacterium Salinibacter ruber. Extremophiles 6:491–498
Rengpipat S, Lowe SE, Zeikus JG (1988) Effect of extreme salt concentrations on the physiology and biochemistry of Halobacteroides acetoethylicus. J Bacteriol 170:3065–3071
Roessler M, Müller V (1998) Quantitative and physiological analysis of chloride dependence of growth in Halobacillus halophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3813–3817
Roessler M, Müller V (2001) Chloride dependence of glycine betaine transport in Halobacillus halophilus. FEBS Lett 489:125–128
Roessler M, Müller V (2002) Chloride, a new environmental signal molecule involved in gene regulation in a moderately halophilic bacterium, Halobacillus halophilus. J Bacteriol 184:6207–6215
Roessler M, Wanner G, Müller V (2000) Motility and flagellum synthesis in Halobacillus halophilus are chloride dependent. J Bacteriol 182:532–535
Schobert B, Lanyi JK (1982) Halorhodopsin is a light-driven chloride pump. J Biol Chem 257:10306–10313
Schobert B, Lanyi JK, Cragoe EJ Jr (1983) Evidence for a halide-binding site in halorhodopsin. J Biol Chem 258:15158–15164
Severin J (1993) Kompatible Solute und Wachstumskinetik bei halophilen aeroben heterotrophen Eubakterien. PhD thesis, University of Bonn, Germany
Shindler DB, Wydro RM, Kushner DJ (1977) Cell-bound cations of the moderately halophilic bacterium Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol 130:698–703
Spring S, Ludwig W, Marquez MC, Ventosa A, Schleifer KH (1996) Halobacillus gen. nov., with descriptions of Halobacillus litoralis sp. nov. and Halobacillus trueperi sp. nov., and transfer of Sporsarcina halophila to Halobacillus halophilus comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:492–496
Tittor J, Oesterhelt D, Maurer R, Desel H, Uhl R (1987) The photochemical cycle of halorhodopsin: absolute spectra of intermediates obtained by flash photolysis and fast difference spectra measurements. Biophys J 52:999–1006
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:504–544
Weisser J, Trüper HG (1985) Osmoregulation in a new haloalkaliphilic Bacillus from the Wadi Natrun (Egypt). Syst Appl Microbiol 6:7–11
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a grant from the German Israeli Foundation for Scientific Research and Development (G.I.F.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D.A. Cowan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, V., Oren, A. Metabolism of chloride in halophilic prokaryotes. Extremophiles 7, 261–266 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-003-0332-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-003-0332-9