Abstract
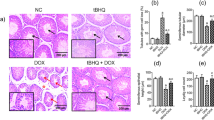
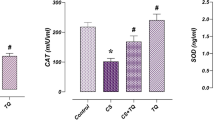
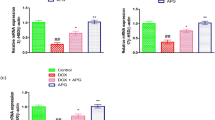
The protective effect of taurine against doxorubicin-induced testicular oxidative stress and apoptosis was investigated in rats. Male rats 8 weeks of age were treated with doxorubicin alone (3 mg/kg, i.p. every other day for 3 doses), taurine alone (150 mg/kg, i.p. every other day for 3 doses) or taurine plus doxorubicin (each dose given 1 day post-taurine). After 28 days, rat testes were collected and analysed. Rats treated with doxorubicin alone displayed reduced body and testicular weights, decreased sperm counts, increased the extent of testicular toxicity (as evident from the decreased activity of testicular marker enzyme, SDH) and oxidative stress (reduced GSH, increased GSSG and MDA levels), decreased antioxidant (SOD, CAT, GST, GPx, GR) and membrane-bound (Na+–K+ and Ca2+ ATPases) enzyme activities as well as plasma testosterone. Reverse transcriptase-PCR analysis revealed that doxorubicin induced a marked decrease in the expression of key enzymes for testicular androgenesis (3β-HSD, 17β-HSD) and testicular steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein. Western blot analysis showed that doxorubicin administration markedly increased the levels of caspase-9, 3, -8, -12, Fas, Bid and disturbed the Bcl-2 family protein balance. These results suggest that doxorubicin can trigger intrinsic, extrinsic and endoplasmic reticulum-associated apoptotic pathways in testicular pathophysiology. Doxorubicin also triggered activation of JNK, p38MAP kinases and p53. However, taurine could effectively prevent nearly all of these doxorubicin-induced testicular abnormalities, thereby proving to be an effective cytoprotectant.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- DOX:
-
Doxorubicin
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSSG:
-
Glutathione disulfide
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- G6PD:
-
Glutathione 6 peroxidase
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- 3β-HSD:
-
3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
- 17β-HSD:
-
17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
- MDA:
-
Malonaldehyde
- MAPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SDH:
-
Sorbitol dehydrogenase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- StAR protein:
-
Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein
- TAU:
-
Taurine
References
Alvarez JG, Storey BT (1983) Taurine, hypotaurine, epinephrine and albumin inhibit lipid peroxidation in rabbit spermatozoa and protect against loss of motility. Biol Reprod 29:548–555
Arola OJ, Saraste A, Pulkki K, Kallajoki M, Parvinen M, Voipio-Pulkki LM (2000) Acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity involves cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Cancer Res 60:1789–1792
Aruoma OI, Halliwell B, Hoey BM, Butler J (1988) The antioxidant action of taurine, hypotaurine and their metabolic precursors. Biochem J 256:251–255
Atessahin A, Turk G, Karahan I, Yolmaz S, Ceribasi AO, Bulmus O (2006) Lycopene prevents adriamycin-induced testicular toxicity in rats. Fertil Steril 85:1216–1222
Au WW, Hsu TC (1980) The genotoxic effects of adriamycin in somatic and germinal cells of the mouse. Mutat Res 79:351–361
Beere HM, Wold BB, Caines K, Mosser DD, Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, Morimoto RI, Cohen GM, Green DR (2000) Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol 2:469–475
Bergmeyer HU (1974) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp 744–761
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cozzi R, Ricordy R, Bartolini F et al (1995) Taurine and ellagic acid: two differently-acting natural antioxidants. Environ Mol Mutagen 26:248–254
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sil PC (2008) Taurine provides antioxidant defense against NaF-induced cytotoxicity in murine hepatocytes. Pathophysiology 15:181–190
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2009a) Taurine protects rat testes against NaAsO(2)-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via mitochondrial dependent and independent pathways. Toxicol Lett 187:201–210
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2009b) Arsenic-induced oxidative cerebral disorders: protection by taurine. Drug Chem Toxicol 32:93–102
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sil PC (2010a) Protective role of taurine against arsenic-induced mitochondria-dependent hepatic apoptosis via the inhibition of PKCd-JNK pathway. PLoS ONE 5:e12602
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sil PC (2010b) Acetaminophen induced acute liver failure via oxidative stress and JNK activation: protective role of taurine by the suppression of cytochrome P450 2E1. Free Radic Res 44:340–355
