Abstract
Objective
This systematic review aims to answer the following question: What is the psychological impact of orthognathic surgery on patients with dentofacial deformities undergoing orthodontic-surgical treatment?
Material and methods
The search was adapted for each of the following databases: American and Caribbean Center on Health Sciences (LILACS), Cochrane Library, Embase, Psychinfo, PubMed/Medline, Scopus and Web of Science, and gray literature using Google Scholar, OpenGrey, and ProQuest. The risk of bias was assessed using the Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Assessment Checklist. This study performed estimates of interest, random-effects meta-analyses, and calculated heterogeneity using Higgins inconsistency index (I2).
Results
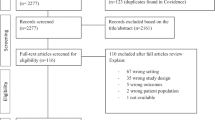
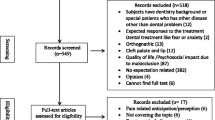
A total of 6751 references were found in all searches. After applying the eligibility criteria after full-text reading, 37 studies comprised the final qualitative synthesis. Thirteen studies were included in quantitative synthesis, and it was possible to meta-analyze data from the following questionnaires: GHQ-28, MMPI, RSES, and SCL-90-R. There was an improvement in psychological aspects related to depression, hysteria, self-esteem, anxiety, obsessive-compulsiveness, interpersonal sensitivity, paranoid ideas, and psychoticism (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Correction of dentofacial deformity through orthodontic-surgical treatment is associated with improvements observed in several psychological domains, especially in relation to depressive states.
Clinical relevance.
This result highlights the importance of surgeons and orthodontists in promoting adequate control of patients’ expectations and treatment goals taking into account the individual's psychological aspects.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denadai R, Chou PY, Su YY, Lo CC, Lin HH, Ho CT, Lo LJ (2019) Facial Appearance and Psychosocial Features in Orthognathic Surgery: A FACE-Q- and 3D Facial Image-Based Comparative Study of Patient-, Clinician-, and Lay-Observer-Reported Outcomes. J Clin Med 8:909. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8060909
Zamboni R, de Moura FRR, Brew MC, Rivaldo EG, Braz MA, Grossmann E, Bavaresco CS (2019) Impacts of Orthognathic Surgery on Patient Satisfaction, Overall Quality of Life, and Oral Health-Related Quality of Life: A Systematic Literature Review. Int J Dent 2019:2864216. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2864216
Palomares NB, Celeste RK, Miguel JA (2016) Impact of orthosurgical treatment phases on oral health-related quality of life. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 149:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2015.07.032
Su YY, Denadai R, Ho CT, Lai BR, Lo LJ (2020) Measuring patient-reported outcomes in orthognathic surgery: Linguistic and psychometric validation of the Mandarin Chinese version of FACE-Q instrument. Biomed J 43:62–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bj.2019.05.011
Larsson P, Bondemark L, Haggman-Henrikson B (2021) The impact of oro-facial appearance on oral health-related quality of life: A systematic review. J Oral Rehabil 48:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.12965
Brucoli M, Baena RRY, Boffano P, Benech A (2019) Psychological profiles in patients undergoing orthognathic surgery or rhinoplasty: a preoperative and preliminary comparison. Oral Maxillofac Surg 23:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-019-00758-1
Cunha HS, da Costa Moraes CA, de Faria VDR, da Rosa ELS (2020) Accuracy of three-dimensional virtual simulation of the soft tissues of the face in OrtogOnBlender for correction of class II dentofacial deformities: an uncontrolled experimental case-series study. Oral Maxillofac Surg 25:319–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-020-00920-0
Alanko OM, Svedstrom-Oristo AL, Tuomisto MT (2010) Patients’ perceptions of orthognathic treatment, well-being, and psychological or psychiatric status: a systematic review. Acta Odontol Scand 68:249–260. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016357.2010.494618
Broers DLM, van der Heijden G, Rozema FR, de Jongh A (2017) Do patients benefit from orthognathic surgery? A systematic review on the effects of elective orthognathic surgery on psychosocial functioning and patient satisfaction. Eur J Oral Sci 125:411–418. https://doi.org/10.1111/eos.12371
Hunt OT, Johnston CD, Hepper PG, Burden DJ (2001) The psychosocial impact of orthognathic surgery: a systematic review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 120:490–497. https://doi.org/10.1067/mod.2001.118402
Brignardello-Petersen R (2018) No evidence about the effects of orthognathic surgery in psychosocial functioning owing to limitations in the systematic review. J Am Dental Assoc 149:e21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adaj.2017.09.047
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hrobjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, Moher D (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A (2016) Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev 5:210. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4
Institute TJB (2014) Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewers' Manual. The Joanna Briggs Institute, Australia
Andrade C (2020) Mean Difference, Standardized Mean Difference (SMD), and Their Use in Meta-Analysis: As Simple as It Gets. J Clin Psychiatry 81:20f13681. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.20f13681
