Abstract
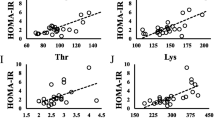
Essential amino acids (EAAs) are involved in growth and development in children and adolescents. This study was aimed at exploring the relationship between dietary EAA intakes and metabolic biomarker, and the influence of obesity in children and adolescents. A total of 3566 subjects were analysed. Participators were classified according to weight status. Metabolic biomarkers were determined using standardized methods and conditions. Normal, overweight, and obesity statuses were defined according to the Working Group on Obesity in China (WGOC) BMI cutoff points based on age- and sex-specific screening criteria. In normal-weight group, blood uric acid was negatively correlated with dietary Ile, Leu, Lys, Phe, Thr, Val, and His, and zinc was negatively correlated with Ile, Leu, Lys, Phe, Thr, Val, His, Met, and Trp. In overweight group, TC was negatively correlated with Ile, Leu, Phe, Val, and His, and LDL-C was negatively correlated with Ile, Leu, Lys, Phe, Thr, Val, His, and Met, while TG was positively correlated with Leu, Lys, Phe, Thr, Val, and Met. In obesity group, hemoglobin was positively related to Ile, Leu, Lys, Phe, Thr, Val, His, and Trp, while vitamin D was positively correlated with His and Trp. The serum creatinine was negatively correlated with Ile, Leu, Phe, Val, His, and Met in normal-weight group, and positively correlated with Ile, Leu, Lys, Phe, Thr, Val, His, Met, Trp, His, and Trp in obesity group. Dietary amino acid score (AAS) and Leu intake were protective factors for obesity. The association between fasting blood glucose and EAAs intake was weak and labile. Metabolic biomarkers and EAA intakes were only related under certain weight status. The dietary AAS is positively correlated with HDL-C, LDL-C, serum creatinine, albumin, serum vitamin D, and zinc. The subtle relationship of EAAs and kidney function should be explored further. There is a complex relationship between EAAs and metabolic biomarkers, and overweight and obesity have a certain influence on this relationship.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bipath P, Levay PF, Viljoen M (2016) Tryptophan depletion in context of the inflammatory and general nutritional status of a low-income South African HIV-infected population. J Health Popul Nutr 17(35):5
Brenachot X, Ramadori G, Ioris RM, Veyrat-Durebex C, Altirriba J, Aras E, Ljubicic S, Kohno D, Fabbiano S, Clement S, Goossens N, Trajkovski M, Harroch S, Negro F, Coppari R (2017) Hepatic protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor gamma links obesity-induced inflammation to insulin resistance. Nat Commun 8(1):1820
Caro P, Gomez J, Sanchez I, Naudi A, Ayala V, Lopez-Torres M et al (2009) Forty percent methionine restriction decreases mitochondrial oxygen radical production and leak at complex I during forward electron flow and lowers oxidative damage to proteins and mitochondrial DNA in rat kidney and brain mitochondria. Rejuvenation Res 12(6):421–434
Cesari M, Landi F, Vellas B, Bernabei R, Marzetti E (2014) Sarcopenia and physical frailty: two sides of the same coin. Front Aging Neurosci 6:192
Wang G (1991) China food composition table 1991. China’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing
Churchward-Venne TA, Breen L, Phillips SM (2014) Alterations in human muscle protein metabolism with aging: protein and exercise as countermeasures to offset sarcopenia. BioFactors 40:199–205
Dong Z, Gao X, Chinchilli VM, Sinha R, Muscat J, Winkels RM, Richie JP Jr (2020) Association of sulfur amino acid consumption with cardiometabolic risk factors: Cross-sectional findings from NHANES III. EClinicalMedicine 3(19):100248
Duque EJ, Elias RM, Moysés RMA (2020) Parathyroid hormone: a uremic toxin. Toxins (Basel) 12(3):189
Floyd JC Jr, Fajans SS, Conn JW, Knopf RF, Rull J (1966) Stimulation of insulin secretion by amino acids. J Clin Investig 45:1487–1502
Force GOCOT (2004) Body mass index reference norm for screening overweight and obesity in Chinese children and adolescents. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology. 25(2):97
Galarregui C, Cantero I, Marin-Alejandre BA, Monreal JI, Elorz M, Benito-Boillos A, Herrero JI, de la O V, Ruiz-Canela M, Hermsdorff HHM, Bressan J, Tur JA, Martínez JA, Zulet MA, Abete I (2020) Dietary intake of specific amino acids and liver status in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: fatty liver in obesity (FLiO) study. Eur J Nutr
Gannon MC, Nuttall FQ (2010) Amino acid ingestion and glucose metabolism–a review. IUBMB Life 62(9):660–668
