Abstract
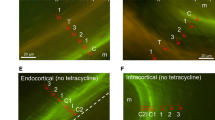
In order to evaluate the efficacy and safety of intermittent subcutaneous administration of 1-34 N-terminal peptide of human parathyroid hormone (hPTH 1–34), 100 units of hPTH 1-34 was subcutaneously injected once a week for 1 year in ten patients with primary osteoporsis (one male and nine females) with no qualitative abnormality of the bone according to the results of iliac crest biopsy performed previously, followed by a second biopsy after the end of the 1-year administration. Written consent of the patients for participation in the study was obtained. The mean lumbar bone mineral density (LBMD) definitely increased, by 1.8%, 3.4%, and 4.6% after 12, 24, and 48 weeks of hPTH administration, in accordance with previous clinical studies. Histomorphometric analysis after double-tetracycline labeling was completed in six patients (one male and five females) after the exclusion of those who dropped out because of adverse events unrelated to the test drug, or refusal of continuation. Examination of thin hard-tissue sections revealed no qualitative abnormalities of bone tissue or bone marrow cavity, such as osteomalacia, woven bone, or osteitis fibrosa, precluding the contribution of qualitatively abnormal tissue elements to any changes of LBMD in response to hPTH 1-34 administration. Histomorphometric measurement in the second biopsy revealed a tendency for an increase of bone volume, a significant increase of osteoid surface, and a tendency for an increase in other parameters of bone formation, compared with values obtained in the preadministration biopsy. Indices of two-dimensional microstructure obtained by microfocus computed tomography (CT) and results of node-strut analysis indicated improvement of trabecular continuity. In five patients in whom three-dimensional reconstruction images were analyzed, there were significant increases of bone volume and trabecular thickness, and a significant decrease in the trabecular bone pattern factor, a parameter related to the continuity, suggesting an improvement of the three-dimensional trabcular microstructure. Intermittent weekly subcutaneous injections of hPTH (1-34) for 48 weeks increased trabecular bone volume and improved microstructure, without causing the appearance of abnormal bone elements in primary osteoporosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A summary of this paper was presented at the 20th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society of Bone Morphometry, June 23–24, 2000, in Nagasaki, Japan and at the First Joint Meeting of the IBMS and the European Calcified Tissue Society, June 5–10, 2000, in Madrid, Spain. Kiyoshi Nakatsuka, the main investigator of the study, received the Young Investigator Award of the Japanese Society of Bone Morphometry.
About this article
Cite this article
Miki, T., Nakatsuka, K., Naka, H. et al. Effect and safety of intermittent weekly administration of human parathyroid hormone 1-34 in patients with primary osteoporosis evaluated by histomorphometry and microstructural analysis of iliac trabecular bone before and after 1 year of treatment. J Bone Miner Metab 22, 569–576 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-004-0525-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-004-0525-z