Higgins JP (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1. 0 The Cochrane Collaboration.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schunemann HJ, Group GW (2008) GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 336:924–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD
Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, Norris S, Falck-Ytter Y, Glasziou P, DeBeer H, Jaeschke R, Rind D, Meerpohl J, Dahm P, Schunemann HJ (2011) GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol 64:383–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026
Alanko OM, Svedstrom-Oristo AL, Peltomaki T, Kauko T, Tuomisto MT (2014) Psychosocial well-being of prospective orthognathic-surgical patients. Acta Odontol Scand 72:887–897. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016357.2014.920107
Burden DJ, Hunt O, Johnston CD, Stevenson M, O’Neill C, Hepper P (2010) Psychological status of patients referred for orthognathic correction of skeletal II and III discrepancies. Angle Orthod 80:43–48. https://doi.org/10.2319/022709-114.1
Lee L, Chen SH, Yu CC, Lo LJ, Lee SR, Chen YR (2007) Stigma, body image, and quality of life in women seeking orthognathic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:225–231. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000264100.57630.c7
Ryan FS, Moles DR, Shute JT, Clarke A, Cunningham SJ (2016) Social anxiety in orthognathic patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 45:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2015.05.021
Williams DM, Bentley R, Cobourne MT, Gibilaro A, Good S, Huppa C, Matthews NS, O’Higgins E, Patel S, Newton JT (2009) Psychological characteristics of women who require orthognathic surgery: comparison with untreated controls. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 47:191–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2008.07.187
Yao S, Zhou J, Li ZB (2014) Psychologic Health Status of Patients Undergoing Orthognathic Surgery. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 25:E540–E543. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000001042
Gobic BM, Kralj M, Harmicar D, Cerovic R, Mady Maricic B, Spalj S (2021) Dentofacial deformity and orthognatic surgery: Influence on self-esteem and aspects of quality of life. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 49:277–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2021.01.024
Al-Bitar ZB, Al-Ahmad HT (2017) Anxiety and post-traumatic stress symptoms in orthognathic surgery patients. Eur J Orthod 39:92–97. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjw029
Auerbach SM et al (1984) Psychological factors in adjustment to orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42:435–440
Finlay PM, Moos SF, Atkinson JM (1995) Orthognathic surgery: patient expectations; psychological profile and satisfaction with outcome. Brit J Oral Maxillofac Surg 33:9–14
Kim SJ, Kim MR, Shin SW, Chun YS, Kim EJ (2009) Evaluation on the psychosocial status of orthognathic surgery patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 108:828–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.07.044
Lazaridou-Terzoudi T, Kiyak HA, Moore R, Athanasiou AE, Melsen B (2003) Long-term assessment of psychologic outcomes of orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 61:545–552. https://doi.org/10.1053/joms.2003.50107
Oland J, Jensen J, Elklit A, Melsen B (2011) Motives for surgical-orthodontic treatment and effect of treatment on psychosocial well-being and satisfaction: a prospective study of 118 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2010.06.203
Suen KS, Lai Y, Ho SMY, Cheung LK, Choi WS (2018) A longitudinal evaluation of psychosocial changes throughout orthognathic surgery. PLoS ONE 13:e0203883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203883
Alanko O, Tuomisto MT, Peltomaki T, Tolvanen M, Soukka T, Svedstrom-Oristo AL (2017) A longitudinal study of changes in psychosocial well-being during orthognathic treatment. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46:1380–1386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2017.05.004
Agirnasligil MO, Gul Amuk N, Kilic E, Kutuk N, Demirbas AE, Alkan A (2019) The changes of self-esteem, sensitivity to criticism, and social appearance anxiety in orthognathic surgery patients: A controlled study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 155:482-489 e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajodo.2018.05.019
Guimarães FR, Oliveira EC, Gomes TR, Souza TD (2014) Quality of life in patients who undergo orthognathic surgery: oral health and self-esteem. Psicologia: Ciência e Profissão 34:242–251
Gerzanic L, Jagsh R, Watzke IM (2002) Psychologic implications of orthognathic surgery in patients with skeletal Class II or Class III malocclusion. Int J Adult Orthod Orthognath Surg 17:75–81
Hatch JPRJ, Bays RA, Van Sickels JE, Keeling SD, Clark GM (1999) Psychological function in orthognathic surgical patients before and after bilateral sagittal split osteotomy with rigid and wire fixation. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 115:536–543
Takatsuji H, Kobayashi T, Kojima T, Hasebe D, Izumi N, Saito I, Saito C (2015) Effects of orthognathic surgery on psychological status of patients with jaw deformities. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44:1125–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2015.02.003
Flanary CM (1990) Impact of orthognathic surgery on normal and abnormal personality dimensions: a 2-year follow-up study of 61 patients. Am J Orthodont Dentofac Orthoped 98:313–322
Jung MH (2016) Quality of Life and Self-Esteem of Female Orthognathic Surgery Patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 74(1240):e1-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2016.01.046
