Abstract
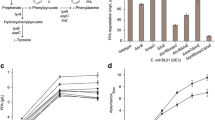
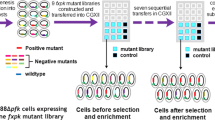
In our previous study, one-step pyruvate and d-alanine production from d,l-alanine by a whole-cell biocatalyst Escherichia coli expressing l-amino acid deaminase (Pm1) derived from Proteus mirabilis was investigated. However, due to the low catalytic efficiency of Pm1, the pyruvate titer was relatively low. Here, semi-rational design based on site-directed saturation mutagenesis was carried out to improve the catalytic efficiency of Pm1. A novel high-throughput screening (HTS) method for pyruvate based on 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine indicator was then established. The catalytic efficiency (kcat/Km) of the mutant V437I screened out by this method was 1.88 times higher than wild type. Next, to improve the growth of the engineered strain BLK07, the genes encoding for Xpk and Fbp were integrated into its genome to construct non-oxidative glycolysis (NOG) pathway. Finally, the CRISPR/Cas9 system was used to integrate the N6-pm1-V437I gene into the genome of BLK07. Pyruvic acid titer of the plasmid-free strain reached 42.20 g/L with an l-alanine conversion rate of 77.62% and a d-alanine resolution of 82.4%. This work would accelerate the industrial production of pyruvate and d-alanine by biocatalysis, and the HTS method established here could be used to screen other Pm1 mutants with high pyruvate titers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek J-O, Seo J-W, Kwon O, Seong S-I, Kim I-H, Kim CH (2011) Expression and characterization of a second L-amino acid deaminase isolated from Proteus mirabilis in Escherichia coli. J Basic Microbiol 51:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201000086
Bogorad IW, Lin T-S, Liao JC (2013) Synthetic non-oxidative glycolysis enables complete carbon conservation. Nature 502:693–697. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12575
Buto S, Pollegioni L, Dangiuro L, Pilone MS (1994) Evaluation of D-amino-acid oxidase from Rhodotorula-gracilis for the production of α-keto acids: a reactor system. Biotechnol Bioeng 44:1288–1294. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.260441104
Dinmukhamed T, Huang Z, Liu Y, Lv X, Liu L (2020) Current advances in design and engineering strategies of industrial enzymes. Syst Microbiol Biomanuf 1:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-020-00005-9
Fell DA, Wagner A (2000) The small world of metabolism. Nat Biotechnol 18:1121–1122. https://doi.org/10.1038/81025
Godwin D, Slater JH (1979) The influence of the growth environment on the stability of a drug resistance plasmid in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol 111:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-111-1-201
Gu L, Yuan H, Lv X, Li G, Cong R, Li J, Du G, Liu L (2020) High-yield and plasmid-free biocatalytic production of 5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxylic acid by combinatorial genetic elements engineering and genome engineering of Escherichia coli. Enzyme Microb Technol 134:109488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.109488
Hao J, Ma C, Gao C, Qiu J, Wang M, Zhang Y, Cui X, Xu P (2007) Pseudomonas stutzeri as a novel biocatalyst for pyruvate production from D, L-lactate. Biotechnol Lett 29:105–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9204-6
Hou Y, Hossain GS, Li J, Shin H-d, Liu L, Du G (2015) Production of phenylpyruvic acid from L-phenylalanine using an L-amino acid deaminase from Proteus mirabilis: comparison of enzymatic and whole-cell biotransformation approaches. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:8391–8402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6757-0
Hou Y, Hossain GS, Li J, Shin H-d, Du G, Liu L (2016) Combination of phenylpyruvic acid (PPA) pathway engineering and molecular engineering of L-amino acid deaminase improves PPA production with an Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalyst. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:2183–2191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7048-5
Howard JW (1932) Preparation of pyruvic acid. Orgsynthcoll 1:75–80
Jiang Y, Chen B, Duan C, Sun B, Yang J, Yang S, Kelly RM (2015) Multigene editing in the Escherichia coli genome via the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:2506–2514. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.04023-14
Jiang Z, Niu T, Lv X, Liu Y, Li J, Lu W, Du G, Chen J, Liu L (2019) Secretory expression fine-tuning and directed evolution of diacetylchitobiose deacetylase by Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 85:e01076-e1019. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01076-19
Juhas M, Ajioka JW (2015) Flagellar region 3b supports strong expression of integrated DNA and the highest chromosomal integration efficiency of the Escherichia coli flagellar regions. Microb Biotechnol 8:726–738. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12296
Labun K, Montague TG, Gagnon JA, Thyme SB, Valen E (2016) CHOPCHOP v2: a web tool for the next generation of CRISPR genome engineering. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W272–W276. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw398