Gheller ME, Vermeylen F, Handzlik MK, Gheller BJ, Bender E, Metallo C, Aydemir TB, Smriga M, Thalacker-Mercer AE (2020) Tolerance to graded dosages of histidine supplementation in healthy human adults. Am J Clin Nutr 112(5):1358–1367
Giallongo F, Harper MT, Oh J, Parys C, Shinzato I, Hristov AN (2017) Histidine deficiency has a negative effect on lactational performance of dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 100(4):2784–2800
Grant L, Lees EK, Forney LA, Mody N, Gettys T, Brown PA et al (2016) Methionine restriction improves renal insulin signalling in aged kidneys. Mech Ageing Dev 157:35–43
Heilberg IP, Goldfarb DS (2013) Optimum nutrition for kidney stone disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 20(2):165–174
Ikehara O, Kawasaki N, Maezono K, Komatsu M, Konishi A (2008) Acute and chronic treatment of L-isoleucine ameliorates glucose metabolism in glucose-intolerant and diabetic mice. Biol Pharm Bull 31:469–472
Kim JH, Lee C, Lee M, Wang H, Kim K, Park SJ, Yoon I, Jang J, Zhao H, Kim HK, Kwon NH, Jeong SJ, Yoo HC, Kim JH, Yang JS, Lee MY, Lee CW, Yun J, Oh SJ, Kang JS, Martinis SA, Hwang KY, Guo M, Han G, Han JM, Kim S (2017) Control of leucine-dependent mTORC1 pathway through chemical intervention of leucyl-tRNA synthetase and RagD interaction. Nat Commun 8(1):732. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00785-0.PMID:28963468;PMCID:PMC5622079
Kristbjornsdottir OK, Halldorsson TI, Thorsdottir I, Gunnarsdottir I (2012) Association between 24-hour urine sodium and potassium excretion and diet quality in six-year-old children: a cross sectional study. Nutr J 15(11):94
Lapierre H, Ouellet DR, Lobley GE (2014) Estimation of histidine requirement in lactating dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 97(Suppl. 1):757–758
Malloy VL, Krajcik RA, Bailey SJ, Hristopoulos G, Plummer JD, Orentreich N (2006) Methi onine restriction decreases visceral fat mass and preserves insulin action in aging male Fischer 344 rats independent of energy restriction. Aging Cell 5(4):305–314
Martínez-Negro M, Blanco-Fernández L, Tentori PM, Pérez L, Pinazo A, Tros de Ilarduya C, Aicart E, Junquera E (2018) A gemini cationic lipid with histidine residues as a novel lipid-based gene nanocarrier: a biophysical and biochemical study. Nanomaterials (Basel). 8(12):1061
Meijer AJ, Dubbelhuis PF (2004) Amino acid signalling and the integration of metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:397–403
Miller RA, Buehner G, Chang Y, Harper JM, Sigler R, Smith-Wheelock M (2005) Methionine-defificient diet extends mouse lifespan, slows immune and lens aging, alters glucose, T4, IGF-I and insulin levels, and increases hepatocyte MIF levels and stress resistance. Aging Cell 4(3):119–125
Multhaup ML, Seldin MM, Jaffe AE, Lei X, Kirchner H, Mondal P, Li Y, Rodriguez V, Drong A, Hussain M, Lindgren C, McCarthy M, Näslund E, Zierath JR, Wong GW, Feinberg AP (2015) Mouse-human experimental epigenetic analysis unmasks dietary targets and genetic liability for diabetic phenotypes. Cell Metab 21(1):138–149
Newgard CB, An J, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Stevens RD, Lien LF, Haqq AM, Shah SH, Arlotto M, Slentz CA, Rochon J, Gallup D, Ilkayeva O, Wenner BR, Yancy WS Jr, Eisenson H, Musante G, Surwit RS, Millington DS, Butler MD, Svetkey LP (2009) A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab 9:11–326
Nishimura J, Masaki T, Arakawa M, Seike M, Yoshimatsu H (2010) Isoleucine prevents the accumulation of tissue triglycerides and upregulates the expression of paralpha and uncoupling protein in diet-induced obese mice. J Nutr 140:496–500
O’Rielly R, Li H, Lim SM, Yazbeck R, Kritas S, Ullrich SS, Feinle-Bisset C, Heilbronn L, Page AJ (2020) The effect of isoleucine supplementation on body weight gain and blood glucose response in lean and obese mice. Nutrients 12(8):2446
Oshima S, Shiiya S, Nakamura Y (2019) Serum uric acid-lowering effects of combined glycine and tryptophan treatments in subjects with mild hyperuricemia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Nutrients 11(3):564
Phillips SM (2017) Current concepts and unresolved questions in dietary protein requirements and supplements in adults. Front Nutr 8(4):13
Samad N (2017) Serum levels of leptin, zinc and tryptophan with obesity: a case-control study. Pak J Pharm Sci 30(5):1691–1696
Schmeisser DD, Kummerow FA, Baker DH (1983) Effect of excess dietary lysine on plasma lipids of the chick. J Nutr 113:1777–1783
Schüle R, Evans RM (1991) Cross-coupling of signal transduction pathways: zinc finger meets leucine zipper. Trends Genet 7(11–12):377–381
