Abstract
Study design
A genetic association meta-analysis of estrogen receptor α gene (ERα) polymorphisms with idiopathic scoliosis.
Objective
To determine whether the ERα gene polymorphisms correlate with idiopathic scoliosis.
Summary of background data
Idiopathic scoliosis represents a complex genetic trait under the influence of multiple predisposition genes. Several studies showed that single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in ERα was associated with idiopathic scoliosis, but the results from some studies were conflicting.
Methods
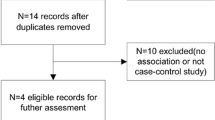
We searched PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane CENTRAL databases from January 1994 to January 2014. All the case–control studies included should mainly study the relationship between XbaI A/G, PvuII T/C polymorphisms and the susceptibility of idiopathic scoliosis.
Results
A total of 299 articles were found, six of which fulfilled the inclusion criteria after being assessed by two reviewers. A pooled odds ratio (OR) with 95 % confidence interval (95 % CI) was calculated to assess the associations. Subgroup meta-analyses were performed according to ethnicity. Overall, ERα Xbal A/G polymorphism was not associated with risk of idiopathic scoliosis (G versus A, OR 1.07, 95 % CI 0.88–1.30, P = 0.51; AG versus AA, OR 1.03, 95 % CI 0.89–1.21, P = 0.67; GG versus AA, OR 1.12, 95 % CI 0.72–1.73, P = 0.61; AG/GG versus AA, OR 1.05, 95 % CI 0.91–1.22, P = 0.49; GG versus AG/AA, OR 1.10, 95 % CI 0.75–1.63, P = 0.62). ERα PvuII T/C polymorphism was also not associated with risk of idiopathic scoliosis under five models (C versus T, OR 0.93, 95 % CI 0.75–1.14, P = 0.48; TC versus TT, OR 0.99, 95 % CI 0.80–1.23, P = 0.93; CC versus TT, OR 1.05, 95 % CI 0.80–1.39, P = 0.72; TC/CC versus TT, OR 1.01, 95 % CI 0.83–1.23, P = 0.93; CC versus TC/TT, OR 1.05, 95 % CI 0.82–1.33, P = 0.72).
Conclusion
ERα Xbal and ERα PvuII polymorphisms are not obviously associated with risk of idiopathic scoliosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zaidman AM, Zaidman MN, Korel AV, Mikhailovsky MA, Eshchenko TY, Grigorjeva EV. Aggrecan gene expression disorder as aetiologic factor of idiopathic scoliosis. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2006;123:14–7.
Leboeuf D, Letellier K, Alos N, Edery P, Moldovan F. Do estrogens impact adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009;20(4):147–52.
Peng Y, Liang G, Pei Y, Ye W, Liang A, Su P. Genomic polymorphisms of G-protein estrogen receptor 1 are associated with severity of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Int Orthop. 2012;36(3):671–7.
Zhang HQ, Lu SJ, Tang MX, Chen LQ, Liu SH, Guo CF, Wang XY, Chen J, Xie L. Association of estrogen receptor β gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2009;34(8):760–4.
Qiu XS, Tang NL, Yeung HY, Lee KM, Hung VW, Ng BK, Ma SL, Kwok RH, Qin L, Qiu Y, Cheng JC. Melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B) gene polymorphism is associated with the occurrence of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2007;32(16):1748–53.
Birchall D, Hughes D, Gregson B, Williamson B. Demonstration of vertebral and disc mechanical torsion in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using three-dimensional MR imaging. Eur Spine J. 2005;14(2):123–9.
Lee WT, Cheung CS, Tse YK, Guo X, Qin L, Ho SC, Lau J, Cheng JC. Generalized low bone mass of girls with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is related to inadequate calcium intake and weight bearing physical activity in peripubertal period. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(9):1024–35.
Ahn UM, Ahn NU, Nallamshetty L, Buchowski JM, Rose PS, Miller NH, Kostuik JP, Sponseller PD. The etiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2002;31(7):387–95.
Herrington DM, Howard TD, Brosnihan KB, McDonnell DP, Li X, Hawkins GA, Reboussin DM, Xu J, Zheng SL, Meyers DA, Bleecker ER. Common estrogen receptor polymorphism augments effects of hormone replacement therapy on E-selectin but not C-reactive protein. Circulation. 2002;105(16):1879–82.
Safarinejad MR, Safarinejad S, Shafiei N, Safarinejad S. Estrogen receptors alpha (rs2234693 and rs9340799), and beta (rs4986938 and rs1256049) genes polymorphism in prostate cancer: evidence for association with risk and histopathological tumor characteristics in Iranian men. Mol Carcinog. 2012;51(Suppl 1):E104–17.
Beleza-Meireles A, Omrani D, Kockum I, Frisen L, Lagerstedt K, Nordenskjöld A. Polymorphisms of estrogen receptor beta gene are associated with hypospadias. J Endocrinol Investig. 2006;29(1):5–10.