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sil PC (2010c) Taurine protects acetaminophen-induced oxidative damage in mice kidney through APAP urinary excretion and CYP2E1 inactivation. Toxicology 269:24–34
Das J, Ghosh J, Manna P, Sil PC (2011) Taurine suppresses doxorubicin-triggered oxidative stress and cardiac apoptosis in rat via up-regulation of PI3-K/Akt and inhibition of p53, p38-JNK. Biochem Pharmacol (in press). doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2011.01.008
Ferreira MPLVO, Nunes MV, Mendes E, Remiilo F, Ferreirat IMA (1997) Development of an HPLC-UV method for determination of taurine in infant formulae and breast milk. J Liq Chrom Rel Techno 20:1269–1278
Fraser LR (1986) Both taurine and albumin support mouse sperm motility and fertilizing ability in vitro but there is no obligatory requirement for taurine. J Reprod Fertil 77:271–280
Ghosh J, Das J, Manna P, Sil PC (2009) Taurine prevents arsenic-induced cardiac oxidative stress and apoptotic damage: role of NF-kappaB, p38 and JNK MAPK pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 240:73–87
Ghosh J, Das J, Manna P, Sil PC (2010) Hepatotoxicity of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate is attributed to calcium aggravation, ROS-mediated mitochondrial depolarization, and ERK/NF-κB pathway activation. Free Radic Biol Med 49:1779–1791
Goodman J, Hochstein P (1977) Generation of free radicals and lipid peroxidation by redox cycling of adriamycin and daunomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 77:797–803
Gordon RE, Heller RF (1992) Taurine protection of lungs in hamster models of oxidant injury: a morphologic time study of paraquat and bleomycin treatment. In: Lombardini JB, Schaffer SW, Azuma J (eds) Taurine: nutritional value and mechanisms of action. Plenum Press, New York, pp 319–323
Green DR (2000) Apoptotic pathways: paper wraps stone blunts scissors. Cell 102:1–4
Hayes J, Tipton KF, Bianchi L, Corte LD (2001) Complexities in the neurotoxic actions of 6-hydroxydopamine in relation to the cytoprotective properties of Taurine. Brain Res Bull 55:239–245
Herman EH, Ferrans VJ (1998) Animal models of anthracycline cardiotoxicity: basic mechanisms and cardioprotective activity. Prog Pediatr Cardiol 8:49–58
Holloway C, Kotsanas G, Wendt I (1999) Acute effects of taurine on intracellular calcium in normal and diabetic cardiac myocytes. Pflugers Arch 438:384–391
Huxtable RJ (1989) Taurine in the central nervous system and the mammalian actions of taurine. Prog Neurobiol 32:471–533
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev 72:101–163
Jahnukainen K, Jahnukainen T, Salmi TT, Svechnikov K, Eksborg S, Soder O (2001) Amifostine protects against early but not late toxic effects of doxorubicin in infant rats. Cancer Res 61:6423–6427
Jana K, Jana S, Samanta PK (2006) Effects of chronic exposure to sodium arsenite on hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular activities in adult rats: possible an estrogenic mode of action. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 4:9–22
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (1996) Sounding the alarm: protein kinase cascades activated by stress and inflammation. J Biol Chem 271:24313–24316
Lambert IH (2004) Regulation of the cellular content of the organic osmolyte taurine, in mammalian cells. Neurochem Res 29:27–63
Lamkanfi M, Kalai M, Vandenabeele P (2004) Caspase-12: an overview. Cell Death Differ 11:365–368
Llanos MN, Ronco AM (1994) Sperm phospholipid methyltransferase activity during preparation for exocytosis. Cell Biochem Funct 12:289–296
Lui RC, Laregina MC, Herbold DR, Johnson FE (1986) Testicular cytotoxicity of intravenous doxorubicin in rats. J Urol 136:940–943
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2008a) Amelioration of cadmium-induced cardiac impairment by taurine. Chem Biol Interact 174:88–97
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2008b) Taurine triggers a chemoprevention against cadmium induced testicular oxidative injury. Reprod Toxicol 26:282–291
Manna P, Sinha M, Sil PC (2009) Taurine plays a beneficial role against cadmium-induced oxidative renal dysfunction. Amino Acids 36:417–428
Meizel S, Lui CW, Working PK, Mrsny RJ (1980) Taurine and hypotaurine: their effects on motility, capacitation and the acrosome reaction of hamster sperm in vitro and their presence in sperm and reproductive tract fluids of several mammals. Dev Growth Differ 22:483–494
Mills NC, Means AR (1972) Sorbitol dehydrogenase of rat testis, changes of activity during development after hypophysectomy and following gonadotrophic hormone administration. Endocrinology 91:47–56
Mrsny RJ, Meizel S (1985) Inhibition of hamster sperm Na+, K+-ATPase activity by taurine and hypotaurine. Life Sci 36:271–275
