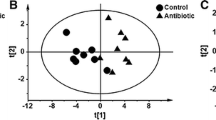
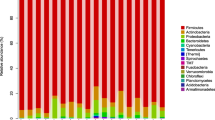
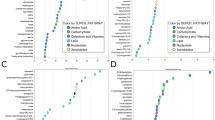
Abstract
In-feed antibiotics have been used to promote growth in piglets, but its impact on metabolomics profiles associated with host metabolism is largely unknown. In this study, to test the hypothesis that antibiotic treatment may affect metabolite composition both in the gut and host biofluids, metabolomics profiles were analyzed in antibiotic-treated piglets. Piglets were fed a corn-soy basal diet with or without in-feed antibiotics from postnatal day 7 to day 42. The serum biochemical parameters, metabolomics profiles of the serum, urine, and jejunal digesta, and indicators of microbial metabolism (short-chain fatty acids and biogenic amines) were analyzed. Compared to the control group, antibiotics treatment did not have significant effects on serum biochemical parameters except that it increased (P < 0.05) the concentration of urea. Antibiotics treatment increased the relative concentrations of metabolites involved in amino-acid metabolism in the serum, while decreased the relative concentrations of most amino acids in the jejunal content. Antibiotics reduced urinary 2-ketoisocaproate and hippurate. Furthermore, antibiotics decreased (P < 0.05) the concentrations of propionate and butyrate in the feces. Antibiotics significantly affected the concentrations of biogenic amines, which are derived from microbial amino-acid metabolism. The three major amines, putrescine, cadaverine, and spermidine, were all increased (P < 0.05) in the large intestine of antibiotics-treated piglets. These results identified the phenomena that in-feed antibiotics may have significant impact on the metabolomic markers of amino-acid metabolism in piglets.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander AN, Carey HV (1999) Oral IGF-I enhances nutrient and electrolyte absorption in neonatal piglet intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 277:G619–G625
Anderson DB, McCracken VJ, Aminovi RI, Simpson JM, Mackie RI, Verstegen MWA, Gaskins HR (2000) Gut microbiology and growth-promoting antibiotics in swine. Pig News Inf 70:101–108
Antunes LCM, Han J, Ferreira RBR, Lolic P, Borchers CH, Finlay BB (2011) Effect of antibiotic treatment on the intestinal metabolome. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:1494–1503
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate—a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Statist Soc Ser B 57:289–300
Brosnan JT (2000) Glutamate, at the interface between amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism. J Nutr 130:988s–990s
Buraczewska L (1981) Absorption of amino acids in different parts of the small intestine in growing pigs. III. Absorption of constituents of protein hydrolysates. Acta Physiol Pol 32:569–584
Chen LX, Li P, Wang JJ, Li XL, Gao HJ, Yin YL, Hou YQ, Wu GY (2009) Catabolism of nutritionally essential amino acids in developing porcine enterocytes. Amino Acids 37:143–152
Dai ZL, Zhang J, Wu GY, Zhu WY (2010) Utilization of amino acids by bacteria from the pig small intestine. Amino Acids 39:1201–1215
Dai ZL, Wu GY, Zhu WY (2011) Amino acid metabolism in intestinal bacteria: links between gut ecology and host health. Front Biosci 16:1768–1786
Davila AM, Blachier F, Gotteland M, Andriamihaja M, Benetti PH, Sanz Y, Tome D (2013) Intestinal luminal nitrogen metabolism: role of the gut microbiota and consequences for the host. Pharmacol Res 68:95–107
Dogan A, Celik I (2012) Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of grapeseeds against ethanol-induced oxidative stress in rats. Br J Nutr 107:45–51
Elliott P, Posma JM, Chan Q, Garcia-Perez I, Wijeyesekera A, Bictash M, Ebbels TMD, Ueshima H, Zhao LC, van Horn L, Daviglus M, Stamler J, Holmes E, Nicholson JK (2015) Urinary metabolic signatures of human adiposity. Sci Transl Med 7:285ra62
Eriksson L, Trygg J, Wold S (2008) CV-ANOVA for significance testing of PLS and OPLS (R) models. J Chemom 22:594–600
Feighner SD, Dashkevicz MP (1987) Subtherapeutic levels of antibiotics in poultry feeds and their effects on weight gain, feed efficiency, and bacterial cholyltaurine hydrolase activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:331–336
Holmes E, Li JV, Athanasiou T, Ashrafian H, Nicholson JK (2011) Understanding the role of gut microbiome-host metabolic signal disruption in health and disease. Trends Microbiol 19:349–359
Hutson SM, Sweatt AJ, LaNoue KF (2005) Branched-chain amino acid metabolism: implications for establishing safe intakes. J Nutr 135:1557S–1564S
Hyde R, Taylor PM, Hundal HS (2003) Amino acid transporters: roles in amino acid sensing and signalling in animal cells. Biochem J 373:1–18
Jiye A, Trygg J, Gullberg J, Johansson AI, Jonsson P, Antti H, Marklund SL, Moritz T (2005) Extraction and GC/MS analysis of the human blood plasma metabolome. Anal Biochem 77:8086–8094
Jiye A, Huang Q, Wang GJ, Zha WB, Yan B, Ren HC, Gu SH, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Shao F, Sheng LS, Sun JG (2008) Global analysis of metabolites in rat and human urine based on gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 379:20–26
Laeger T, Metges CC, Kuhla B (2010) Role of beta-hydroxybutyric acid in the central regulation of energy balance. Appetite 54:450–455
