Abstract
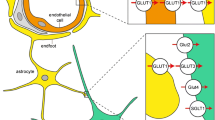
Glutathione (GSH) plays essential roles in different processes such as antioxidant defenses, cell signaling, cell proliferation, and apoptosis in the central nervous system. GSH is a tripeptide composed of glutamate, cysteine, and glycine. The concentration of cysteine in neurons is much lower than that of glutamate or glycine, so that cysteine is the rate-limiting substrate for neuronal GSH synthesis. Most neuronal cysteine uptake is mediated through the neuronal sodium-dependent glutamate transporter, known as excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1). Glutamate transporters are vulnerable to oxidative stress and EAAC1 dysfunction impairs neuronal GSH synthesis by reducing cysteine uptake. This may start a vicious circle leading to neurodegeneration. Intracellular signaling molecules functionally regulate EAAC1. Glutamate transporter-associated protein 3-18 (GTRAP3-18) activation down-regulates EAAC1 function. Here, we focused on the interaction between EAAC1 and GTRAP3-18 at the plasma membrane to investigate their effects on neuronal GSH synthesis. Increased level of GTRAP3-18 protein induced a decrease in GSH level and, thereby, increased the vulnerability to oxidative stress, while decreased level of GTRAP3-18 protein induced an increase in GSH level in vitro. We also confirmed these results in vivo. Our studies demonstrate that GTRAP3-18 regulates neuronal GSH level by controlling the EAAC1-mediated uptake of cysteine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiduki S, Ikemoto MJ (2008) Modulation of the neural glutamate transporter EAAC1 by the addicsin-interacting protein ARL6IP1. J Biol Chem 283:31323–31332
Ammon HP, Melien MC, Verspohl EJ (1986) Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered glutathione in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 38:721–725
Anderson CM, Swanson RA (2000) Astrocyte glutamate transport: review of properties, regulation, and physiological functions. Glia 32:1–14
Aoyama K, Suh SW, Hamby AM et al (2006) Neuronal glutathione deficiency and age-dependent neurodegeneration in the EAAC1 deficient mouse. Nat Neurosci 9:119–126
Arrigo AP (1999) Gene expression and the thiol redox state. Free Radic Biol Med 27:936–944
Arriza JL, Eliasof S, Kavanaugh MP, Amara SG (1997) Excitatory amino acid transporter 5, a retinal glutamate transporter coupled to a chloride conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:4155–4160
Aw TY, Ookhtens M, Ren C, Kaplowitz N (1986) Kinetics of glutathione efflux from isolated rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol 250:G236–G243
Bains JS, Shaw CA (1997) Neurodegenerative disorders in humans: the role of glutathione in oxidative stress-mediated neuronal death. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 25:335–358
Bellomo G, Vairetti M, Stivala L et al (1992) Demonstration of nuclear compartmentalization of glutathione in hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:4412–4416
Bendahan A, Armon A, Madani N et al (2000) Arginine 447 plays a pivotal role in substrate interactions in a neuronal glutamate transporter. J Biol Chem 275:37436–37442
Bianchi MG, Gazzola GC, Tognazzi L, Bussolati O (2008) C6 glioma cells differentiated by retinoic acid overexpress the glutamate transporter excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1). Neuroscience 151:1042–1052
Bolanos JP, Heales SJ, Peuchen S et al (1996) Nitric oxide-mediated mitochondrial damage: a potential neuroprotective role for glutathione. Free Radic Biol Med 21:995–1001
Chance B, Sies H, Boveris A (1979) Hydroperoxide metabolism in mammalian organs. Physiol Rev 59:527–605
Chen R, Qiu W, Liu Z et al (2007) Identification of JWA as a novel functional gene responsive to environmental oxidative stress induced by benzo[a]pyrene and hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Biol Med 42:1704–1714
Cho Y, Bannai S (1990) Uptake of glutamate and cysteine in C-6 glioma cells and in cultured astrocytes. J Neurochem 55:2091–2097
Clancy RM, Levartovsky D, Leszczynska-Piziak J et al (1994) Nitric oxide reacts with intracellular glutathione and activates the hexose monophosphate shunt in human neutrophils: evidence for S-nitrosoglutathione as a bioactive intermediary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3680–3684
Commandeur JN, Stijntjes GJ, Vermeulen NP (1995) Enzymes and transport systems involved in the formation and disposition of glutathione S-conjugates. Role in bioactivation and detoxication mechanisms of xenobiotics. Pharmacol Rev 47:271–330
Cornford EM, Braun LD, Crane PD, Oldendorf WH (1978) Blood–brain barrier restriction of peptides and the low uptake of enkephalins. Endocrinology 103:1297–1303
Dalton TP, Chen Y, Schneider SN et al (2004) Genetically altered mice to evaluate glutathione homeostasis in health and disease. Free Radic Biol Med 37:1511–1526
Davis KE, Straff DJ, Weinstein EA et al (1998) Multiple signaling pathways regulate cell surface expression and activity of the excitatory amino acid carrier 1 subtype of Glu transporter in C6 glioma. J Neurosci 18:2475–2485
de Rey-Pailhade MJ (1888) Sur un corps d’ origine organique hydrogénant le soufre á froid. C R Acad Sci 106:1683–1684
Dringen R (2000) Metabolism and functions of glutathione in brain. Prog Neurobiol 62:649–671
