Abstract
Background
There have been few reports on falls in patients who have undergone total hip arthroplasty (THA). In the present study, we aimed to investigate the incidence and circumstances of falls in post-THA patients and to identify the factors associated with falling.
Materials and methods
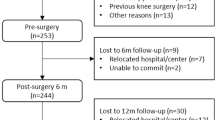
After excluding comorbidities, osteoarthritis without THA, and patients who had undergone THA within the previous 1 year, 214 patients [11 males, 203 females; mean (SD) age, 66.0 (8.7) years] living independently for at least 1 year after THA were analyzed as available data. Using a self-administered questionnaire, we investigated the number and circumstances of falls in the preceding year, as well as functional outcome and ambulatory ability via the Oxford Hip Score. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to identify factors influencing falls in post-THA patients.
Results
The incidence of at least one fall in the past year was 36 %. Falls were most often caused by tripping and falling forward during the daytime. In the present study, 37.7 % of falls resulted in injuries and 5.2 % resulted in fractures. Experience of fall was significantly related to medication [odds ratio (OR) 4.09, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.90–8.80, P < 0.001] and postoperative duration (OR 0.89, 95 % CI 0.81–0.98, P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Thus, patients have an increased risk for falls and fall-induced injuries after THA. Falls in post-THA patients are associated with medication and shorter postoperative duration. Therefore, it is essential to prevent falls in patients who have undergone THA, particularly during the early postoperative period and among patients administered medications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kannus P, Parkkari J, Koskinen S, Niemi S, Palvanen M, Jarvinen M, Vuori I. Fall-induced injuries and deaths among older adults. JAMA. 1999;281(20):1895–9.
Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF. Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in the community. N Engl J Med. 1988;319(26):1701–7.
Campbell AJ, Borne MJ, Spears GF, Jackson SL, Brown JS, Fitzgerald JL. Circumstances and consequences of falls experienced by a community population 70 years and over during a prospective study. Age Ageing. 1990;19(2):136–41.
Yasumura S, Haga H, Niino N. Circumstances of injurious falls leading to medical care among elderly people living in a rural community. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 1996;23(2):95–109.
Aoyagi K, Ross PD, Davis JW, Wasnich RD, Hayashi T, Takemoto T. Falls among community-dwelling elderly in Japan. J Bone Miner Res. 1998;13(9):1468–74.
Yamada M, Nishiguchi S, Fukutani N, Tanigawa T, Yukutake T, Kayama H, Aoyama T, Arai H. Prevalence of sarcopenia in community-dwelling Japanese older adults. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2013;14(12):911–5.
Shimada H, Suzukawa M, Tiedemann A, Kobayashi K, Yoshida H, Suzuki T. Which neuromuscular or cognitive test is the optimal screening tool to predict falls in frail community-dwelling older people? Gerontology. 2009;55(5):532–8.
Hill K, Schwarz J, Flicker L, Carroll S. Falls among healthy, community-dwelling, older women: a prospective study of frequency, circumstances consequences and prediction accuracy. Aust NZ J Public Health. 1999;23(1):41–8.
Sturnieks DL, Tiedemann A, Chapman K, Munro B, Murray SM, Lord SR. Physiological risk factors for falls in older people with lower limb arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2004;31(11):2272–9.
Leveille SG, Jones RN, Kiely DK, Hausdorff JM, Shmerling RH, Guralnik JM, Kiel DP, Lipsitz LA, Bean JF. Chronic musculoskeletal pain and the occurrence of falls in an older population. JAMA. 2009;302(20):2214–21.
Levinger P, Menz HB, Wee E, Feller JA, Bartlett JR, Bergman NR. Physiological risk factors for falls in people with knee osteoarthritis before and early after knee replacement surgery. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(7):1082–9.
Matsumoto H, Okuno M, Nakamura T, Yamamoto K, Hagino H. Fall incidence and risk factors in patients after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(4):555–63.
Arnold CM, Faulkner RA. The history of falls and the association of the timed up and go test to falls and near-falls in older adults with hip osteoarthritis. BMC Geriatr. 2007;4(7):17.
Nahit ES, Silman AJ, Macfarlane GJ. The occurrence of falls among patients with a new episode of hip pain. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998;57(3):166–8.
Jogensen CC, Kehlet H. Lundbeck Foundation Centre for Fast-track Hip and Knee Replacement Collaborative Group. Fall-related admissions after fast-track total hip and knee arthroplasty—cause of concern or consequence of success? Clin Interv Aging. 2013;8:1569–77.
Lamb SE, Jorstad-Stein EC, Hauer K, Becker C. Development of a common outcome data set for fall injury prevention trials: the prevention of falls network Europe consensus. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005;53(9):1618–22.
Dawson J, Fitzpatrick R, Carr A, Murray D. Questionnaire on the perceptions of patients about total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78(2):185–90.
Uesugi Y, Makimoto K, Fujita K, Nishii T, Sakai T, Sugano N. Validity and responsiveness of the Oxford hip score in a prospective study with Japanese total hip arthroplasty patients. J Orthop Sci. 2009;14(1):35–9.
Remerand F, Le Tendre C, Baud A, Couvret C, Pourrat X, Favard L, Laffon M, Fusciardi J. The early and delayed analgesic effects of ketamine after total hip arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blind study. Anesth Analg. 2009;109(6):1963–71.
Hwang HF, Lee HD, Huang HH, Chen CY, Lin MR. Fall mechanisms, bone strength, and hip fractures in elderly men and women in Taiwan. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(8):2385–93.
Leipzig RM, Cumming RG, Tinetti ME. Drugs and falls in order people: a systematic review and meta-analysis: I. psychotropic drugs. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1999;47(1):30–9.
Haritikainen S, Lonnroos E, Louhivuori K. Medication as a risk factor for falls: critical systematic review. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2007;62(10):1172–81.
Robbins AS, Rubenstein LZ, Josphson KR, Schulman BL, Osterweil D, Fine G. Predictors of falls among elderly people: results of two population-based studies. Arch Intern Med. 1989;149(7):1628–33.
Rubenstein LZ, Josephson KR. The epidemiology of falls and syncope. Clin Geriatric Med. 2002;18(2):141–58.
Vissers MM, Bussmann JB, Verhaar JA, Arends LR, Furlan AD, Reijman M. Recovery of physical functioning after total hip arthroplasty: systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Phys Ther. 2011;91(5):615–29.
Ewen AM, Stewart S. St Clair Gibson A, Kashyap SN, Caplan N. Post-operative gait analysis in total hip replacement patients: a review of current literature and meta-analysis. Gait Posture. 2012;36(1):1–6.
Sicard-Rosenbaum L, Light KE, Behrman AL. Gait, lower extremity strength, and self-assessed mobility after hip arthroplasty. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2002;57(1):M47–51.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the patients who kindly agreed to participate. We are grateful to Keiichi Tagomori and Namika Miura for their help and support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ikutomo, H., Nagai, K., Nakagawa, N. et al. Falls in patients after total hip arthroplasty in Japan. J Orthop Sci 20, 663–668 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-015-0715-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-015-0715-7