Abstract
Background
To assess the usefulness of the urinary crosslinked C-telopeptide of type II collagen (uCTX-II) or crosslinked N-telopeptide of type I collagen (uNTX-I) for evaluating radiological knee osteoarthritis (OA), a cross-sectional study was conducted in the cohorts of the Matsudai knee osteoarthritis survey performed in Niigata, Japan.
Methods
Urine specimens and standing knee AP X-rays were obtained from 1040 subjects who provided informed consent. The relationship between these markers and gender, age (patients aged 40–59 or 60–79 years), use of bisphosphonates, and OA grades (K–L classification) were analyzed. The diagnostic ability of uCTX-II to detect radiological knee OA was confirmed in the over 60-year-old subjects using a ROC curve.
Results
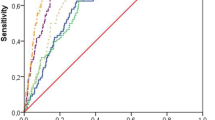
The over 60-year-old men with OA grade 3,4 group had significantly higher uCTX-II levels than the other OA grade groups. In the over 60-year-old women, the uCTX-II levels significantly increased according to the progression of the knee OA grade. No significant difference was observed between the uNTX-I levels in the different OA grade groups. From the standpoint of biomarkers, the higher quartiles of the uCTX-II and uNTX-I levels gradually included higher numbers of grade ≥2 OA subjects in the over 60 year-old women. The area under the curve (AUC) in ROC analysis of uCTX-II exhibited a significant association with the diagnosis of knee OA in women (AUC 0.63), although the accuracy was evaluated to be low in the single measurement of our health checkup-based analysis.
Conclusions
This population-based study indicates that the uCTX-II level is strongly correlated with the knee OA grade in women over age 60. A further analysis is needed to clarify its predictive accuracy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rousseau JCh, Garnero P. Biological markers in osteoarthritis. Bone. 2012;51:265–77.
Garnero P, Landewé R, Boers M, Verhoeven A, Van Der Linden S, Christgau S, Van Der Heijde D, Boonen A, Geusens P. Association of baseline levels of markers of bone and cartilage degradation with long-tern progression of joint damage in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. The COBRA study. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:2847–56.
Landewé R, Geusens P, Boers M, van der Heijde D, Lems W, Koppele J, van der Linden S, Garnero P. Markers for type II collagen breakdown predict the effect of disease-modifying treatment on long-term radiographic progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1390–9.
Garnero P, Conrozier T, Christgau S, Mathieu P, Delmas PD, Vignon E. Urinary type II collagen C-telopeptide levels are increased in patients with rapidly destructive hip osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:939–43.
Garnero P, Piperno M, Gineyts E, Christgau S, Delmas PD, Vignon E. Cross sectional evaluation of biochemical markers of bone, cartilage, and synovial tissue metabolism in patients with knee osteoarthritis: relations with disease activity and joint damage. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001;60:619–26.
Jordan KM, Syddall HE, Garnero P, Gineyts E, Dennison EM, Sayer AA, Delmas PD, Cooper C, Arden NK. Urinary CTX-II and glucosyl-galactosyl-pyridinoline are associated with the presence and severity of radiographic knee osteoarthritis in men. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:871–7.
Hayami T, Pickarski M, Wesolowski GA, McLane J, Bone A, Destefano J, Rodan GA, le Duong T. The role of subchondral bone remodeling in osteoarthritis: reduction of cartilage degeneration and prevention of osteophyte formation by alendronate in the rat anterior cruciate ligament transection model. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1193–206.
Shiozaki H, Koga Y, Omori G, Yamamoto G, Takahashi HE. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis of the knee in a rural Japanese population. Knee. 1999;6:183–8.
Shiozaki H, Koga Y, Omori G, Tamaki M. Obesity and osteoarthritis of the knee in women; results of Matsudai Knee Osteoarthritis Survey. Knee. 1999;6:189–92.
Tanishi N, Yamagiwa H, Hayami T, Mera H, Koga Y, Omori G, Endo N. Relationship between radiological knee osteoarthritis and biochemical markers of cartilage and bone degradation (urine CTX-II and NTX-I): the Matsudai Knee Osteoarthritis Survey. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27:605–12.
Mouritzen U, Christgau S, Lehmann HJ, Tankó LB, Christiansen C. Cartilage turnover assessed with a newly developed assay measuring collagen type II degradation products: influence of age, sex, menopause, hormone replacement therapy, and body mass index. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62:332–6.
Lehmann HJ, Mouritzen U, Christgau S, Cloos PA, Christiansen C. Effect of bisphosphonates on cartilage turnover assessed with a newly developed assay for collagen type II degradation products. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61:530–3.
Sone T, Miyake M, Takeda N, Fukunaga M. Urinary excretion of type I collagen crosslinked N-telopeptides in healthy Japanese adults: age- and sex-related changes and reference limits. Bone. 1995;17:335–9.
Bauer DC, Hunter DJ, Abramson SB, Attur M, Corr M, Felson D, Heinegård D, Jordan JM, Kepler TB, Lane NE, Saxne T, Tyree B, Kraus VB, Osteoarthritis Biomarkers Network. Classification of osteoarthritis biomarkers: a proposed approach. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14:723–7.
Sowers MF, Karvonen-Gutierrez CA, Yosef M, Jannausch M, Jiang Y, Garnero P, Jacobson J. Longitudinal changes of serum COMP and urinary CTX-II predict X-ray defined knee osteoarthritis severity and stiffness in women. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17:1609–14.
Kong SY, Stabler TV, Criscione LG, Elliott AL, Jordan JM, Kraus VB. Diurnal variation of serum and urine biomarkers in patients with radiographic knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2496–504.
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to all of the people involved in the Matsudai district resident health check, and to all the residents who consented to participate in the study and provided samples. We also wish to thank SRL, Inc., (Tokyo, Japan) for their cooperation in collecting the samples and performing the measurements, and the staff of Niigata Medical Center Hospital, Niigata Institute of Health and Sports Medicine, and Niigata University of Health and Welfare for their cooperation in conducting the knee examinations. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research B (19390389) and C (40377164).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tanishi, N., Yamagiwa, H., Hayami, T. et al. Usefulness of urinary CTX-II and NTX-I in evaluating radiological knee osteoarthritis : the Matsudai knee osteoarthritis survey. J Orthop Sci 19, 429–436 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-014-0535-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-014-0535-1