Abstract
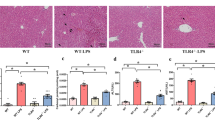
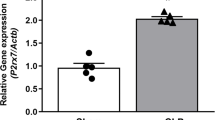
Acute sepsis can be induced by cytokines such as TNF-α and biological products such as LPS. All of these agents cause systemic inflammation, which is characterized by hemodynamic shock and liver toxicity. However, the outcomes of different septic shock models were totally opposite in transglutaminase 2 knockout (TGase 2−/−) mice. The aim of our study was to clarify the role of TGase 2 in liver injury. Therefore, we explored the role of TGase 2 in liver damage using two different stress models: LPS-induced endotoxic shock and TNF-α/actinomycin D (ActD)-induced sepsis. TNF-α-dependent septic shock resulted in increased liver damage in TGase 2−/− mice compared with wild-type (WT) mice, and was accompanied by increased levels of caspase 3 and cathepsin D (CTSD) in the damaged liver. Conversely, LPS-induced septic shock resulted in ablation of inflammatory endotoxic shock in TGase 2−/− mice and decreased liver injury. We found that TGase 2 protected liver tissue from TNF-α-dependent septic shock by reducing the expression of caspase 3 and CTSD. However, TGase 2 differently participated in increased the hemodynamic shock in LPS-induced septic shock through macrophage activation rather than protecting direct liver damage. Therefore, these findings demonstrate that septic shock caused by different agents may induce different results in TGase 2−/− mice depending on the primary target organs affected.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beninati S, Piacentini M (2004) The transglutaminase family: an overview (minireview article). Amino Acids 26:367–372
D’Eletto M, Farrace MG, Falasca L, Reali V, Oliverio S, Melino G et al (2009) Transglutaminase 2 is involved in autophagosome maturation. Autophagy 5:1145–1154
De Laurenzi V, Melino G (2001) Gene disruption of tissue transglutaminase. Mol Cell Biol 21:148–155
Delhase M, Kim SY, Lee H, Naiki-Ito A, Chen Y, Ahn ER et al (2012) TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) controls cell survival through PAI-2/serpinB2 and transglutaminase 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:E177–E186
Falasca L, Iadevaia V, Ciccosanti F, Melino G, Serafino A, Piacentini M (2005) Transglutaminase type II is a key element in the regulation of the anti-inflammatory response elicited by apoptotic cell engulfment. J Immunol 174:7330–7340
Falasca L, Farrace MG, Rinaldi A, Tuosto L, Melino G, Piacentini M (2008) Transglutaminase type II is involved in the pathogenesis of endotoxic shock. J Immunol 180:2616–2624
Folk JE (1983) Mechanism and basis for specificity of transglutaminase-catalyzed epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl) lysine bond formation. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 54:1–56
Jang GY, Jeon JH, Cho SY, Shin DM, Kim CW, Jeong EM et al (2010) Transglutaminase 2 suppresses apoptosis by modulating caspase 3 and NF-kappaB activity in hypoxic tumor cells. Oncogene 29:356–367
Kim SY (2004) New target against inflammatory diseases: transglutaminase 2. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 52:332–337
Kim SY (2011) Transglutaminase 2: a new paradigm for NF-kappaB involvement in disease. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 78:161–195
Kim DS, Kim B, Tahk H, Kim DH, Ahn ER, Choi C et al (2010) Transglutaminase 2 gene ablation protects against renal ischemic injury by blocking constant NF-kappaB activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 403:479–484
Kim SJ, Kim KH, Ahn ER, Yoo BC, Kim SY (2011) Depletion of cathepsin D by transglutaminase 2 through protein cross-linking promotes cell survival. Amino Acids [Epub ahead of print]
Kuncio GS, Tsyganskaya M, Zhu J, Liu SL, Nagy L, Thomazy V et al (1998) TNF-alpha modulates expression of the tissue transglutaminase gene in liver cells. Am J Physiol 274:G240–G245
Lee J, Kim YS, Choi DH, Bang MS, Han TR, Joh TH et al (2004) Transglutaminase 2 induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation via a novel pathway in BV-2 microglia. J Biol Chem 279:53725–53735
Mirza A, Liu SL, Frizell E, Zhu J, Maddukuri S, Martinez J et al (1997) A role for tissue transglutaminase in hepatic injury and fibrogenesis, and its regulation by NF-kappaB. Am J Physiol 272:G281–G288
Muto Y, Nouri-Aria KT, Meager A, Alexander GJ, Eddleston AL, Williams R (1988) Enhanced tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in fulminant hepatic failure. Lancet 2:72–74
Nanda N, Iismaa SE, Owens WA, Husain A, Mackay F, Graham RM (2001) Targeted inactivation of Gh/tissue transglutaminase II. J Biol Chem 276:20673–20678
Nardacci R, Lo Iacono O, Ciccosanti F, Falasca L, Addesso M, Amendola A et al (2003) Transglutaminase type II plays a protective role in hepatic injury. Am J Pathol 162:1293–1303
Oh K, Park HB, Byoun OJ, Shin DM, Jeong EM, Kim YW et al (2011) Epithelial transglutaminase 2 is needed for T cell interleukin-17 production and subsequent pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in bleomycin-treated mice. J Exp Med 208:1707–1719
Park SS, Kim JM, Kim DS, Kim IH, Kim SY (2006) Transglutaminase 2 mediates polymer formation of I-kappaBalpha through C-terminal glutamine cluster. J Biol Chem 281:34965–34972
Park KS, Kim DS, Ko C, Lee SJ, Oh SH, Kim SY (2011) TNF-alpha mediated NF-kappaB activation is constantly extended by transglutaminase 2. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 3:341–354
Sarang Z, Molnar P, Nemeth T, Gomba S, Kardon T, Melino G et al (2005) Tissue transglutaminase (TG2) acting as G protein protects hepatocytes against Fas-mediated cell death in mice. Hepatology 42:578–587
Tacke F, Luedde T, Trautwein C (2009) Inflammatory pathways in liver homeostasis and liver injury. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 36:4–12
Tatsukawa H, Fukaya Y, Frampton G, Martinez-Fuentes A, Suzuki K, Kuo TF et al (2009) Role of transglutaminase 2 in liver injury via cross-linking and silencing of transcription factor Sp1. Gastroenterology 136(1783–1795):e1710
Vereyken EJ, Heijnen PD, Baron W, de Vries EH, Dijkstra CD, Teunissen CE (2011) Classically and alternatively activated bone marrow derived macrophages differ in cytoskeletal functions and migration towards specific CNS cell types. J Neuroinflammation 8:58
Yamaguchi H, Wang HG (2006) Tissue transglutaminase serves as an inhibitor of apoptosis by cross-linking caspase 3 in thapsigargin-treated cells. Mol Cell Biol 26:569–579
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a research grant (NCC1110011-2) from the National Cancer Center of Korea and by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 20110027248).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Yoo and E.-R. Ahn contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, H., Ahn, ER., Kim, SJ. et al. Divergent results induced by different types of septic shock in transglutaminase 2 knockout mice. Amino Acids 44, 189–197 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1412-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1412-x