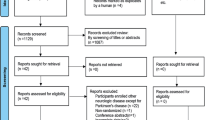
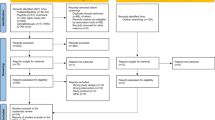
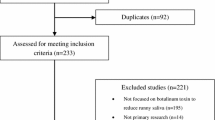
Abstract
Objectives
The present systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized control trials (RCTs) aimed to establish whether there are evidence-based differences in the pharmacological agents used to manage sialorrhea in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Material and methods
The authors searched the databases: MEDLINE via PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library for clinical trials. Unpublished trials were searched on clinicaltrials.gov and the Brazilian Clinical Trials Registry. Means and standard deviations of changes in the salivary flow or drooling reported by participants due to the interventions were recorded.
Results
The authors analyzed 13 RCTs. Compared to the placebo, types A and B of the botulinum toxin effectively reduced the salivary flow and the severity or frequency of drooling. However, the network meta-analysis did not differentiate between the botulinum toxin types. Ipratropium bromide and glycopyrrolate did not differ from the placebo. Indirect evidence showed that ipratropium had similar results to those obtained with both types of botulinum toxin. The CINeMA approach estimated the quality of the evidence as very low for all comparisons.
Conclusion
The best treatment for sialorrhea in patients with PD is not fully elucidated yet. Therefore, more well-conducted randomized clinical trials are required to increase the level of evidence.
Clinical relevance
There needs to be more evidence defining the best intervention to treat sialorrhea in patients with PD. However, botulinum toxin types A and B seem to reduce sialorrhea in patients effectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author, P.C.L., upon reasonable request.
References
Dexter DT, Jenner P (2013) Parkinson disease: from pathology to molecular disease mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med 62:132–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.018
Hirsch L, Jette N, Frolkis A, Steeves T, Pringsheim T (2016) The incidence of Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology 46:292–300. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445751
Hayes MT (2019) Parkinson’s disease and Parkinsonism. Am J Med 132:802–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2019.03.001
Armstrong MJ, Okun MS (2020) Diagnosis and treatment of parkinson disease: a review. JAMA 323(6):548–560. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.22360
Van Wamelen DJ, Leta V, Johnson J, Ocampo CL, Podlewska AM, Rukavina K, Rizos A, Martinez-martin P, Chaudhuri KR (2020) Drooling in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence and progression from the non-motor international longitudinal study. Dysphagia 35:955–961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-020-10102-5
Jost WH, Steffen A, Steffen B (2021) A critical review of incobotulinumtoxinA in the treatment of chronic sialorrhea in pediatric patients. Expert Rev Neurother 21(10):1059–1068. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2021.1979959
Srivanitchapoom P, Pandey S, Hallett M (2014) Drooling in Parkinson’s disease: a review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20:1109–1118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.08.013
Isaacson J, Patel S, Torres-Yaghi Y, Pagán F (2020) Sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease. Toxins (Basel) 12(11):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110691
Mcgeachan AJ, Mcdermott CJ (2017) Management of oral secretions in neurological disease. Pract Neurol 17:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1136/practneurol-2016-001515
Tiigimäe-Saar J, Taba P, Tamme T (2017) Does Botulinum neurotoxin type A treatment for sialorrhea change oral health? Clin Oral Investig 21:795–800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-016-1826-z
Sridharan K, Sivaramakrishnan G (2018) Pharmacological interventions for treating sialorrhea associated with neurological disorders: a mixed treatment network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Neurosci 51:12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2018.02.011
Isaacson J, Patel S, Torres-yaghi Y, Pagán F (2020) Sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease. Toxins (Basel) 12:691. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110691
Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM, Chaimani A, Schmid CH, Cameron C, Ioannidis JP, Straus S, Thorlund K, Jansen JP, Mulrow C, Catalá-López F, Gøtzsche PC, Dickersin K, Boutron I, Altman DG, Moher D (2015) The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med 162:777–784. https://doi.org/10.7326/M14-2385
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (eds) (2011) Cochrane Handbook for systematic reviews of Interventions 5.1.0. Available at: https://handbook-5-1.cochrane.org/. Accessed 8 Nov 2021
Steinlechner S, Klein C, Moser A, Lencer R, Hagenah J (2010) Botulinum toxin B as an effective and safe treatment for neuroleptic-induced sialorrhea. Psychopharmacology 207:593–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1689-y
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, Cates CJ, Cheng HY, Corbett MS, Eldridge SM, Emberson JR, Hernán MA, Hopewell S, Hróbjartsson A, Junqueira DR, Jüni P, Kirkham JJ, Lasserson T, Li T, McAleenan A, Reeves BC, Shepperd S, Shrier I, Stewart LA, Tilling K, White IR, Whiting PF, Higgins JPT (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing the risk of bias in randomized trials. BMJ 366:l4898. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4898
Harrer M, Cuijpers P, Furukawa TA, Ebert DD (2021) Doing meta-analysis with R: a hands-on guide. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Rücker G, Schwarzer G (2015) Ranking treatments in frequentist network meta-analysis works without resampling methods. BMC Med Res Methodol 31(15):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-015-0060-8
Salanti G, Del Giovane C, Chaimani A, Caldwell DM, Higgins JP (2014) Evaluating the quality of evidence from a network meta-analysis. PLoS One 9:e99682. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099682
