Abstract
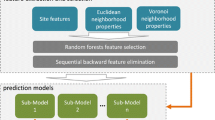
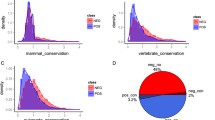
Reversible protein phosphorylation is one of the most important post-translational modifications, which regulates various biological cellular processes. Identification of the kinase-specific phosphorylation sites is helpful for understanding the phosphorylation mechanism and regulation processes. Although a number of computational approaches have been developed, currently few studies are concerned about hierarchical structures of kinases, and most of the existing tools use only local sequence information to construct predictive models. In this work, we conduct a systematic and hierarchy-specific investigation of protein phosphorylation site prediction in which protein kinases are clustered into hierarchical structures with four levels including kinase, subfamily, family and group. To enhance phosphorylation site prediction at all hierarchical levels, functional information of proteins, including gene ontology (GO) and protein–protein interaction (PPI), is adopted in addition to primary sequence to construct prediction models based on random forest. Analysis of selected GO and PPI features shows that functional information is critical in determining protein phosphorylation sites for every hierarchical level. Furthermore, the prediction results of Phospho.ELM and additional testing dataset demonstrate that the proposed method remarkably outperforms existing phosphorylation prediction methods at all hierarchical levels. The proposed method is freely available at http://bioinformatics.ustc.edu.cn/phos_pred/.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aponte AM, Phillips D, Harris RA, Blinova K, French S, Johnson DT, Balaban RS (2009) <sup> 32 </sup> P labeling of protein phosphorylation and metabolite association in the mitochondria matrix. Methods Enzymol 457:63–80
Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, Rush J, Gygi SP (2006) A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization. Nat Biotechnol 24(10):1285–1292
Blom N, Gammeltoft S, Brunak S (1999) Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J Mol Biol 294(5):1351–1362
Blom N, Sicheritz-Pontén T, Gupta R, Gammeltoft S, Brunak S (2004) Prediction of post-translational glycosylation and phosphorylation of proteins from the amino acid sequence. Proteomics 4(6):1633–1649
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32
Dinkel H, Chica C, Via A, Gould CM, Jensen LJ, Gibson TJ, Diella F (2011) Phospho. ELM: a database of phosphorylation sites—update 2011. Nucleic Acids Res 39 (suppl 1):D261–D267
Dondoshansky I, Wolf Y (2002) Blastclust (NCBI Software Development Toolkit). NCBI, Bethesda
Fang B, Haura EB, Smalley KS, Eschrich SA, Koomen JM (2010) Methods for investigation of targeted kinase inhibitor therapy using chemical proteomics and phosphorylation profiling. Biochem Pharmacol 80(5):739–747
Gao J, Thelen JJ, Dunker AK, Xu D (2010) Musite, a tool for global prediction of general and kinase-specific phosphorylation sites. Mol Cell Proteomics 9(12):2586–2600
Gastwirth JL (1972) The estimation of the Lorenz curve and Gini index. Review Econ Stat 54(3):306–316
Harris M, Clark J, Ireland A, Lomax J, Ashburner M, Foulger R, Eilbeck K, Lewis S, Marshall B, Mungall C (2004) The Gene Ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Research 32 (Database issue):D258–2D61
Huang Y, Niu B, Gao Y, Fu L, Li W (2010) CD-HIT suite: a web server for clustering and comparing biological sequences. Bioinformatics 26(5):680–682
Jung H-J, Kim Y-J, Eggert S, Chung KC, Choi KS, Park SA (2013) Age-dependent increases in tau phosphorylation in the brains of type 2 diabetic rats correlate with a reduced expression of p62. Exp Neurol 248:441–450
Lagranha CJ, Deschamps A, Aponte A, Steenbergen C, Murphy E (2010) Sex differences in the phosphorylation of mitochondrial proteins result in reduced production of reactive oxygen species and cardioprotection in females. Circ Res 106(11):1681–1691
Li T, Du P, Xu N (2010) Identifying human kinase-specific protein phosphorylation sites by integrating heterogeneous information from various sources. PLoS One 5(11):e15411
Lou Y, Yao J, Zereshki A, Dou Z, Ahmed K, Wang H, Hu J, Wang Y, Yao X (2004) NEK2A interacts with MAD1 and possibly functions as a novel integrator of the spindle checkpoint signaling. J Biol Chem 279(19):20049–20057
