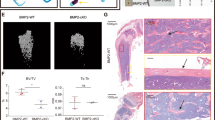
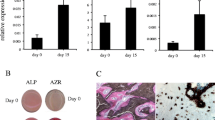
Abstract
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) inhibit myogenesis and induce osteoblastic differentiation in myoblasts. They also induce the transcription of several common genes, such as Id1, Id2 and Id3, in various cell types. We have reported that a GC-rich element in the Id1 gene functions as a BMP-responsive element (BRE) that is regulated by Smads. In this study, we analyzed and identified BREs in the 5′-flanking regions of the mouse Id2 and Id3 genes. The core GGCGCC sequence was conserved among the BREs in the Id1, Id2 and Id3 genes and was essential for the response to BMP signaling via Smads. We found a novel BRE on mouse chromosome 13 at position 47,723,740–47,723,768 by searching for conserved sequences containing the Id1 BRE. This potential BRE was found in the 5′-flanking region of a novel gene that produces a non-coding transcript, termed BMP-inducible transcript-1 (BIT-1), and this element regulated the expression of this gene in response to BMP signaling. We found that BIT-1 is expressed in BMP target tissues such as the testis, brain, kidney and cartilage. These findings suggest that the transcriptional induction of the Ids, BIT-1 and additional novel genes containing the conserved BRE sequence may play an important role in the regulation of the differentiation and/or function of target cells in response to BMPs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attisano L, Wrana JL (2002) Signal transduction by the TGF-beta superfamily. Science 296:1646–1647
Urist MR (1965) Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science 150:893–899
Katagiri T, Yamaguchi A, Komaki M, Abe E, Takahashi N, Ikeda T, Rosen V, Wozney JM, Fujisawa-Sehara A, Suda T (1994) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 converts the differentiation pathway of C2C12 myoblasts into the osteoblast lineage. J Cell Biol 127:1755–1766
Katagiri T, Suda T, Miyazono K (2008) The bone morphogenetic proteins. In: Derynck R, Miyazono K (eds) TGF-β family. Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York, pp 121–149
Wan M, Cao X (2005) BMP signaling in skeletal development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 328:651–657
Miyazono K, Maeda S, Imamura T (2005) BMP receptor signaling: transcriptional targets, regulation of signals, and signaling cross-talk. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:251–263
Katagiri T, Imada M, Yanai T, Suda T, Takahashi N, Kamijo R (2002) Identification of a BMP-responsive element in Id1, the gene for inhibition of myogenesis. Genes Cells 7:949–960
Lopez-Rovira T, Chalaux E, Massague J, Rosa JL, Ventura F (2002) Direct binding of Smad1 and Smad4 to two distinct motifs mediates bone morphogenetic protein-specific transcriptional activation of Id1 gene. J Biol Chem 277:3176–3185
Korchynskyi O, ten Dijke P (2002) Identification and functional characterization of distinct critically important bone morphogenetic protein-specific response elements in the Id1 promoter. J Biol Chem 277:4883–4891
Kim J, Johnson K, Chen HJ, Carroll S, Laughon A (1997) Drosophila Mad binds to DNA and directly mediates activation of vestigial by Decapentaplegic. Nature 388:304–308
Xu X, Yin Z, Hudson JB, Ferguson EL, Frasch M (1998) Smad proteins act in combination with synergistic and antagonistic regulators to target Dpp responses to the Drosophila mesoderm. Genes Dev 12:2354–2370
Ishida W, Hamamoto T, Kusanagi K, Yagi K, Kawabata M, Takehara K, Sampath TK, Kato M, Miyazono K (2000) Smad6 is a Smad1/5-induced smad inhibitor. Characterization of bone morphogenetic protein-responsive element in the mouse Smad6 promoter. J Biol Chem 275:6075–6079
Kusanagi K, Inoue H, Ishidou Y, Mishima HK, Kawabata M, Miyazono K (2000) Characterization of a bone morphogenetic protein-responsive Smad-binding element. Mol Biol Cell 11:555–565
Karaulanov E, Knochel W, Niehrs C (2004) Transcriptional regulation of BMP4 synexpression in transgenic Xenopus. EMBO J 23:844–856
Goldman LA, Cutrone EC, Kotenko SV, Krause CD, Langer JA (1996) Modifications of vectors pEF-BOS, pcDNA1 and pcDNA3 result in improved convenience and expression. Biotechniques 21:1013–1015
Komaki M, Katagiri T, Suda T (1996) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 does not alter the differentiation pathway of committed progenitors of osteoblasts and chondroblasts. Cell Tissue Res 284:9–17
Shin M, Matsuo K, Tada T, Fukushima H, Furuta H, Ozeki S, Kadowaki T, Yamamoto K, Okamoto M, Jimi E (2011) The inhibition of RANKL/RANK signaling by osteoprotegerin suppresses bone invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 32:1634–1640
Yokoyama S, Ito Y, Ueno-Kudoh H, Shimizu H, Uchibe K, Albini S, Mitsuoka K, Miyaki S, Kiso M, Nagai A, Hikata T, Osada T, Fukuda N, Yamashita S, Harada D, Mezzano V, Kasai M, Puri PL, Hayashizaki Y, Okado H, Hashimoto M, Asahara H (2009) A systems approach reveals that the myogenesis genome network is regulated by the transcriptional repressor RP58. Dev Cell 17:836–848
Nakahiro T, Kurooka H, Mori K, Sano K, Yokota Y (2011) Identification of BMP-responsive elements in the mouse Id2 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 399:416–421
Shepherd TG, Theriault BL, Nachtigal MW (2008) Autocrine BMP4 signalling regulates ID3 proto-oncogene expression in human ovarian cancer cells. Gene 414:95–105
Morikawa M, Koinuma D, Tsutsumi S, Vasilaki E, Kanki Y, Heldin CH, Aburatani H, Miyazono K (2011) ChIP-seq reveals cell type-specific binding patterns of BMP-specific Smads and a novel binding motif. Nucleic Acids Res 39:8712–8727
Takeda K, Ichijo H, Fujii M, Mochida Y, Saitoh M, Nishitoh H, Sampath TK, Miyazono K (1998) Identification of a novel bone morphogenetic protein-responsive gene that may function as a noncoding RNA. J Biol Chem 273:17079–17085
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Health and Labour Sciences Research Grants for Research on Measures for Intractable Research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan, grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan, a grant-in-aid for the Supported Program for the Strategic Research Foundation at Private Universities from the MEXT (S0801004) and a grant-in-aid from the Takeda Science Foundation.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, M., Ohte, S., Fukuda, T. et al. Identification of a novel bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-inducible transcript, BMP-inducible transcript-1, by utilizing the conserved BMP-responsive elements in the Id genes. J Bone Miner Metab 31, 34–43 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0381-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0381-1