Abstract
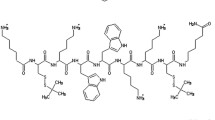
Taking a minimalistic approach in efforts to lower the cost for the development of new synthetic antimicrobial peptides, ultrashort cationic lipopeptides were designed to mimic the amphiphilic nature crucial for their activity but with only a very short peptide sequence ligated to a lipidic acid. Nine ultrashort cationic lipopeptides were prepared to study the effects of ring constraint in the amino acid side chain of the peptide component. USCL-PCat1, consisting of only four l-4R-aminoproline residues and acylated with palmitic acid at the N-terminus, was found to populate a polyproline II helical secondary conformation that is stable to different pHs and temperatures using circular dichroism. The synthesized lipopeptides were found to have a micellar structure in water using negative staining transmission electron microscopy. We found that constraining the side chain of the amino acid component is not beneficial to the antimicrobial activity. USCL-Dab1, USCL-Dab3 and USCL-K1 showed promising activity against a panel of laboratory reference and clinically isolated Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains, some of which are multidrug resistant. No appreciable cytotoxicity against human monocytic THP-1 cells was observed up to concentrations of 20–40 µM for all synthesized compounds. Moreover, all USCLs did not induce the production of either pro-inflammatory cytokines or chemokines up to 40 µM.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adzhubei AA, Sternberg MJ (1993) Left handed polyproline II helices commonly occur in globular proteins. J Mol Biol 229:472–493
Adzhubei AA, Stemberg MJE, Makarov AA (2013) Polyproline-II helix in proteins: structure and function. J Mol Biol 425:2100–2132
Ahn M, Murugan RN, Jacob B, Hyun J-K, Cheong C, Hwang E, Park H-N, Seo J-H, Srinivasrao G, Lee KS, Shin SY, Bang JK (2013) Discovery of novel histidine-derived lipo-amino acids: applied in the synthesis of ultra-short antimicrobial peptidomimetics having potent antimicrobial activity, salt resistance and protease stability. Eur J Med Chem 68:10–18
Chan WC, White PD (2000) Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis: a practical approach, 1st edn. Oxford University Press Inc., New York
Choe J (2012) Fewer drugs, more superbugs: strategies to reverse the problem. APUA Clin Newsl 30:16–19
Choi K-Y, Chow LNY, Mookherjee N (2012) Cationic host defence peptides: multifaceted role in immune modulation and inflammation. J Innate Immun 4:361–370
Eisenstein B, Hermsen ED (2012) Resistant infections: a tragic irony in modern medicine. APUA Clin Newsl 30:11–12
Eker F, Griebenow K, Cao X, Nafie LA, Schweitzer-Stenner R (2004) Tripeptides with ionizable side chains adopt a perturbed polyproline II structure in water. Biochemistry 43:613–621
Findlay B, Zhanel GG, Schweizer F (2010) Cationic amphiphiles, a new generation of antimicrobials inspired by the natural antimicrobial peptide scaffold. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:4049–4058
Findlay B, Zhanel GG, Schweizer F (2012a) Investigating the antimicrobial peptide ‘window of activity’ using cationic lipopeptides with hydrocarbons and fluorinated tails. Int J Antimicrob Agents 40:36–42
Findlay B, Szelemej Zhanel GG, Schweizer F (2012b) Guanidylation and tail effects in cationic antimicrobial lipopeptoids. PLoS One 7:e41141
Findlay B, Mookherjee N, Schweizer F (2013) Ultrashort cationic lipopeptides and lipopeptoids selective induce cytokine production in macrophages. PLoS One 8:e54280
Hancock RE, Scott MG (2000) The role of antimicrobial peptides in animal defenses. PNAS 97:8856–8861
Haney EF, Hunter HN, Matsuzaki K, Vogel HJ (2009) Solution NMR studies of amphibian antimicrobial peptides: linking structure to function? Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:1639–1655
Jabes D (2011) The antibiotic R&D pipeline: an update. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:564–569
Kang S-J, Kim D-H, Mishig-Ochir T, Lee B-J (2012) Antimicrobial peptides: their physicochemical properties and therapeutic application. Arch Pharm Res 35:409–413
Laverty G, McLaughlin M, Shaw C, Gorman SP, Gilmore BF (2010) Antimicrobial activity of short, synthetic cationic lipopeptides. Chem Biol Drug Des 75:563–569
Makovitzki A, Avrahami D, Shai Y (2006) Ultrashort antibacterial and antifungal lipopeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15997–16002
Makovitzki A, Baram J, Shai Y (2008) Antimicrobial lipopolypeptides composed of palmitoyl di- and tricationic peptides: in vitro and in vivo activities, self-assembly to nanostructures, and a plausible mode of action. Biochemistry 47:10630–10636
Mikhonin AV, Myshakina NS, Bykov SV, Asher SA (2005) UV resonance raman determination of polyproline II, extended 2.51-helix, and β-sheet Ψ angle energy landscape in poly-l-lysine and poly-l-glutamic acid. J Am Chem Soc 127:7712–7720
Mookherjee N, Hancock RE (2007) Cationic host defence peptides: innate immune regulatory peptides as a novel approach for treating infections. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:922–933