Muller I, Niethammer D, Bruchelt G (1998) Anthracycline-derived chemotherapeutics in apoptosis and free radical cytotoxicity (review). Int J Mol Med 1:491–494
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid. Nature 403:98–103
Patil L, Balaraman R (2009) Effect of melatonin on doxorubicin induced testicular damage in rats. Int J Pharm Tech Res 1:879–884
Pollack M, Leeuwenburgh C (2001) Apoptosis and aging: role of the mitochondria. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 56:475–482
Poulsen KA, Litman T, Eriksen J, Mollerup J, Lambert IH (2002) Downregulation of taurine uptake in multidrug resistant Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Amino Acids 22:333–350
Prasad AK, Pant N, Srivastava SC, Kumar R, Srivastava SP (1995) Effect of dermal application of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) on male reproductive system of rat. Hum Exp Toxicol 14:484–488
Quinn R (2005) Comparing rat’s to human’s age: how old is my rat in people years? Nutrition 21:775–777
Redmond HP, Wang JH, Bouchier-Hayes D (1996) Taurine attenuates nitric oxide- and reactive oxygen intermediate-dependent hepatocyte injury. Arch Surg 131:1287–1288
Roy A, Manna P, Sil PC (2009) Prophylactic role of taurine on arsenic mediated oxidative renal dysfunction via MAPKs/NF-kappaB and mitochondria dependent pathways. Free Radic Res 43:995–1007
Sharpe RM, Maddocks S, Millar M, Saunders PTK, Kerr JB, McKinnell C (1992) Testosterone and spermatogenesis: identification of stage dependent, androgen-regulated proteins secreted by adult rat seminiferous tubules. J Androl 13:172–184
Shinoda K, Mitsumori K, Yasuhara K, Uneyama C, Onodera H, Hirose M, Uehara M (1999) Doxorubicin induces male germ cell apoptosis in rats. Arch Toxicol 73:274–281
Sikka SC (1996) Oxidative stress and role of antioxidants in normal and abnormal sperm function. Front Biosci 1:e78–e86
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2007) Taurine, a conditionally essential amino acid, ameliorates arsenic-induced cytotoxicity in murine hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 21:1419–1428
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2008a) Taurine protects antioxidant defense system in the erythrocytes of cadmium treated mice. BMB Rep 41:657–663
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2008b) Cadmium induced neurological disorders: prophylactic role of taurine. J Appl Toxicol 28:974–986
Sinha M, Manna P, Sil PC (2009) Induction of necrosis in cadmium-induced hepatic oxidative stress and its prevention by the prophylactic properties of taurine. J Trace Elem Med Biol 23:300–313
Stocco DM (2001) StAR protein and the regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol 63:193–213
Sun XM, MacFarlane M, Zhuang J, Wolf BB, Green DR, Cohen GM (1999) Distinct caspase cascades are initiated in receptor-mediated and chemical-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274:5053–5060
Tabassum H, Rehman H, Banerjee BD, Raisuddin S, Parvez S (2006) Attenuation of tamoxifen-induced hepatotoxicity by taurine in mice. Clin Chim Acta 370:129–136
Tastesen HS, Holm JB, Møller J, Poulsen KA, Møller C, Stürup S, Hoffmann EK, Lambert IH (2010) Pinpointing differences in cisplatin-induced apoptosis in adherent and non-adherent cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 26:809–820
Timbrell JA, Seabra V, Watereld CJ (1995) The in vivo and in vitro protective properties of taurine. Gen Pharmacol 26:453–462
Van Der Horst CJG, Grooten HJG (1966) The occurrence of hypotaurine and other sulfur containing amino acids in seminal plasma and spermatozoa of boar, bull and dog. Biochim Biophys Acta 117:495–497
Wright CE, Tallan HH, Lin YY (1986) Taurine: biological update. Annu Rev Biochem 55:427–453
Wyrobek AJ, Bruce WR (1975) Chemical induction of sperm abnormalities in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:4425–4429
Yeh YC, Lai HC, Ting CT, Lee WL, Wang LC, Wang KY, Lai HC, Liu TJ (2007) Protection by doxycycline against doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in mouse testes. Biochem Pharmacol 74:969–980
Yeh YC, Liu TJ, Wang LC, Lee HW, Ting CT, Lee WL, Hung CJ, Wang KY, Lai HC, Lai HC (2009) A standardized extract of Ginkgo biloba suppresses doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress and p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis in rat testes. Br J Pharmacol 156:48–61
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Mr. Prasanta Pal for excellent technical assistance for the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, J., Ghosh, J., Manna, P. et al. Taurine protects rat testes against doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress as well as p53, Fas and caspase 12-mediated apoptosis. Amino Acids 42, 1839–1855 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0904-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0904-4