Abstract
Objectives
MI Paste Plus remineralizer (Rem) strengthens dental structures after bleaching. We investigated the effect of Rem on the penetration of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), bleaching effectiveness, and pulp inflammation after bleaching.
Materials and methods
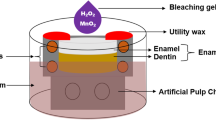
Bovine disks were grouped as follows (n = 10): control (untreated), bleached (Ble; 35% H2O2, 30 min), Ble-Rem (H2O2 followed by Rem, 30 min), Rem-Ble (Rem followed by H2O2), Rem-Ble-Rem (Rem before and after H2O2), and Ble+Rem (mixture of Rem with H2O2, 1:1, 30 min). The penetration of H2O2 was quantified and bleaching efficacy was analyzed. Upper rat molars (n = 10) received the same treatments at random. The rats were euthanized after two days and 30 days, and their jaws were removed for histological analysis. Statistical tests were performed (P < 0.05).
Results
The bleached groups, except Ble+Rem (P > 0.05), showed significant H2O2 penetration compared with control (P < 0.05). Color alteration analysis showed that ΔL and ΔE were significantly higher in the bleached groups than those in control (P < 0.05); the Δb of the bleached groups differed from that of control at 24 h (P < 0.05). At two days, necrosis or inflammation was observed in the bleached groups compared with control (P < 0.05), except Ble+Rem, which was similar to control (P > 0.05). At 30 days, tertiary dentin formation was significant in the bleached groups (P < 0.05), except Ble+Rem (P > 0.05).
Conclusion
The mixture of MI Paste Plus and bleaching gel reduces H2O2 penetration and pulp damage and maintains bleaching effectiveness.
Clinical relevance
Because bleaching can damage dental tissues, we studied a new bleaching protocol that reduces damage to the pulp tissue while maintaining bleaching efficiency: a single application of 30 min of MI Paste Plus mixed with 35% H2O2 bleaching gel (1:1).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Samorodnitzky-Naveh GR, Geiger SB, Levin L (2007) Patients’ satisfaction with dental esthetics. J Am Dent Assoc 138:805–808. https://doi.org/10.14219/jada.archive.2007.0269
Van der Geld P, Oosterveld P, Van Heck G, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM (2007) Smile attractiveness. Self-perception and influence on personality. Angle Orthod 77:759–765. https://doi.org/10.2319/082606-349
Chen P, Yu S, Zhu G (2012) The psychosocial impacts of implantation on the dental aesthetics of missing anterior teeth patients. Br Dent J 213:e20. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bdj.2012.1090
Tin-Oo MM, Saddki N, Hassan N (2011) Factors influencing patient satisfaction with dental appearance and treatments they desire to improve aesthetics. BMC Oral Health 23(11):6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6831-11-6
Maghaireh GA, Alzraikat H, Taha NA (2016) Satisfaction with dental appearance and attitude toward improving dental esthetics among patients attending a dental teaching center. J Contemp Dent Pract 17:16–21. https://doi.org/10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1796
Trindade FZ, Ribeiro AP, Sacono NT, Oliveira CF, Lessa FC, Hebling J, Costa CA (2009) Trans-enamel and trans-dentinal cytotoxic effects of a 35% H2O2 bleaching gel on cultured odontoblast cell lines after consecutive applications. Int Endod J 42(649):516–524. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2591.2009.01544.x
Cintra LT, Benetti F, da Silva Facundo AC, Ferreira LL, Gomes-Filho JE, Ervolino E, Rahal V, Briso AL (2013) The number of bleaching sessions influences pulp tissue damage in rat teeth. J Endod 39:1576–1580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2013.08.007
Soares DG, Basso FG, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA (2014) Concentrations of and application protocols for hydrogen peroxide bleaching gels: effects on pulp cell viability and whitening efficacy. J Dent 42:185–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2013.10.021
Cintra LT, Benetti F, Ferreira LL, Gomes-Filho JE, Ervolino E, Gallinari Mde O, Rahal V, Briso AL (2016) Penetration capacity, color alteration and biological response of two in-office bleaching protocols. Braz Dent J 27:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-6440201600329
Cintra LT, Benetti F, Ferreira LL, Rahal V, Ervolino E, Jacinto R de C, Gomes Filho JE, Briso AL (2016) Evaluation of an experimental rat model for comparative studies of bleaching agents. J Appl Oral Sci 24:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-775720150393
Borges BC, Pinheiro MH, Feitosa DA, Correia TC, Braz R, Montes MA, Pinheiro IV (2012) Preliminary study of a novel in-office bleaching therapy modified with a casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate. Microsc Res Tech 75:1571–1575. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.22102