Li Y, Chen J, Lun SY (2001) Biotechnological production of pyruvic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:451–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100804
Li R, Wijma HJ, Song L, Cui Y, Otzen M, Tian Ye DuJ, Li T, Niu D, Chen Y, Feng J, Han J, Chen H, Tao Y, Janssen DB, Wu B (2018) Computational redesign of enzymes for regio- and enantioselective hydroamination. Nat Chem Biol 14:664–670. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0053-0
Liu L, Xu Q, Li Y, Shi Z, Zhu Y, Du G, Chen J (2007) Enhancement of pyruvate production by osmotic-tolerant mutant of Torulopsis glabrata. Biotechnol Bioeng 97:825–832. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.21290
Liu L, Hossain GS, Shin HD, Li J, Du G, Chen J (2013) One-step production of α-ketoglutaric acid from glutamic acid with an engineered L-amino acid deaminase from Proteus mirabilis. J Biotechnol 164:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.01.005
Liu K, Huang X, Pidko EA, Hensen EJM (2017) MoO3-TiO2 synergy in oxidative dehydrogenation of lactic acid to pyruvic acid. Green Chem 19:3014–3022. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7gc00807d
Liu K, Gong M, Lv X, Li J, Du G, Liu L (2020) Biotransformation and chiral resolution of D, L-alanine into pyruvate and D-alanine with a whole-cell biocatalyst expressing L-amino acid deaminase. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 67:668–676. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2011
Massad G, Zhao H, Mobley HLT (1995) Proteus mirabilis amino acid deaminase: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of aad. J Bacteriol 177:5878–5883. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.177.20.5878-5883.1995
Miyazaki M, Shibue M, Ogino K, Nakamura H, Maeda H (2001) Enzymatic synthesis of pyruvic acid from acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide. Chem Commun 18:1800–1801. https://doi.org/10.1039/b104873m
Motta P, Molla G, Pollegioni L, Nardini M (2016) Structure-function relationships in L-amino acid deaminase, a flavoprotein belonging to a novel class of biotechnologically relevant enzymes. J Biol Chem 291:10457–10475. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.703819
Ogawa J, Soong CL, Ito M, Shimizu S (2001) Enzymatic production of pyruvate from fumarate—an application of microbial cyclic-imide-transforming pathway. J Mol Catal B Enzym 11:355–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1177(00)00024-2
Pang C, Yin X, Zhang G, Liu S, Du G (2020) Current progress and prospects of enzyme technologies in future foods. Syst Microbiol Biomanuf 1:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43393-020-00008-6
Reitman S, Frankel S (1957) A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol 28:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/28.1.56
Rosini E, Melis R, Molla G, Tessaro D, Pollegioni L (2017) Deracemization and stereoinversion of alpha-amino acids by L-amino acid deaminase. Adv Synth Catal 359:3773–3781. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201700806
Xu P, Qiu J, Gao C, Ma C (2008) Biotechnological routes to pyruvate production. J Biosci Bioeng 105:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.105.169
Yonehara T, Miyata R (1994) Fermentative production of pyruvate from glucose by Torulopsis glabrata. J Ferment Bioeng 78:155–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/0922-338X(94)90255-0
Yu H, Dalby PA (2018) Exploiting correlated molecular-dynamics networks to counteract enzyme activity-stability trade-off. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E12192–E12200. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1812204115
Yu H, Huang H (2014) Engineering proteins for thermostability through rigidifying flexible sites. Biotechnol Adv 32:308–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.10.012
Zhu Y, Eiteman MA, Altman R, Altman E (2008) High glycolytic flux improves pyruvate production by a metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6649–6655. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01610-08
Zhuang Y, Yang G-Y, Chen X, Liu Q, Zhang X, Deng Z, Feng Y (2017) Biosynthesis of plant-derived ginsenoside Rh2 in yeast via repurposing a key promiscuous microbial enzyme. Metab Eng 42:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.04.009
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0900504), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870069, 32021005) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (USRP52019A, JUSRP121010, JUSRP221013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KL performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. HY and GS polished the manuscript. XL and LL conceived the project and revised the manuscript. YL, JL and GD were responsible for revising and supervising.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
This article does not contain individual participants requiring informed consent.
Additional information
Handling editor: S. Stuchlík.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, K., Yu, H., Sun, G. et al. Semi-rational design of L-amino acid deaminase for production of pyruvate and d-alanine by Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalyst. Amino Acids 53, 1361–1371 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03067-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03067-8