Inoue M, Minami S, Nakata Y, Kitahara H, Otsuka Y, Isobe K, Takaso M, Tokunaga M, Nishikawa S, Maruta T, Moriya H. Association between estrogen receptor gene polymorphisms and curve severity of idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2002;27(21):2357–62.
Inoue M, Minami S, Nakata Y, Takaso M, Otsuka Y, Kitahara H, Isobe K, Kotani T, Maruta T, Moriya H. Prediction of curve progression in idiopathic scoliosis from gene polymorphic analysis. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2002;91:90–6.
Wu J, Qiu Y, Zhang L, Sun Q, Qiu X, He Y. Association of estrogen receptor gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2006;31(10):1131–6.
Janusz P, Kotwicki T, Andrusiewicz M, Kotwicka M. XbaI and PvuII polymorphisms of estrogen receptor 1 gene in females with idiopathic scoliosis: no association with occurrence or clinical form. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e76806.
Tang NL, Yeung HY, Lee KM, Hung VW, Cheung CS, Ng BK, Kwok R, Guo X, Qin L, Cheng JC. A relook into the association of the estrogen receptor α gene (PvuII, XbaI) and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a study of 540 Chinese cases. Spine. 2006;31(21):2463–8.
Takahashi Y, Matsumoto M, Karasugi T, Watanabe K, Chiba K, Kawakami N, Tsuji T, Uno K, Suzuki T, Ito M, Sudo H, Minami S, Kotani T, Kono K, Yanagida H, Taneichi H, Takahashi A, Toyama Y, Ikegawa S. Replication study of the association between adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and two estrogen receptor genes. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(6):834–7.
Zhao D, Qiu GX, Wang YP, Zhang JG, Shen JX, Wu ZH. Association between adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with double curve and polymorphisms of calmodulin 1 gene/estrogen receptor-α gene. Orthop Surg. 2009;1(3):222–30.
Zhao D, Qiu G, Wang Y. Is calmodulin 1 gene/estrogen receptor-alpha gene polymorphisms correlated with double curve pattern of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008;88(35):2452–6.
Zhao D. Study of association between CALM1 gene/ER1 gene with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Peking Union Medical College. 2007 June.
Chen Z, Tang NL, Cao X, Qiao D, Yi L, Cheng JC, Qiu Y. Promoter polymorphism of matrilin-1 gene predisposes to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in a Chinese population. Eur J Hum Genet. 2009;17(4):525–32.
Hu Z, Song CG, Lu JS, Luo JM, Shen ZZ, Huang W, Shao ZM. A multigenic study on breast cancer risk associated with genetic polymorphisms of ER Alpha, COMT and CYP19 gene in BRCA1/BRCA2 negative Shanghai women with early onset breast cancer or affected relatives. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007;133(12):969–78.
Deng J, Shen C, Wang Y, Zhang M, Yan J, Fu X, Chen Y, Zhou H. Association between the polymorphism of estrogen receptor alpha and Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese population. Clin Lab. 2013;59(7–8):741–6.
Xie J, Wang S, He B, Pan Y, Li Y, Zeng Q, Jiang H, Chen J. Association of estrogen receptor alpha and interleukin-10 gene polymorphisms with endometriosis in a Chinese population. Fertil Steril. 2009;92(1):54–60.
Iwamoto I, Fujino T, Douchi T, Nagata Y. Association of estrogen receptor α and β3-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms with endometrial cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2003;102(3):506–11.
Wang Z, Yoshida S, Negoro K, Kennedy S, Barlow D, Maruo T. Polymorphisms in the estrogen receptor β gene but not estrogen receptor α gene affect the risk of developing endometriosis in a Japanese population. Fertil Steril. 2004;81(6):1650–6.
Li L, Zhang X, Xia Q, Ma H, Chen L, Hou W. Association between estrogen receptor alpha PvuII polymorphism and prostate cancer risk. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(5):4629–35.
Ding J, Xu H, Yin X, Zhang FR, Pan XP, Gu YA, Chen JZ, Guo XG. Estrogen receptor alpha gene PvuII polymorphism and coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis of 21 studies. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2014;15(3):243–55.
Ryan J, Carrière I, Carcaillon L, Dartigues JF, Auriacombe S, Rouaud O, Berr C, Ritchie K, Scarabin PY, Ancelin ML. Estrogen receptor polymorphisms and incident dementia: the prospective 3C study. Alzheimers Dement. 2014;10(1):27–35.
Patnam AK, Vinu R, Vijayalakshmi J, Venkatachalam P, Rani GU. Association of ESR and FOXP3 gene polymorphisms with outcome of ovarian stimulation in infertile females undergoing IVF. Mol Cyt. 2014;7(Suppl 1):P61.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Yang and C. Li contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Li, C. & Li, M. The estrogen receptor α gene (XbaI, PvuII) polymorphisms and susceptibility to idiopathic scoliosis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Sci 19, 713–721 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-014-0597-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-014-0597-0