Heshmat H, Ganjkar MH, Jaberi S, Fard MJ (2014) The effect of remin pro and MI paste plus on bleached enamel surface roughness. J Dent (Tehran) 11:131–136
Rezende M, Loguercio AD, Kossatz S, Reis A (2016) Predictive factors on the efficacy and risk/intensity of tooth sensitivity of dental bleaching: a multi regression and logistic analysis. J Dent 45:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2015.11.003
Charakorn P, Cabanilla LL, Wagner WC, Foong WC, Shaheen J, Pregitzer R, Schneider D (2009) The effect of preoperative ibuprofen on tooth sensitivity caused by in-office bleaching. Oper Dent 34:131–135. https://doi.org/10.2341/08-33
Rezende M, Loguercio AD, Reis A, Kossatz S (2013) Clinical effects of exposure to coffee during at-home vital bleaching. Oper Dent 38:E229–E236. https://doi.org/10.2341/12-188-C
Bonafe E, Loguercio AD, Reis A, Kossatz S (2014) Effectiveness of a desensitizing agent before in-office tooth bleaching in restored teeth. Clin Oral Investig 18:839–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-1055-7
Loguercio AD, Servat F, Stanislawczuk R, Mena-Serrano A, Rezende M, Prieto MV, Cereño V, Rojas MF, Ortega K, Fernandez E, Reis A (2017) Effect of acidity of in-office bleaching gels on tooth sensitivity and whitening: a two-center double-blind randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig 21:2811–2818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2083-5
Faria-E-Silva AL, Nahsan FP, Fernandes MT, Martins-Filho PR (2015) Effect of preventive use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on sensitivity after dental bleaching: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Dent Assoc 146:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adaj.2014.10.007
Cartagena AF, Parreiras SO, Loguercio AD, Reis A, Campanha NH (2015) In-office bleaching effects on the pulp flow and tooth sensitivity - case series. Braz Oral Res 29:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-3107BOR-2015.vol29.0026
Benetti AR, Valera MC, Mancini MNG, Miranda CB, Balducci I (2004) In vitro penetration of bleaching agents into the pulp chamber. Int Endod J 37:120–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0143-2885.2004.00761.x
Markowitz K (2010) Pretty painful: why does tooth bleaching hurt? Med Hypotheses 74:835–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2009.11.044
Mena-Serrano AP, Parreiras SO, do Nascimento EM, Borges CP, Berger SB, Loguercio AD, Reis A (2015) Effects of the concentration and composition of in-office bleaching gels on hydrogen peroxide penetration into the pulp chamber. Oper Dent 40:e76–e82. https://doi.org/10.2341/13-352-L
Benetti F, Lemos CAA, de Oliveira Gallinari M, Terayama AM, Briso ALF, de Castilho Jacinto R, Sivieri-Araújo G, Cintra LTA (2017) Influence of different types of light on the response of the pulp tissue in dental bleaching: a systematic review. Clin Oral Investig 22:1825–1837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2278-9
Alexandrino LD, Alencar CM, da Silveira ADS, Alves EB, Silva CM (2017) Randomized clinical trial of the effect of NovaMin and CPP-ACPF in combination with dental bleaching. J Appl Oral Sci 25:335–340. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-7757-2016-0408
Gomes MN, Rodrigues FP, Silikas N, Francci CE (2018) Micro-CT and FE-SEM enamel analyses of calcium-based agent application after bleaching. Clin Oral Investig 22:961–970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2175-2
Manton DJ, Bhide R, Hopcraft MS, Reynolds EC (2008) Effect of ozone and tooth mousse on the efficacy of peroxide bleaching. Aust Dent J 53:128–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1834-7819.2008.00021.x
Reynolds EC (2009) Casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate: the scientific evidence. Adv Dent Res 21:25–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/0895937409335619
Borges BC, Borges JS, de Melo CD, Pinheiro IV, Santos AJ, Braz R, Montes MA (2011) Efficacy of a novel at-home bleaching technique with carbamide peroxides modified by CPP-ACP and its effect on the microhardness of bleached enamel. Oper Dent 36:521–528. https://doi.org/10.2341/11-013-L
Rechmann P, Bekmezian S, Rechmann BMT, Chaffee BW, Featherstone JDB (2018) MI Varnish and MI Paste Plus in a caries prevention and remineralization study: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Investig 22:2229–2239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2314-9
Oshiro M, Yamaguchi K, Takamizawa T, Inage H, Watanabe T, Irokawa A, Ando S, Miyazaki M (2007) Effect of CPP-ACP paste on tooth mineralization: an FE-SEM study. J Oral Sci 49:115–120. https://doi.org/10.2334/josnusd.49.115
