Abstract
Background
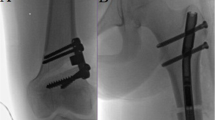
Options for lower limb realignment in skeletal dysplasia are acute versus gradual correction, internal versus external fixation, and external fixation with or without intramedullary nailing. The safety and versatility of the Ilizarov method in skeletal dysplasia patients makes it a procedure of choice.
Materials and methods
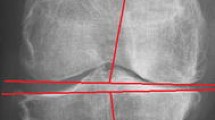
We describe here our experience with this procedure with 48 skeletal dysplasia patients, with a mean age of 15 years, and a minimum follow-up of 2 years. Preoperative, postoperative, and latest follow-up measurements of tibia–femur (T–F) angle, conventional mechanical axis deviation (MAD-C), ground mechanical axis deviation (MAD-G), lateral distal femoral angle (LDFA), medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA), posterior distal femoral angle (PDFA), and posterior proximal tibial angle (PPTA) were compared.
Results
The mean lengthening amount (LA) was 7.4 cm, mean lengthening percentage (LP) was 35.5%, mean external fixation index (EFI) was 28 days/cm, and mean healing index (HI) was 35 days/cm. Mean MAD-C and MAD-G correction were 9.3 mm and 11.8 mm, respectively. T–F angles, PPTA, MAD-C, and MAD-G were significantly improved. Equinus deformity was the most prominent obstacle, and varus recurrence was the most frequent sequela.
Conclusion
In most skeletal dysplasia patients, lower limb realignment with gradual deformity correction using the Ilizarov method may be a reliable option. Equinus deformity occurs in those with more than 40% lengthening, but can be easily corrected. In addressing varus recurrence after gradual correction, the intrinsic and extrinsic factors should be sought first then treated accordingly.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaidya SV, Song HR, Lee SH, Suh SW, Keny SM, Telang SS. Bifocal tibial corrective osteotomy with lengthening in achondroplasia: an analysis of results and complications. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006;26:788–93.
Brooks WC, Gross RH. Genu varum in children: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1995;3:326–35.
Shirley ED, Ain MC. Achondroplasia: manifestations and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17:231–41.
Goldman V, Green DW. Advances in growth plate modulation for lower extremity malalignment (knock knees and bow legs). Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22:47–53.
Steel HH, Sandrow RE, Sullivan PD. Complications of tibial osteotomy in children for genu varum or valgum: evidence that neurological changes are due to ischemia. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]. 1971;53:1629–35.
Pinkowski JL, Weiner DS. Complications in proximal tibial osteotomies in children with presentation of technique. J Pediatr Orthop. 1995;15(3):307–12.
Li QW, Song HR, Mahajan RH, Suh SW, Lee SH. Deformity correction with external fixator in pseudoachondroplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;454:174–9.
Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Tetsworth K, McKie J, Bhave A. Deformity planning for frontal and sagittal plane corrective osteotomies. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994;25:425–65.
Lee ST, Song HR, Mahajan R, Makwana V, Suh SW, Lee SH. Development of genu varum in achondroplasia: relation to fibular overgrowth. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 2007;89-B:57–61.
Paley D. Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;250:81–104.
Matsubara H, Tsuchiya H, Sakurakichi K, Watanabe K, Tomita K. Deformity correction and lengthening of lower legs with an external fixator. Int Orthop (SICOT). 2006;30:550–4.
Donnan LT, Saleh M, Rigby AS. Acute correction of lower limb deformity and simultaneous lengthening with a monolateral fixator. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 2003;85-B:254–60.
Bilen FE, Kocaoglu M, Eralp L, Balci HI. Fixator-assisted nailing and consecutive lengthening over an intramedullary nail for the correction of tibial deformity. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 2010;92-B (1):146–52.
Scheidel F, Probst A, Buller TC, Rodl R. The postoperative patella height: a comparison of additive and subtractive high tibial osteotomy in correcting the genu varum. Acta Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129:1271–7.
Wilson NA, Scherl SA, Cramer KE. Complications of high tibial osteotomy with external fixation in adolescent Blount’s disease. Orthop. 2007;30(10):848–52.
Blondel B, Launay F, Glard Y, Jacopin S, Jouve JL, Bollini G. Limb lengthening and deformity correction in children using hexapodal external fixation: preliminary results for 36 cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2009;95:425–30.
Song HR, Soma Raju VVJ, Kumar S, Lee SH, Suh SW, Kim JR, Hong JS. Deformity correction by external fixation and/or intramedullary nailing in hypophosphatemic rickets. Acta Orthop. 2006;77(2):307–14.
Choi IH, Kim JK, Chung CY, Cho TJ. Deformity correction of the knee and leg lengthening by the Ilizarov method in children with vitamin D resistant rickets. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2000;35:711–7.
Stuart MJ, Grace JN, Ilstrup DM, Kelly CM, Adams RA, Morrey BF. Late recurrence of varus deformity after proximal tibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;260:61–5.
Terauchi M, Shirakura K, Katayama M, Higuchi H, Takagishi K, Kimura M. Varus inclination of the distal femur and high tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 2002;84 (B):223–6.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A090084).
Conflict of interest
All authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SJ., Cielo, B., Song, SH. et al. Gradual bilateral genu varum correction in skeletal dysplasia using the Ilizarov method. J Orthop Sci 16, 405–412 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-011-0063-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-011-0063-1