Ma L, Chen Z, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Pandolfi PP (2005) Phosphorylation and functional inactivation of TSC2 by Erk: implications for tuberous sclerosis and cancer pathogenesis. Cell 121(2):179–193
Maeshima Y, Fukatsu K, Kang W, Ueno C, Moriya T, Saitoh D, Mochizuki H (2007) Lack of enteral nutrition blunts extracellular-regulated kinase phosphorylation in gut-associated lymphoid tissue. Shock 27(3):320–325
Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S (2002) The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 298(5600):1912–1934
Newman RH, Hu J, Rho H-S, Xie Z, Woodard C, Neiswinger J, Cooper C, Shirley M, Clark HM, Hu S (2013) Construction of human activity-based phosphorylation networks. Mol Syst Biol 9(1):655. doi:10.1038/msb.2013.12
Pawson T (2004) Specificity in signal transduction: from phosphotyrosine-SH2 domain interactions to complex cellular systems. Cell 116(2):191–203
Peng H, Long F, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. Pattern Anal Mach Intell IEEE Trans 27(8):1226–1238
Peng C, Wang M, Shen Y, Feng H, Li A (2013) Reconstruction and analysis of transcription factor–miRNA co-regulatory feed-forward loops in human cancers using filter-wrapper feature selection. PLoS One 8(10). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078197
Schafmeier T, Haase A, Káldi K, Scholz J, Fuchs M, Brunner M (2005) Transcriptional feedback of neurospora circadian clock gene by phosphorylation-dependent inactivation of its transcription factor. Cell 122(2):235–246
Singh CR, Curtis C, Yamamoto Y, Hall NS, Kruse DS, He H, Hannig EM, Asano K (2005) Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5 is critical for integrity of the scanning preinitiation complex and accurate control of GCN4 translation. Mol Cell Biol 25(13):5480–5491
Teng S, Luo H, Wang L (2012) Predicting protein sumoylation sites from sequence features. Amino Acids 43(1):447–455
Trost B, Kusalik A (2013) Computational phosphorylation site prediction in plants using random forests and organism-specific instance weights. Bioinformatics 29(6):686–694
Von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt S, Bork P, Snel B (2003) STRING: a database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 31(1):258–261
Waddick KG, Chae HP, Tuel-Ahlgren L, Jarvis LJ, Dibirdik I, Myers DE, Uckun FM (1993) Engagement of the CD19 receptor on human B-lineage leukemia cells activates LCK tyrosine kinase and facilitates radiation-induced apoptosis. Radiat Res 136(3):313–319
Wang M, Chen X, Zhang M, Zhu W, Cho K, Zhang H (2009) Detecting significant single-nucleotide polymorphisms in a rheumatoid arthritis study using random forests. In: BMC proceedings. BioMed Central Ltd, p S69
Wang M, Chen X, Zhang H (2010) Maximal conditional Chi square importance in random forests. Bioinformatics 26(6):831–837
Wong Y-H, Lee T-Y, Liang H-K, Huang C-M, Wang T-Y, Yang Y-H, Chu C-H, Huang H-D, Ko M-T, Hwang J-K (2007) KinasePhos 2.0: a web server for identifying protein kinase-specific phosphorylation sites based on sequences and coupling patterns. Nucleic acids research 35 (suppl 2):W588–W594
Wood CD, Thornton TM, Sabio G, Davis RA, Rincon M (2009) Nuclear localization of p38 MAPK in response to DNA damage. Int J Biol Sci 5(5):428
Xue Y, Li A, Wang L, Feng H, Yao X (2006) PPSP: prediction of PK-specific phosphorylation site with Bayesian decision theory. BMC Bioinform 7(1):163
Xue Y, Ren J, Gao X, Jin C, Wen L, Yao X (2008) GPS 2.0, a tool to predict kinase-specific phosphorylation sites in hierarchy. Mol Cell Proteomics 7(9):1598–1608
Yang ZR (2009) Predicting sulfotyrosine sites using the random forest algorithm with significantly improved prediction accuracy. BMC Bioinform 10(1):361
Zhang H, Wang M, Chen X (2009) Willows: a memory efficient tree and forest construction package. BMC Bioinform 10(1):130
Zou L, Huang Q, Li A, Wang M (2012) A genome-wide association study of Alzheimer’s disease using random forests and enrichment analysis. Sci China Life Sci 55(7):618–625
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61101061, 31100955), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (WK2100230011).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, W., Xu, X., Shen, Y. et al. Prediction of protein kinase-specific phosphorylation sites in hierarchical structure using functional information and random forest. Amino Acids 46, 1069–1078 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1669-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1669-3