Rahiotis C, Vougiouklakis L (2007) Effect of a CPP-ACP agent on the demineralization and remineralization of dentine in vitro. J Dent 35:695–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2007.05.008
Bayrak S, Tunc ES, Sonmez IS, Egilmez T, Ozmen B (2009) Effects of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP) application on enamel microhardness after bleaching. Am J Dent 22:393–396
Khoroushi M, Mazaheri H, Manoochehri A (2011) Effect of CPP-ACP application on flexural strength of bleached enamel and dentin complex. Oper Dent 36:372–379. https://doi.org/10.2341/10-280-L
Bader JD (2010) Casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate shows promise for preventing caries. Evid Based Dent 11:11–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ebd.6400701
Nongonierma AB, Fitzgerald RJ (2012) Biofunctional properties of caseinophosphopeptides in the oral cavity. Caries Res 46:234–267. https://doi.org/10.1159/000338381
Cunha AG, De Vasconcelos AA, Borges BC, Vitoriano Jde O, Alves-Junior C, Machado CT, Dos Santos AJ (2012) Efficacy of in-office bleaching techniques combined with the application of a casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate paste at different moments and its influence on enamel surface properties. Microsc Res Tech 75:1019–1025. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.22026
Giniger M, Macdonald J, Ziemba S, Felix H (2005) The clinical performance of professionally dispensed bleaching gel with added amorphous calcium phosphate. J Am Dent Assoc 136:383–392. https://doi.org/10.14219/jada.archive.2005.0181
Nanjundasetty JK, Mohammed A (2016) Efficacy of desensitizing agents on postoperative sensitivity following an in-office vital tooth bleaching: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Conserv Dent 19:207–211. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-0707.181927
Yassin O, Milly H (2018) Effect of CPP-ACP on efficacy and postoperative sensitivity associated with at-home vital tooth bleaching using 20% carbamide peroxide. Clin Oral Investig 23:1555–1559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-018-2574-z
Sa Y, Chen D, Liu Y, Wen W, Xu M, Jiang T, Wang Y (2012) Effects of two in-office bleaching agents with different pH values on enamel surface structure and color: an in situ vs. in vitro study. J Dent 40(Suppl 1):e26–e34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2012.02.010
Marson FC, Gonçalves RS, Silva CO, Cintra LT, Pascotto RC, Santos PH, Briso AL (2015) Penetration of hydrogen peroxide and degradation rate of different bleaching products. Oper Dent 40:72–79. https://doi.org/10.2341/13-270-L
Duque CC, Soares DG, Basso FG, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA (2014) Bleaching effectiveness, hydrogen peroxide diffusion, and cytotoxicity of a chemically activated bleaching gel. Clin Oral Investig 18:1631–1637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-1147-4
Moreira JC, Gallinari Mde O, Rahal V, Fagundes TC, Santos PH, Moura MR, Briso AL (2016) Effect of dental pigmentation intensity on the transenamel and transdentinal penetration of hydrogen peroxide. Braz Dent J 27:399–403. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-6440201600838
Jacques P, Hebling J (2005) Effect of dentin conditioners on the microtensile bond strength of a conventional and a self-etching primer adhesive system. Dent Mater 21:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2003.12.004
de Almeida LC, Soares DG, Gallinari MO, de Souza Costa CA, Dos Santos PH, Briso AL (2015) Color alteration, hydrogen peroxide diffusion, and cytotoxicity caused by in-office bleaching protocols. Clin Oral Investig 19:673–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-014-1285-3
Benetti F, Gomes-Filho JE, Ferreira LL, Sivieri-Araújo G, Ervolino E, Briso ALF, Cintra LTA (2018) Concentration-dependent effect of bleaching agents on the immunolabelling of interleukin-6, interleukin-17 and CD5-positive cells in the dental pulp. Int Endod J 51:789–799. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12891
Benetti F, Briso ALF, Carminatti M, Lopes JMA, Barbosa JG, Ervolino E, Gomes-Filho JE, Cintra LTA (2018) Presence of osteocalcin, osteopontin, and reactive oxygen species-positive cells in pulp tissue after dental bleaching. Int Endod J, in press. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.13049, 52, 665, 675
Benetti F, Gomes-Filho JE, Ferreira LL, Ervolino E, Briso ALF, Sivieri-Araújo G, Dezan-Júnior E, Cintra LTA (2017) Hydrogen peroxide induces cell proliferation and apoptosis in pulp of rats after dental bleaching in vivo: effects of the dental bleaching in pulp. Arch Oral Biol 81:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.04.013