Nikolakopoulou A, Higgins JPT, Papakonstantinou T, Chaimani A, Del Giovane C, Egger M, Salanti G (2020) CINeMA: an approach for assessing confidence in the results of a network meta-analysis. CINeMA: an approach for assessing confidence in the results of a network meta-analysis. PLoS Med 17:e1003082. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1003082
Lipp A, Trottenberg T, Schink T, Kupsch A, Arnold G (2003) A randomized trial of botulinum toxin A for treatment of drooling. Neurology 61:1279–1281. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.61.9.1279
Mancini F, Zangaglia R, Cristina S, Sommaruga MG, Martignoni E, Nappi G, Pacchetti C (2003) Double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of drooling in parkinsonism. Mov Disord 18:685–688. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.10420
Ondo WG, Hunter C, Moore W (2004) A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of botulinum toxin B for sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 62:37–40. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000101713.81253.4c
Lagalla G, Millevolte M, Capecci M, Provinciali L, Ceravolo MG (2006) Botulinum toxin type A for drooling in Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Mov Disord 21:704–707. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20793
Thomsen TR, Galpern WR, Asante A, Arenovich T, Fox SH (2007) Ipratropium bromide spray as a treatment for sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22:2268–2273. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21730
Lagalla G, Millevolte M, Capecci M, Provinciali L, Ceravolo MG (2009) Long-lasting benefits of botulinum toxin type B in Parkinson’s disease-related drooling. J Neurol 256:563–567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-0085-1
Arbouw ME, Movig KL, Koopmann M, Poels PJ, Guchelaar HJ, Egberts TC, Neef C, van Vugt JP (2010) Glycopyrrolate for sialorrhea in Parkinson disease: a randomized, double-blind, crossover trial. Neurology 74:1203–1207. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181d8c1b7
Guidubaldi A, Fasano A, Ialongo T, Piano C, Pompili M, Mascianà R, Siciliani L, Sabatelli M, Bentivoglio AR (2011) Botulinum toxin A versus B in sialorrhea: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, crossover pilot study in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23473
Chinnapongse R, Gullo K, Nemeth P, Zhang Y, Griggs L (2012) Safety and efficacy of botulinum toxin type B for treatment of sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease: a prospective, double-blind trial. Mov Disord 27:219–226. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23929
Jost WH, Friedman A, Michel O, Oehlwein C, Slawek J, Bogucki A, Ochudlo S, Banach M, Pagan F, Flatau-Baqué B, Csikós J, Cairney CJ, Blitzer A (2019) SIAXI: placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study of incobotulinumtoxinA for sialorrhea. Neurology 92:e1982–e1991. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000007368
Isaacson SH, Ondo W, Jackson CE, Trosch RM, Molho E, Pagan F, Lew M, Dashtipour K, Clinch T, Espay AJ, MYSTICOL Study Group (2020) Safety and efficacy of rimabotulinumtoxinB for treatment of sialorrhea in adults: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol 77:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4565
Mestre TA, Freitas E, Basndwah A, Lopez MR, de Oliveira LM, Al-Shorafat DM, Zhang T, Lui JP, Grimes D, Fox SH (2020) Glycopyrrolate improves disability from sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease: a 12-week controlled trial. Mov Disord 35:2319–2323. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.28196
Krahn U, Binder H, König J (2013) A graphical tool for locating inconsistency in network meta-analyses. BMC Med Res Methodol 13:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-13-35
Salanti G, Ades AE, Ioannidis JP (2011) Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J Clin Epidemiol 64:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.03.016
Mbuagbaw L, Rochwerg B, Jaeschke R, Heels-Andsell D, Alhazzani W, Thabane L, Guyatt GH (2017) Approaches to interpreting and choosing the best treatments in network meta-analyses. Syst Rev 6(1):79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0473-z
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Routledge, Oxfordshire
Ruiz-Roca JA, Pons-Fuster E, Lopez-Jornet P (2019) Effectiveness of the botulinum toxin for treating sialorrhea in patients with parkinson’s disease: a systematic review. J Clin Med 8:317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030317
Filho Oliveira AF, Silva GA, Almeida DM (2016) Application of botulinum toxin to treat sialorrhea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients: a literature review. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 14:431–434. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1679-45082016RB3594
Dashtipour K, Bhidayasiri R, Chen JJ, Jabbari B, Lew M, Torres-Russotto D (2017) RimabotulinumtoxinB in sialorrhea: systematic review of clinical trials. J Clin Mov Disord 4:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40734-017-0055-1
Hung SA, Liao CL, Lin WP, Hsu JC, Guo YH, Lin YC (2021) Botulinum toxin injections for treatment of drooling in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Children (Basel) 8:1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8121089
Funding
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brazil (CAPES, Finance Code 001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: José Ronaldo dos Santos, Pollyana Caldeira Leal.
Methodology: Alessandra Reis.
Formal analysis and investigation: Luiz Carlos Santos Junior, Alessandra Reis, André Luís Faria-e-Silva, Pollyana Caldeira Leal.
Writing—original draft preparation: Luiz Carlos Santos Junior, José Ronaldo dos Santos, Alessandra Reis, André Luís Faria-e-Silva, Pollyana Caldeira Leal.
Writing—review and editing: Luiz Carlos Santos Junior, José Ronaldo dos Santos, Alessandra Reis, André Luís Faria-e-Silva, Pollyana Caldeira Leal.
Funding acquisition: Pollyana Caldeira Leal.
Resources: Pollyana Caldeira Leal.
Supervision: Pollyana Caldeira Leal.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Santos Junior, L.C., Santos, J.R., Reis, A. et al. Effectiveness of the pharmacological treatments for sialorrhea in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin Oral Invest 27, 2449–2463 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-023-04981-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-023-04981-9