Looft T, Johnson TA, Allen HK, Bayles DO, Alt DP, Stedtfeld RD, Sul WJ, Stedtfeld TM, Chai BL, Cole JR, Hashsham SA, Tiedje JM, Stanton TB (2012) In-feed antibiotic effects on the swine intestinal microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:1691–1696
Lopez CA, Kingsbury DD, Velazquez EM, Baumler AJ (2014) Collateral damage: microbiota-derived metabolites and immune function in the antibiotic era. Cell Host Microbe 16:156–163
Macfarlane GT, Macfarlane S (2012) Bacteria, colonic fermentation, and gastrointestinal health. J AOAC Int 95:50–60
Madge DS (1969) Effect of antibiotics on intestinal absorption in mice. Br J Nutr 23:637–646
Mu CL, Yang YX, Luo Z, Zhu WY (2015) Metabolomic analysis reveals distinct profiles in the plasma and urine of rats fed a high-protein diet. Amino Acids 47:1225–1238
Nichols NL, Bertolo RF (2008) Luminal threonine concentration acutely affects intestinal mucosal protein and mucin synthesis in piglets. J Nutr 138:1298–1303
Ravindran V, Kornegay ET, Webb KE Jr (1984) Effects of fiber and virginiamycin on nutrient absorption, nutrient retention and rate of passage in growing swine. J Anim Sci 59:400–408
Reitman S, Frankel S (1957) A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase and serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase. Am J Clin Path 28:56–62
Rezaei R, Wang WW, Wu ZL, Dai ZL, Wang JJ, Wu GY (2013) Biochemical and physiological bases for utilization of dietary amino acids by young pigs. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 4:1
Romick-Rosendale LE, Goodpaster AM, Hanwright PJ, Patel NB, Wheeler ET, Chona DL, Kennedy MA (2009) NMR-based metabonomics analysis of mouse urine and fecal extracts following oral treatment with the broad-spectrum antibiotic enrofloxacin (Baytril). Magn Reson Chem 47:S36–S46
Theriot CM, Koenigsknecht MJ, Carlson PE, Hatton GE, Nelson AM, Li B, Huffnagle GB, Li JZ, Young VB (2014) Antibiotic-induced shifts in the mouse gut microbiome and metabolome increase susceptibility to Clostridium difficile infection. Nat Commun 5
Tremaroli V, Backhed F (2012) Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 489:242–249
Visek WJ (1978) Mode of growth promotion by antibiotics. J Anim Sci 46:1447–1469
Wagenmakers AJM, Brookes JH, Coakley JH, Reilly T, Edwards RHT (1989) Exercise-induced activation of the branched-chain 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase in human muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 59:159–167
Wallace RJ (1996) Ruminal microbial metabolism of peptides and amino acids. J Nutr 126:S1326–S1334
Wang XF, Mao SF, Liu JH, Zhang LL, Cheng YF, Zhu WY (2011) Effect of gynosaponins on methane production and microbe numbers in a fungus-methanogen co-culture. J Anim Feed Sci 20:272–284
Wijeyesekera A, Clarke PA, Bictash M, Brown IJ, Fidock M, Ryckmans T, Yap IKS, Chan Q, Stamler J, Elliott P, Holmes E, Nicholson JK (2012) Quantitative UPLC-MS/MS analysis of the gut microbial co-metabolites phenylacetylglutamine, 4-cresyl sulphate and hippurate in human urine: INTERMAP Study. Anal Methods 4:65–72
Williams BB, Van Benschoten AH, Cimermancic P, Donia MS, Zimmermann M, Taketani M, Ishihara A, Kashyap PC, Fraser JS, Fischbach MA (2014) Discovery and characterization of gut microbiota decarboxylases that can produce the neurotransmitter tryptamine. Cell Host Microbe 16:495–503
Willing BP, Russell SL, Finlay BB (2011) Shifting the balance: antibiotic effects on host-microbiota mutualism. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:233–243
Wu GY (2014) Dietary requirements of synthesizable amino acids by animals: a paradigm shift in protein nutrition. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 5
Xia JG, Sinelnikov IV, Han B, Wishart DS (2015) MetaboAnalyst 3.0-making metabolomics more meaningful. Nucleic Acids Res 43:W251–W257
Yang YX, Dai ZL, Zhu WY (2014a) Important impacts of intestinal bacteria on utilization of dietary amino acids in pigs. Amino Acids 46:2489–2501
Yang YX, Mu CL, Zhang JF, Zhu WY (2014b) Determination of biogenic amines in digesta by high performance liquid chromatography with precolumn dansylation. Anal Lett 47:1290–1298
Yano JM, Yu K, Donaldson GP, Shastri GG, Ann P, Ma L, Nagler CR, Ismagilov RF, Mazmanian SK, Hsiao EY (2015) Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 161:264–276
Yap IKS, Li JV, Saric J, Martin FP, Davies H, Wang YL, Wilson ID, Nicholson JK, Utzinger J, Marchesi JR, Holmes E (2008) Metabonomic and microbiological analysis of the dynamic effect of vancomycin-induced gut microbiota modification in the mouse. J Proteome Res 7:3718–3728
Zhang Q, Wang GJ, Du Y, Zhu LL, Jiye A (2007) GC/MS analysis of the rat urine for metabonomic research. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 854:20–25
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2013CB127300) and Natural Science Foundation of China (31430082). W. Zhu also thanks Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Meat Production and Processing, Quality and Safety Control for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: C.-A. A. Hu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, C., Yang, Y., Yu, K. et al. Alteration of metabolomic markers of amino-acid metabolism in piglets with in-feed antibiotics. Amino Acids 49, 771–781 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2379-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2379-4