Benetti F, Briso ALF, Ferreira LL, Carminatti M, Álamo L, Ervolino E, Dezan-Júnior E, Cintra LTA (2018) In vivo study of the action of a topical anti-inflammatory drug in rat teeth submitted to dental bleaching. Braz Dent J 29:555–561. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-6440201802177
Seghi RR, Denry I (1992) Effects of external bleaching on indentation and abrasion characteristics of human enamel in vitro. J Dent Res 71:1340–1344. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345920710061201
Hegedüs C, Bistey T, Flóra-Nagy E, Keszthelyi G, Jenei A (1999) An atomic force microscopy study on the effect of bleaching agents on enamel surface. J Dent 27:509–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-5712(99)00006-8
Tam LE, Noroozi A (2007) Effects of direct and indirect bleach on dentin fracture toughness. J Dent Res 86:1193–1197. https://doi.org/10.1177/154405910708601210
Kumar VL, Itthagarun A, King NM (2008) The effect of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate on remineralization of artificial caries-like lesions: an in vitro study. Aust Dent J 53:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1834-7819.2007.00006.x
Azarpazhooh A, Limeback H (2008) Clinical efficacy of casein derivatives: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Dent Assoc 139:915–924. https://doi.org/10.14219/jada.archive.2008.0278
Penumatsa NV, Kaminedi RR, Baroudi K, Barakath O (2015) Evaluation of remineralization capacity of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate on the carbamide peroxide treated enamel. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 7:S583–S586. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.163556
Costa CA, Riehl H, Kina JF, Sacono NT, Hebling J (2010) Human pulp responses to in-office tooth bleaching. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 109:e59–e64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.12.002
Poggio C, Grasso N, Ceci M, Beltrami R, Colombo M, Chiesa M (2016) Ultrastructural evaluation of enamel surface morphology after tooth bleaching followed by the application of protective pastes. Scanning 38:221–226. https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.21263
Soares DG, Basso FG, Pontes EC, Garcia Lda F, Hebling J, de Souza Costa CA (2014) Effective tooth-bleaching protocols capable of reducing H(2)O(2) diffusion through enamel and dentine. J Dent 42:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2013.09.001
Xu B, Li Q, Wang Y (2011) Effects of pH values of hydrogen peroxide bleaching agents on enamel surface properties. Oper Dent 36:554–562. https://doi.org/10.2341/11-045-1
Griffiths CE, Bailey JR, Jarad FD, Youngson CC (2008) An investigation into most effective method of treating stained teeth: an in vitro study. J Dent 2008 36:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2007.10.009
Cintra LTA, Ferreira LL, Benetti F, Gastélum AA, Gomes-Filho JE, Ervolino E, Briso ALF (2017) The effect of dental bleaching on pulpal tissue response in a diabetic animal model. Int Endod J 50:790–798. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12692
Ferreira LL, Gomes-Filho JE, Benetti F, Carminatti M, Ervolino E, Briso ALF, Cintra LTA (2018) The effect of dental bleaching on pulpal tissue response in a diabetic animal model: a study of immunoregulatory cytokines. Int Endod J 51:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12852
Dammaschke T (2010) Rat molar teeth as a study model for direct pulp capping research in dentistry. Lab Anim 44:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1258/la.2009.008120
Sasaki T, Kawamata-Kido H (1995) Providing an environment for reparative dentine induction in amputated rat molar pulp by high molecular-weight hyaluronic acid. Arch Oral Biol 40:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9969(95)98810-L
Funding
This study was supported by a grant (2015/10984-3) from the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, São Paulo, SP, Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants by any of the authors. The in vitro (CEUA 00568) and in vivo (CEUA 00631) studies using rat molars were approved by the ethics committee of the institution where the study was performed and conducted in accordance with its ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barbosa, J.G., Benetti, F., de Oliveira Gallinari, M. et al. Bleaching gel mixed with MI Paste Plus reduces penetration of H2O2 and damage to pulp tissue and maintains bleaching effectiveness. Clin Oral Invest 24, 1299–1309 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03009-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-019-03009-5