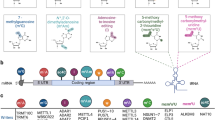
Abstract
Translational control is a crucial component in the development and progression of different diseases. Translational control may involve selective translation of specific mRNAs, which promote cell proliferation or lead to alterations in translation factor levels and activities. Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) is the only known protein to contain the unusual amino acid hypusine [N ε- (4-amino-2-hydroxybutyl)-lysine], which is formed from the polyamine spermidine by two catalytic steps. eIF5A is involved in translation, elongation and stimulating peptide bond formation. Hypusination of eIF5A is essential for its activity in promoting cell proliferation. Meanwhile, there is evidence that eIF5A is a key protein in the pathogenicity of different diseases, such as diabetes, several human cancers, malaria and HIV-1 infections. Hitherto, the available data suggest that eIF5A has a role of a cell context-dependent function being more proliferative in the case of several human cancers and being involved under stress conditions in diabetes. Secondly, in HIV-1 infections and in diabetes, eIF5A also has a nuclear function by its sequence-specific binding of mRNAs as an mRNA-shuttle in conjunction with nuclear membrane export proteins. This binding may also influence the half-lives of mRNAs or their sequestration. Based on these data, there is a considerable therapeutic interest in eIF5A as a selective target for drug development through inhibition of hypusination.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2D-electophoresis:
-
Two dimensional electrophoresis
- MALDI-TOF:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight
- iNos:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon gamma
- GTP:
-
Guanosine triphosphate
- GDP:
-
Guanosine diphosphate
- PKR:
-
Protein kinase R
- PERK:
-
Proline-rich extensin-like receptor protein kinase
- GCN2:
-
General control nonrepressed 2 serine/threonine-protein kinase
- Th1-type-cells:
-
T-helper cells signal 1
- Th2-type-cells:
-
T-helper cells signal 2
References
Alonso PL, Brown G, Arevalo-Herrera M, Binka F, Chitnis C, Collins F, Doumbo OK, Greenwood B, Hall BF, Levine MM, Mendis K, Newman RD, Plowe CV, Rodríguez MH, Sinden R, Slutsker L, Tanner M (2011) A research agenda to underpin malaria eradication. PLoS Med 25:e1000406
Balabanov S, Gontarewicz A, Ziegler P, Hartmann U, Kammer W, Copland M, Brassat U, Priemer M, Hauber I, Wilhelm T, Schwarz G, Kanz L, Bokemeyer C, Hauber J, Holyoake TL, Nordheim A, Brümmendorf TH (2007) Hypusination of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF5A): a novel therapeutic target in BCR-ABL-positive leukemias identified by a proteomics approach. Blood 109(4):1701-1711
Baum J, Papenfuss AT, Mair GR, Janse CJ, Vlachou D, Waters AP, Cowman AF, Crabb CJ, Koning-Ward TF (2010) Molecular genetics and comparative genomics reveal RNAi is not functional in malaria parasites. Nucleic Acids Res 37:3788–3798
Bevec D, Jaksche H, Oft M, Wöhl T, Himmelspach M, Pacher A, Schebesta M, Koettnitz K, Dobrovnik M, Csonga R, Lottspeich F, Hauber J (1996) Inhibition of HIV-1 replication in lymphocytes by mutants of the Rev cofactor eIF-5A. Science 271:1858–1860
Blavid R, Kusch P, Hauber J, Eschweiler U, Sarite SR, Specht S, Deininger S, Hoerauf A, Kaiser A (2010) Down-regulation of hypusine biosynthesis in Plasmodium by inhibition of S-adenosyl-methionine-decarboxylase. Amino Acids 38:461–469
Cracchiolo BM, Heller DS, Clement PM, Wolff EC, Park MH, Hanauske-Abel HM (2004) Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A–1 (eIF5A–1) as a diagnostic marker for aberrant proliferation in intraepithelial neoplasia of the vulva. Gynecol Oncol 94:217–222
Dasaradhi PV, Mohammed A, Kumar A, Hossain MJ, Bhatnagar RK, Chauhan VS, Malhotra P (2005) A role of falcipain-2, principle cysteine proteases of Plasmodium falciparum in merozoite egression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336:1062–1068
Dybul M, Fauci AS, Bartlett JG, Kaplan JE, Pau AK (2002) Guidelines for using antiretroviral agents among HIV-infected adults and adolescents. Ann Intern Med 137:381–433
Evans-Molina C, Robbins RD, Kono T, Tersey SA, Vestermark GL, Nunemaker CS, Garmey JC, Deering TG, Keller SR, Maier B, Mirmira RG (2009) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activation restores islet function in diabetic mice through reduction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and maintenance of euchromatin structure. Mol Cell Biol 29:2053–2067
Gissot M, Brique S, Refour P, Boschet C, Vaquero C (2005) PfMyb1, a Plasmodium falciparum transcription factor, is required for intra-erythrocytic growth and controls key genes for cell cycle regulation. J Mol Biol 34:29–42
Gregio AP, Cano VP, Avaca JS, Valentini SR, Zanelli CF (2009) EIF-5A has a function in the elongation step of translation in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 380:785–790
