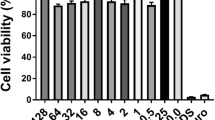
Abstract
Patients with cystic fibrosis require pharmacological treatment against chronic lung infections. The alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides BMAP-27 and BMAP-28 have shown to be highly active in vitro against planktonic and sessile forms of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia cystic fibrosis strains. To develop small antibacterial peptides for therapeutic use, we tested shortened/modified BMAP fragments, and selected the one with the highest in vitro antibacterial activity and lowest in vivo acute pulmonary toxicity. All the new peptides have shown to roughly maintain their antibacterial activity in vitro. The 1–18 N-terminal fragment of BMAP-27, showing MIC90 of 16 µg/ml against P. aeruginosa isolates and strain-dependent anti-biofilm effects, showed the lowest pulmonary toxicity in mice. However, when tested in a murine model of acute lung infection by P. aeruginosa, BMAP-27(1–18) did not show any curative effect. If exposed to murine broncho-alveolar lavage fluid BMAP-27(1–18) was degraded within 10 min, suggesting it is not stable in pulmonary environment, probably due to murine proteases. Our results indicate that shortened BMAP peptides could represent a starting point for antibacterial drugs, but they also indicate that they need a further optimization for effective in vivo use.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benincasa M, Skerlavaj B, Gennaro R, Pellegrini A, Zanetti M (2003) In vitro and in vivo antimicrobial activity of two alpha-helical cathelicidin peptides and of their synthetic analogs. Peptides 24:1723–1731. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2003.07.025
Benincasa M et al (2006) Fungicidal activity of five cathelicidin peptides against clinically isolated yeasts. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:950–959. doi:10.1093/jac/dkl382
Dasenbrook EC, Checkley W, Merlo CA, Konstan MW, Lechtzin N, Boyle MP (2010) Association between respiratory tract methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and survival in cystic fibrosis. JAMA 303:2386–2392. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.791
Di Bonaventura G et al (2007) Molecular characterization of virulence determinants of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia strains isolated from patients affected by cystic fibrosis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 20:529–537
Emerson J, Rosenfeld M, McNamara S, Ramsey B, Gibson RL (2002) Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other predictors of mortality and morbidity in young children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 34:91–100. doi:10.1002/ppul.10127
Emerson J, McNamara S, Buccat AM, Worrell K, Burns JL (2010) Changes in cystic fibrosis sputum microbiology in the United States between 1995 and 2008. Pediatr Pulmonol 45:363–370. doi:10.1002/ppul.21198
Hancock RE, Sahl HG (2006) Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat Biotechnol 24:1551–1557. doi:10.1038/nbt1267
Hansen MB, Nielsen SE, Berg K (1989) Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods 119:203–210
Hoffman LR, D’Argenio DA, MacCoss MJ, Zhang Z, Jones RA, Miller SI (2005) Aminoglycoside antibiotics induce bacterial biofilm formation. Nature 436:1171–1175. doi:10.1038/nature03912
Hsu CY, Lin MH, Chen CC, Chien SC, Cheng YH, Su IN, Shu JC (2011) Vancomycin promotes the bacterial autolysis, release of extracellular DNA, and biofilm formation in vancomycin-non-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 63:236–247. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2011.00846.x
Johansen HK, Espersen F, Pedersen SS, Hougen HP, Rygaard J, Hoiby N (1993) Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in normal and athymic rats. APMIS 101:207–225
Kaplan JB (2011) Antibiotic-induced biofilm formation. Int J Artif Organs 34:737–751. doi:10.5301/ijao.5000027
Lai Y, Gallo RL (2009) AMPed up immunity: how antimicrobial peptides have multiple roles in immune defense. Trends Immunol 30:131–141. doi:10.1016/j.it.2008.12.003
Limoli DH, Rockel AB, Host KM, Jha A, Kopp BT, Hollis T, Wozniak DJ (2014) Cationic antimicrobial peptides promote microbial mutagenesis and pathoadaptation in chronic infections. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004083. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004083
Linares JF, Gustafsson I, Baquero F, Martinez JL (2006) Antibiotics as intermicrobial signaling agents instead of weapons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:19484–19489. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608949103