Kiyak HA, Hohl T, West RA, McNeill RW (1984) Psychologic changes in orthognathic surgery patients: a 24-month follow up. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42:506–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-2391(84)90009-0
Kiyak HAV, P.P., Crinean, J. (1988) Patients’ Expectations as Predictors of Orthognathic Surgery Outcomes. Health Psychol 7:251–268
Kiyak HA, West RA, Hohi T, McNeill RW (1982) The psychological impact of orthognathic surgery: A g-month follow-up. Am J Orthod 81:404–412
Nicodemo D, Peirera MD, Ferreira LM (2008) Self-esteem and depression in patients presenting angle class III malocclusion submitted for orthognathic surgery. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 13:48–51
Sar C, Soydan SS, Ozcirpici AA, Uckan S (2015) Psychosocial and functional outcomes of orthognathic surgery: Comparison with untreated controls. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol 27:451–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajoms.2014.03.001
Yao S, Zhou J, Li Z (2014) Psychologic health status of patients undergoing orthognathic surgery. J Craniofac Surg 25:e540–e543. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000001042
Belusic Gobic M, Kralj M, Harmicar D, Cerovic R, Mady Maricic B, Spalj S (2021) Dentofacial deformity and orthognatic surgery: Influence on self-esteem and aspects of quality of life. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 49:277–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2021.01.024
Cunningham SJ, Hunt NP, Feinmann C (1996) Perceptions of outcome following orthognathic surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34:210–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0266-4356(96)90271-5
Kiyak HA, McNeill RW, West RA, Hohl T, Bucher F, Sherrick P (1982) Predicting psychologic responses to orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 40:150–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-2391(82)90046-5
Kiyak HA, Mcneill RW, West RA (1985) The emotional impact of orthognathic surgery and conventional orthodontics. Am J Orthodont Dentofac Orthoped 88:224–234
Burden DJHO, Johnston CD, Stevenson M, O’Neill C, Hepper P (2010) Psychological status of patients referred for orthognathic correction of skeletal II and III discrepancies. Angle Orthod 80:43–48. https://doi.org/10.2139/022709-114.1
Brunault P, Battini J, Potard C, Jonas C, Zagala-Bouquillon B, Chabut A, Mercier JM, Bedhet N, Réveillère C, Goga D, Courtois R (2016) Orthognathic surgery improves quality of life and depression, but not anxiety, and patients with higher preoperative depression scores improve less. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 45:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2015.07.020
Battini J (2013) Impact psychologique des interventions en chirurgie orthognathique. Université François - Rabelais de Tours.
Brucoli M, Zeppegno P, Benech R, Boffano P, Benech A (2019) Psychodynamic Features Associated With Orthognathic Surgery: A Comparison Between Conventional Orthognathic Treatment and “Surgery-First” Approach. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 77:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2018.06.005
Scott AA et al (1999) Psychosocial predictors of high-risk patients undergoing orthognathic surgery. Int J Adult Orthodont Orthognathic Surg 14:113–124
Motegi E, Hatch JP, Rugh JD, Yamaguchi H (2003) Health-related quality of life and psychosocial function 5 years after orthognathic surgery. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 124:138–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0889-5406(03)00391-3
Ryan FS, Moles DR, Shute JT, Clarke A, Cunningham SJ (2016) Social Anxiety in Orthognathic Patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 45:19–25
Li XR, Chen LQ, Li YL, Sun J (2015) The change of patients’ psychosomatic symptoms after orthognathic surgery. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue 24:107–110
Lovius BBJ, Jones RB et al (1990) The specific psychosocial effects of orthognathic surgery. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg 18:339–342
de Avila ED, de Molon RS, Loffredo LC, Massucato EM, Hochuli-Vieira E (2013) Health-related quality of life and depression in patients with dentofacial deformity. Oral Maxillofac Surg 17:187–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-012-0338-5
Kovalenko A, Slabkovskaya A, Drobysheva N, Persin L, Drobyshev A, Maddalone M (2012) The association between the psychological status and the severity of facial deformity in orthognathic patients. Angle Orthod 82:396–402. https://doi.org/10.2319/060211-363.1
Qian H, Ling Y, Wang C, Lenahan C, Zhang M, Zheng M, Shao A (2021) A Correlative Study Between Personality Traits and the Preference of Site Selection in Cosmetic Treatment. Front Psychiatry 12:648751. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.648751
de Araujo CM, Schroder AGD, de Araujo BMM, Cavalcante-Leao BL, Stechman-Neto J, Zeigelboim BS, Santos RS, Guariza-Filho O (2020) Impact of orthodontic-surgical treatment on quality of life: a meta-analysis. Eur J Orthod 42:281–289. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjz093
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basso, I., Gonçalves, F., Martins, A. et al. Psychosocial changes in patients submitted to orthodontic surgery treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Invest 26, 2237–2251 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-04304-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-04304-w