Smuts CM, Matsungo TM, Malan L, Kruger HS, Rothman M, Kvalsvig JD, Covic N, Joosten K, Osendarp SJM, Bruins MJ, Frenken LGJ, Lombard CJ, Faber M (2019) Effect of small-quantity lipid-based nutrient supplements on growth, psychomotor development, iron status, and morbidity among 6- to 12-mo-old infants in South Africa: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 109(1):55–68
Steinert RE, Luscombe-Marsh ND, Little TJ, Standfield S, Otto B, Horowitz M, Feinle-Bisset C (2014) Effects of intraduodenal infusion of L-tryptophan on ad libitum eating, antropyloroduodenal motility, glycemia, insulinemia, and gut peptide secretion in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:3275–3284
Suzuki Y, Kido J, Matsumoto S, Shimizu K, Nakamura K (2019) Associations among amino acid, lipid, and glucose metabolic profiles in childhood obesity. BMC Pediatr 19(1):273
Troesch B, van Stuijvenberg ME, Smuts CM, Kruger HS, Biebinger R, Hurrell RF, Baumgartner J, Zimmermann MB (2011) A micronutrient powder with low doses of highly absorbable iron and zinc reduces iron and zinc deficiency and improves weight-for-age Z-scores in South African children. J Nutr 141(2):237–242
Trushina EN, Vybornov VD, Riger NA, Mustafina OK, Solntseva TN, Timonin AN, Zilova IS, Radzhabkadiev RM (2019) The efficiency of branched chain aminoacids (BCAA) in the nutrition of combat sport athletes. Vopr Pitan 88(4):48–56
Ullrich SS, Fitzgerald PCE, Giesbertz P, Steinert RE, Horowitz M, Feinle-Bisset C (2018) Effects of intragastric administration of tryptophan on the blood glucose response to a nutrient drink and energy intake, in lean and obese men. Nutrients 10(4):463
Watford M, Wu G (2018) Protein. Adv Nutr 9(5):651–653
Wenninger J, Meinitzer A, Holasek S, Schnedl WJ, Zelzer S, Mangge H, Herrmann M, Enko D (2019) Associations between tryptophan and iron metabolism observed in individuals with and without iron deficiency. Sci Rep 9(1):14548
Xiao CW, Wood C, Bertinato J (2019) Dietary supplementation with L-lysine affects body weight and blood hematological and biochemical parameters in rats. Mol Biol Rep 46(1):433–442
Yang Y, Wang G, Pan X (2002) China food composition table 2002. Beijing Medical University Publishing House, Beijing
Yang Y, Wang G, Pan X (2005) China food composition 2004. Beijing Medical University Publishing House, Beijing
Zhang Y, Launay H, Schramm A, Lebrun R, Gontero B (2018) Exploring intrinsically disordered proteins in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Sci Rep 8(1):6805. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24772-7.Erratum.In:SciRep.2018Aug29;8(1):13171.PMID:29717210;PMCID:PMC5931566
Acknowledgements
The study was financed by National Key R&D Program [2016YFC1305201] of China and Shandong Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Project 2019WS436. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript. This study was supported by the China National Nutrition and Health Survey Program. Surveys are conducted under the auspices of the Shandong Center for Disease Control and Prevention (Shandong CDC), Shibei CDC, Penglai CDC, Lijin CDC, Shouguang CDC, Wucheng CDC, Lanshan CDC, Dong'e CDC, Linzi CDC, Laizhou CDC, Sishui CDC, Yishui CDC, Lingcheng CDC, and Dingtao CDC. We thank all the team members and all participants.
Funding
The study was financed by National Key R&D Program [2016YFC1305201] of China and Shandong Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Project 2019WS436.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ, SL, and WL participated in research conceptualization, design, and supervision as well as analysis and interpretation of data. LY, YL, LZ, ND, and BZ contributed to data analysis and interpretation. QZ and JZ provided administrative, technical, and figure support for the research as well as analyzed and explained the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was obtained from Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Human and animal rights
All laboratory tests and investigations here were conducted under proper ethical standards for either animal or human research.
Informed consent
All participants voluntarily joined this study with informed consent.
Additional information
Handling editor: J. M. Phang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Li, Y., Zhang, Q. et al. Association between dietary essential amino acids intake and metabolic biomarkers: influence of obesity among Chinese children and adolescents. Amino Acids 53, 635–644 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-02970-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-02970-4