Millar FA, Simmonds NJ, Hodson ME (2009) Trends in pathogens colonising the respiratory tract of adult patients with cystic fibrosis, 1985–2005. J Cyst Fibros 8:386–391. doi:10.1016/j.jcf.2009.08.003
Molina A, Del Campo R, Maiz L, Morosini MI, Lamas A, Baquero F, Canton R (2008) High prevalence in cystic fibrosis patients of multiresistant hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST228-SCCmecI capable of biofilm formation. J Antimicrob Chemother 62:961–967. doi:10.1093/jac/dkn302
Palmer KL, Aye LM, Whiteley M (2007) Nutritional cues control Pseudomonas aeruginosa multicellular behavior in cystic fibrosis sputum. J Bacteriol 189:8079–8087. doi:10.1128/JB.01138-07
Pompilio A et al (2011) Antibacterial and anti-biofilm effects of cathelicidin peptides against pathogens isolated from cystic fibrosis patients. Peptides 32:1807–1814. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2011.08.002
Pompilio A et al (2012) Potential novel therapeutic strategies in cystic fibrosis: antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activity of natural and designed alpha-helical peptides against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. BMC Microbiol 12:145. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-12-145
Sajjan US et al (2001) P-113D, an antimicrobial peptide active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, retains activity in the presence of sputum from cystic fibrosis patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:3437–3444. doi:10.1128/AAC.45.12.3437-3444.2001
Schagger H (2006) Tricine-SDS-PAGE Nat Protoc 1:16–22. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.4
Singh PK, Schaefer AL, Parsek MR, Moninger TO, Welsh MJ, Greenberg EP (2000) Quorum-sensing signals indicate that cystic fibrosis lungs are infected with bacterial biofilms. Nature 407:762–764. doi:10.1038/35037627
Skerlavaj B, Gennaro R, Bagella L, Merluzzi L, Risso A, Zanetti M (1996) Biological characterization of two novel cathelicidin-derived peptides and identification of structural requirements for their antimicrobial and cell lytic activities. J Biol Chem 271:28375–28381
Worlitzsch D et al (2002) Effects of reduced mucus oxygen concentration in airway Pseudomonas infections of cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Invest 109:317–325. doi:10.1172/JCI13870
Wu S et al (2014) Beta- lactam antibiotics stimulate biofilm formation in non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae by up-regulating carbohydrate metabolism. PLoS One 9:e99204. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099204
Yang D, Biragyn A, Kwak LW, Oppenheim JJ (2002) Mammalian defensins in immunity: more than just microbicidal. Trends Immunol 23:291–296
Zanetti M (2004) Cathelicidins, multifunctional peptides of the innate immunity. J Leukoc Biol 75:39–48. doi:10.1189/jlb.0403147
Zanetti M, Gennaro R, Scocchi M, Skerlavaj B (2000) Structure and biology of cathelicidins. Adv Exp Med Biol 479:203–218. doi:10.1007/0-306-46831-X_17
Zanetti M, Gennaro R, Skerlavaj B, Tomasinsig L, Circo R (2002) Cathelicidin peptides as candidates for a novel class of antimicrobials. Curr Pharm Des 8:779–793
Zhang L, Parente J, Harris SM, Woods DE, Hancock RE, Falla TJ (2005) Antimicrobial peptide therapeutics for cystic fibrosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:2921–2927. doi:10.1128/AAC.49.7.2921-2927.2005
Acknowledgments
This study was entirely supported by Fondazione per la Ricerca sulla Fibrosi Cistica-Onlus, Verona, Italy (FFC Projects 11#2012 and 14#2014). CF strains have been generously provided by Ersilia Fiscarelli (IRCCS Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Gesù, Rome, Italy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All the procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Animal Care Committee of ‘‘G. d’Annunzio’’ University of Chieti-Pescara, and were carried out according to the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institute of Health. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: J. D. Wade.
M. Mardirossian and A. Pompilio equally contributed to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mardirossian, M., Pompilio, A., Crocetta, V. et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of BMAP-derived peptides for the treatment of cystic fibrosis-related pulmonary infections. Amino Acids 48, 2253–2260 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2266-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2266-4