Abstract
MicroRNAs have emerged as pivotal regulators in various physiological and pathological processes, including osteogenesis. Here we discuss the contribution of miR-5100 to osteoblast differentiation and mineralization. We found that miR-5100 was upregulated during osteoblast differentiation in ST2 and MC3T3-E1 cells. Next, we verified that miR-5100 can promote osteogenic differentiation with gain-of-function and loss-of-function experiments. Target prediction analysis and experimental validation demonstrated that Tob2, which acts as a negative regulator of osteogenesis, was negatively regulated by miR-5100. Furthermore, we confirmed that the important bone-related transcription factor osterix, which can be degraded by binding to Tob2, was influenced by miR-5100 during osteoblast differentiation. Collectively, our results revealed a new molecular mechanism that fine-tunes osteoblast differentiation through miR-5100/Tob2/osterix networks.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bushati N, Cohen SM (2007) MicroRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:175–205
Chua JH, Armugam A, Jeyaseelan K (2009) MicroRNAs: biogenesis, function and applications. Curr Opin Mol Ther 11:189–199
Foshay KM, Ian GG (2007) Small RNAs, big potential: the role of MicroRNAs in stem cell function. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 2:264–271
Kim VN, Nam JW (2006) Genomics of microRNA. Trends Genet 22:165–173
Oliver H (2008) Gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Science 319:1785–1786
Hanna TK, Lea BH, Li C, Sakari K, Moustapha K (2011) Micro-RNAs: targets for enhancing osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Eur J Endocrinol 166:359–371
Yangjin B, Tao Y, Huan-Chang Z, Campeau PM, Yuqing C, Terry B, Dawson BC, Elda M, Jianning T, Lee BH (2012) MiRNA-34c regulates Notch signaling during bone development. Hum Mol Genet 21:2991–3000
Chen L, Holmstrom K, Qiu W, Ditzel N, Shi K, Hokland L, Kassem M (2014) MicroRNA-34a inhibits osteoblast differentiation and in vivo bone formation of human stromal stem cells. Stem Cells 32:902–912
Jia J, Tian Q, Ling S, Liu Y, Yang S, Shao Z (2013) MiR-145 suppresses osteogenic differentiation by targeting Sp7. FEBS Lett 587:3027–3031
Fukuda T, Ochi H, Sunamura S, Haiden A, Bando W, Inose H, Okawa A, Asou Y, Shu T (2015) MicroRNA-145 regulates osteoblastic differentiation by targeting the transcription factor Cbfb. FEBS Lett 589:3302–3308
Seeliger C, Karpinski K, Haug AT, Vester H, Schmitt A, Bauer JS, van Griensven M (2014) Five freely circulating miRNAs and bone tissue miRNAs are associated with osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Res 29:1718–1728
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W (2013) Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol 200:373–383
Clotilde T, Laurence Z, Sebastian A (2002) Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol 2:569–579
Min G, Ronghu K, Tianyi C, Junyi Y, Xiongzheng M (2015) Identification and proteomic analysis of osteoblast-derived exosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 467:27–32
Hadi V, Karin EM, Apostolos B, Margareta SS, Lee JJ, Tvall JOL (2007) Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:654–659
Zhang J, Li S, Li L, Li M, Guo C, Yao J, Mi S (2015) Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 13:17–24
Cui Y, Luan J, Li H, Zhou X, Han J (2016) Exosomes derived from mineralizing osteoblasts promote ST2 cell osteogenic differentiation by alteration of microRNA expression. FEBS Lett 590:185–192
Prockop DJ (1997) Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science 276:71–74
Koike M, Shimokawa H, Kanno Z, Ohya K, Soma K (2005) Effects of mechanical strain on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow stromal cell line ST2. J Bone Miner Metab 23:219–225
Jiang Q, Li Q, Uitto J (2007) Aberrant mineralization of connective tissues in a mouse model of pseudoxanthoma elasticum: systemic and local regulatory factors. J Invest Dermatol 127:1392–1402
Straalen JPV, Sanders E, Prummel MF, Sanders GTB (1991) Bone-alkaline phosphatase as indicator of bone formation. Clin Chim Acta 201:27–33
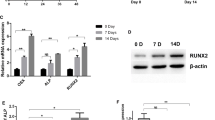
Hu R, Liu W, Li H, Yang L, Chen C, Xia ZY, Guo LJ, Xie H, Zhou HD, Wu XP, Luo XH (2011) A Runx2/miR-3960/miR-2861 regulatory feedback loop during mouse osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem 286:12328–12339
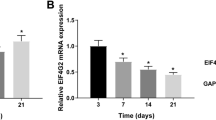
Gamez B, Rodriguez-Carballo E, Bartrons R, Rosa JL, Ventura F (2013) MicroRNA-322 (miR-322) and its target protein Tob2 modulate osterix (Osx) mRNA stability. J Biol Chem 288:14264–14275
Simons M, Raposo G (2009) Exosomes—vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:575–581
Montecalvo A, Larregina AT, Shufesky WJ, Stolz DB, Sullivan MLG, Karlsson JM, Baty CJ, Gibson GA, Erdos G, Wang Z, Milosevic J, Tkacheva OA, Divito SJ, Jordan R, Lyons-Weiler J, Watkins SC, Morelli AE (2012) Mechanism of transfer of functional microRNAs between mouse dendritic cells via exosomes. Blood 119:756–766
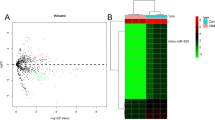
Huang H, Yun J, Wang Y, Chen T, Yang L, He H, Lin Z, Liu T, Teng Y, Kamp DW (2015) MiR-5100 promotes tumor growth in lung cancer by targeting Rab6. Cancer Lett 362:15–24
Sebastiaan WG (2010) The mammalian anti-proliferative BTG/Tob protein family. J Cell Physiol 222:66–72
Mauxion F, Chen CYA, Séraphin B, Shyu AB (2009) BTG/TOB factors impact deadenylases. Trends Biochem Sci 34:640–647
Ikematsu N, Yoshida TJ, Ohsugi M, Onda M, Hirai M, Fujimoto J, Yamamoto T (1999) Tob2, a novel anti-proliferative Tob/BTG1 family member, associates with a component of the CCR4 transcriptional regulatory complex capable of binding cyclin-dependent kinases. Oncogene 18:7432–7441
Tzachanis D, Freeman GJ, Hirano N, Puijenbroek AAFLV, Delfs MW, Berezovskaya A, Nadler LM, Boussiotis VA (2001) Tob is a negative regulator of activation that is expressed in anergic and quiescent T cells. Nat Immunol 2:1174–1182
Karsenty G (2008) Transcriptional control of skeletogenesis. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 9:183–196
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81371909) and the Key Projects in the National Science and Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan period (2013BAI07B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Cui, Y., Luan, J. et al. MiR-5100 promotes osteogenic differentiation by targeting Tob2. J Bone Miner Metab 35, 608–615 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-016-0799-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-016-0799-y