Mookherjee N, Brown KL, Bowdish DM, Doria S, Falsafi R, Hokamp K, Roche FM, Mu R, Doho GH, Pistolic J, Powers JP, Bryan J, Brinkman FS, Hancock RE (2006) Modulation of the TLR-mediated inflammatory response by the endogenous human host defense peptide LL-37. J Immunol 176:2455–2464
Mookherjee N, Rehaume LM, Hancock RE (2007) Cathelicidins and functional analogues as antisepsis molecules. Expert Opin Ther Targets 8:993–1004
Nguyen LT, Haney EF, Vogel HJ (2011) The expanding scope of antimicrobial peptide structures and their modes of action. Trends Biotechnol 29:464–472
Owens NW, Stetefeld J, Lattová E, Schweizer F (2010) Contiguous O-galactosylation of 4R-hydroxy-l-proline residues forms very stable polyproline II helices. J Am Chem Soc 132:5036–5042
Ronish EW, Krimm S (1974) The calculated circular dichroism of polyproline II in the polarizability approximation. Biopolymers 13:1563–1571
Schneider T, Muller A, Miess H, Gross H (2013) Cyclic lipopeptides as antibacterial agents—potent antibiotic activity mediated by intriguing mode of actions. Int J Med Microbiol 304:37–43
Scott MG, Dullaghan E, Mookherjee N, Glavas N, Waldbrook M, Thompson A, Wang A, Lee K, Doria S, Hamill P, Yu JJ, Li Y, Donini O, Guarna MM, Finlay BB, North JR, Hancock RE (2007) An anti-infective peptide that selectively modulates the innate immune response. Nat Biotechnol 25:465–472
Serrano GN, Zhanel GG, Schweizer F (2009) Antibacterial activity of ultrashort cationic lipo-β-peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:2215–2217
Stanton TB (2013) A call for antibiotic alternatives research. Trends Microbiol 21:111–113
Steinstraesser L, Kraneburg U, Jacobsen F, Al-Benna S (2011) Host defense peptides and their antimicrobial-immunomodulatory duality. Immunobiology 216:322–333
Svenson J, Brandsdal BO, Stensen W, Svendsen JS (2007) Albumin binding of short cationic antimicrobial micropeptides and its influence on the in vitro bactericidal effect. J Med Chem 50:3334–3339
Thaker HD, Som A, Ayaz F, Lui D, Pan W, Scott RW, Anguita J, Tew GN (2012) Synthetic mimics of antimicrobial peptides with immunomodulatory responses. J Am Chem Soc 134:11088–11091
Tiffany ML, Krimm S (1968a) New chain conformations of poly(glutamic acid) and polylysine. Biopolymers 6:1379–1382
Tiffany ML, Krimm S (1968b) Circular dichroism of poly-l-proline in an unordered conformation. Biopolymers 6:1767–1770
Turner-Brannen E, Choi KY, Lippert DN, Cortens JP, Hancock RE, El-Gabalawy H, Mookherjee N (2011) Modulation of interleukin-1β-induced inflammatory responses by a synthetic cationic innate defence regulator peptide, IDR-1002, in synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R129
Wayne PA, Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2006) Protocols for evaluating dehydrated Mueller–Hinton agar; approved standard. 2nd edn. Document M6-A2
Yeung ATY, Gellatly SL, Hancock RE (2011) Multifunctional cationic host defence peptides and their clinical applications. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:2161–2176
Yoneyama H, Katsumata R (2006) Antibiotic resistance in bacteria and its future for novel antibiotic development. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:1060–1075
Zasloff M (1987) Magainins, a class of antimicrobial peptides from Xenopus skin—isolation, characterization of 2 active forms, and partial cDNA sequence of a precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5449–5453
Zhanel GG, Adam HJ, Baxter MR, Fuller J, Nichol KA, Denisuik AJ, Lagace-Wiens PRS, Walkty A, Karlowsky JA, Schweizer F, Hoban DJ, on behalf of the Canadian Antimicrobial Resistance Alliance (CARA) (2013) Antimicrobial susceptibility of 22746 pathogens from Canadian hospitals: results of the CANWARD 2007–2011 study. J Antimicrob Chemother 68(Suppl 1):i7–i22
Zhanel GG, DeCorby M, Adam H, Mulvey MR, McCracken M, Lagace-Wiens P, Nichol KA, Wierzbowski A, Baudry PJ, Tailor F, Karlowsky JA, Walkty A, Schweizer F, Johnson J, The Canadian Antimicrobial Resistance Alliance (CARA), Hoban DJ (2010) Prevalence of antimicrobial resistant pathogens in Canadian hospitals: results of the Canadian ward surveillance study (CANWARD 2008). Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:4684–4693
Zhanel GG, DeCorby M, Laing N, Weshnoweski B, Vashisht R, Tailor F, Nichol KA, Wierzbowski A, Baudry PJ, Karlowsky JA, Lagace-Wiens P, Walkty A, McCracken M, Mulvey MR, Johnson J, The Canadian Antimicrobial Resistance Alliance (CARA), Hoban DJ (2008) Antimicrobial resistant pathogens in intensive care units across Canada: results of the Canadian National Intensive Care Unit (CAN-ICU) Study, 2005/2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:1430–1437
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and the Manitoba Health Research Council (MHRC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domalaon, R., Yang, X., O’Neil, J. et al. Structure–activity relationships in ultrashort cationic lipopeptides: the effects of amino acid ring constraint on antibacterial activity. Amino Acids 46, 2517–2530 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1806-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1806-z