Hanauske-Abel HM, Slowinska B, Zagulska S, Wilson RC, Staiano-Coico L, Hanauske AR, McCaffrey T, Szabo P (1995) Detection of a sub-set of polysomal mRNAs associated with modulation of hypusine formation at the G1-S boundary. Proposal of a role for eIF-5A in onset of DNA replication. FEBS Lett 366:92–98
Hauber J (2010) Revisiting an old acquaintance: role for eIF5A in diabetes. J Clin Invest 120:1806–1868
Hauber I, Bevec D, Heukeshoven J, Krätzer F, Horn F, Choidas A, Harrer T, Hauber J (2005) Identification of cellular deoxyhypusine synthase as a novel target for antiretroviral therapy. J Clin Invest 115:76–85
Hofmann W, Reichart B, Ewald A, Müller E, Schmitt I, Stauber RH, Lottspeich F, Jockusch BM, Scheer U, Hauber J, Dabauvalle MC (2001) Cofactor requirements for nuclear export of Rev response element (RRE)- and constitutive transport element (CTE)-containing retroviral RNAs. An unexpected role for actin. J Cell Biol 152:895–910
Igarashi K, Kashiwagi K (2010) Modulation of cellular function by polyamines. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:39–51
Kaiser A (2009) Targeting malaria polyamines: enzymes of the hypusine pathway are novel drug targets in the prevention and therapy of malaria. In: Dendrifosse G (ed) Biological aspects of biogenic amines, polyamines and conjugates. Research Signpost, pp 421–439
Kaiser A, Hammels I, Gottwald A, Nassar M, Zaghloul MS, Motaal BA, Hauber J, Hoerauf A (2007) Modification of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A from Plasmodium vivax by a truncated deoxyhypusine synthase from Plasmodium falciparum : An enzyme with dual enzymatic properties. Bioorg Med Chem 15:6200–6207
Kemper WM, Berry KW, Merrick WC (1976) Purification and properties of rabbit reticulocyte protein synthesis initiation factors M2Balpha and M2Bbeta. J Biol Chem 251:5551–5557
Kumar R, Adams B, Oldenburg A, Musiyenko A, Barik S (2002) Characterisation and expression of a PP1 serine/threonine protein phosphatase (PfPP1) from the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum: demonstration of its essential role using RNA interference. Malar J 145:1245–1254
Lam F, Jankova L, Dent OF, Molloy MP, Kwun SY, Clarke C, Chapuis P, Robertson G, Beale P, Clarke S, Bokey EL, Chan C (2010) Identification of distinctive protein expression patterns in colorectal adenoma. Proteomics Clin Appl 4:60–70
Lee NP, Tsang FH, Shek FH, Mao M, Dai H, Zhang C, Dong S, Guan XY, Poon RT, Luk JM (2010) Prognostic significance and therapeutic potential of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 15:968–976
Maier B, Ogihara T, Trace AP, Tersey SA, Robbins RD, Chakrabarti SK, Nunemaker CS, Stull ND, Taylor CA, Thompson JE, Dondero RS, Lewis EC, Dinarello CA, Nadler JL, Mirmira RG (2010a) The unique hypusine modification of eIF5A promotes islet beta cell inflammation and dysfunction in mice. J Clin Invest 120:2156–2170
Maier B, Tersey SA, Mirmira RG (2010b) Hypusine: a new target for therapeutic intervention in diabetic inflammation. Discov Med. 10(50):18–23
Mathis D, Vence L, Benoist C (2001) Beta-Cell death during progression to diabetes. Nature 13:792–798
McRobert L, McConkey (2002) RNA interference (RNAi) inhibits growth of P. falciparum. Mol Chem Parasitol 119:273–278
Molitor IM, Knöbel S, Dang C, Spielmann T, Alléra A, König GM (2004) Translation initiation factor eIF-5A from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol 137:65–74
Palella FJ Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, Aschman DJ, Holmberg SD (1998) Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 338:853–860
Park MH, Nishimura K, Zanelli CF, Valentini SR (2010) Functional significance of eIF5A and its hypusine modification in eukaryotes. Amino Acids 238:491–500
Pollard VW, Malim MH (1998) The HIV-1 Rev protein. Annu Rev Microbiol 52:491–532
Saini P, Eyler DE, Green R, Dever TE (2009) Hypusine-containing protein eIF-5A promotes translation elongation. Nature 459:118–121
Silvera D, Formenti SC, Schneider RJ (2010) Translational control in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10:254–266
Tuteja R, Pradhan A, Sharma S (2008) Plasmodium falciparum signal peptidase is regulated by phosphorylation and required for intra-erythrocytic growth. Mol Biochem Parasitol 157:137–147
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes:estimates for the year 2010 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27:1047–1053
Wolff EC, Kang KR, Kim YS, Park MH (2007) Posttranslational synthesis of hypusine: evolutionary progression and specificity of the hypusine modification. Amino Acids 33:341–350
Zanelli CF, Valentini SR (2007) Is there a role for eIF5A in translation? Amino Acids 33:351–358
Zanelli CF, Maragno AL, Gregio AP, Komili S, Pandolfi JR, Mestriner CA, Lustri WR, Valentini SR (2006) eIF5A binds to translational machinery components and affects translation in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348:1358–1366
Zender L, Xue W, Zuber J, Semighini CP, Krasnitz A, Ma B, Zender P, Kubicka S, Luk JM, Schirmacher P, McCombie WR, Wigler M, Hicks J, Hannon GJ, Powers S, Lowe SW (2008) An oncogenomics-based in vivo RNAi screen identifies tumor suppressors in liver cancer. Cell 135:852–864