Dringen R, Hamprecht B (1998) Glutathione restoration as indicator for cellular metabolism of astroglial cells. Dev Neurosci 20:401–407
Dringen R, Hirrlinger J (2003) Glutathione pathways in the brain. Biol Chem 384:505–516
Dringen R, Kranich O, Hamprecht B (1997a) The gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase inhibitor acivicin preserves glutathione released by astroglial cells in culture. Neurochem Res 22:727–733
Dringen R, Kranich O, Loschmann PA, Hamprecht B (1997b) Use of dipeptides for the synthesis of glutathione by astroglia-rich primary cultures. J Neurochem 69:868–874
Dringen R, Pfeiffer B, Hamprecht B (1999a) Synthesis of the antioxidant glutathione in neurons: supply by astrocytes of CysGly as precursor for neuronal glutathione. J Neurosci 19:562–569
Dringen R, Kussmaul L, Gutterer JM et al (1999b) The glutathione system of peroxide detoxification is less efficient in neurons than in astroglial cells. J Neurochem 72:2523–2530
Fairman WA, Vandenberg RJ, Arriza JL et al (1995) An excitatory amino-acid transporter with properties of a ligand-gated chloride channel. Nature 375:599–603
Fournier KM, Gonzalez MI, Robinson MB (2004) Rapid trafficking of the neuronal glutamate transporter, EAAC1: evidence for distinct trafficking pathways differentially regulated by protein kinase C and platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem 279:34505–34513
Gazit V, Ben-Abraham R, Coleman R et al (2004) Cysteine-induced hypoglycemic brain damage: an alternative mechanism to excitotoxicity. Amino Acids 26:163–168
Gendreau S, Voswinkel S, Torres-Salazar D et al (2004) A trimeric quaternary structure is conserved in bacterial and human glutamate transporters. J Biol Chem 279:39505–39512
Giustarini D, Rossi R, Milzani A et al (2004) S-glutathionylation: from redox regulation of protein functions to human diseases. J Cell Mol Med 8:201–212
Gonzalez MI, Kazanietz MG, Robinson MB (2002) Regulation of the neuronal glutamate transporter excitatory amino acid carrier-1 (EAAC1) by different protein kinase C subtypes. Mol Pharmacol 62:901–910
Gonzalez MI, Bannerman PG, Robinson MB (2003) Phorbol myristate acetate-dependent interaction of protein kinase Calpha and the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAC1. J Neurosci 23:5589–5593
Gras G, Samah B, Hubert A et al (2011) EEAT expression by macrophages and microglia: still more question than answers. Amino Acids (this issue)
Griffith OW, Meister A (1979) Glutathione: interorgan translocation, turnover, and metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5606–5610
Griffith OW, Meister A (1985) Origin and turnover of mitochondrial glutathione. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4668–4672
Had-Aissouni L (2011) Toward a new role for plasma membrane sodium-dependent glutamate transporters of astrocytes: maintenance of antioxidant defenses beyond extracellular glutamate clearance. Amino Acids (this issue)
Haugeto O, Ullensvang K, Levy LM et al (1996) Brain glutamate transporter proteins form homomultimers. J Biol Chem 271:27715–27722
Himi T, Ikeda M, Yasuhara T et al (2003) Role of neuronal glutamate transporter in the cysteine uptake and intracellular glutathione levels in cultured cortical neurons. J Neural Transm 110:1337–1348
Hirrlinger J, Resch A, Gutterer JM, Dringen R (2002) Oligodendroglial cells in culture effectively dispose of exogenous hydrogen peroxide: comparison with cultured neurones, astroglial and microglial cells. J Neurochem 82:635–644
Hopkins FG (1921) On an autoxidisable constituent of the cell. Biochem J 15:286–305
Hosoya K, Tomi M, Ohtsuki S et al (2002) Enhancement of l-cystine transport activity and its relation to xCT gene induction at the blood–brain barrier by diethyl maleate treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:225–231
Huang Y, Feng X, Sando JJ, Zuo Z (2006) Critical role of serine 465 in isoflurane-induced increase of cell-surface redistribution and activity of glutamate transporter type 3. J Biol Chem 281:38133–38138
Huerta I, McCullumsmith RE, Haroutunian V et al (2006) Expression of excitatory amino acid transporter interacting protein transcripts in the thalamus in schizophrenia. Synapse 59:394–402
Ikemoto MJ, Inoue K, Akiduki S et al (2002) Identification of addicsin/GTRAP3–18 as a chronic morphine-augmented gene in amygdala. Neuroreport 13:2079–2084
Janaky R, Varga V, Hermann A et al (2000) Mechanisms of l-cysteine neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 25:1397–1405
Jenner P (1994) Oxidative damage in neurodegenerative disease. Lancet 344:796–798
Kanai Y, Hediger MA (1992) Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature 360:467–471
Kanai Y, Hediger MA (2003) The glutamate and neutral amino acid transporter family: physiological and pharmacological implications. Eur J Pharmacol 479:237–247
Kaplowitz N, Eberle DE, Petrini J et al (1983) Factors influencing the efflux of hepatic glutathione into bile in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:141–147
Kendall EC, Mason HL, McKenzie BF (1930) A study of glutathione. J Biol Chem 88:409–423
Koch HP, Larsson HP (2005) Small-scale molecular motions accomplish glutamate uptake in human glutamate transporters. J Neurosci 25:1730–1736
Koppal T, Drake J, Yatin S et al (1999) Peroxynitrite-induced alterations in synaptosomal membrane proteins: insight into oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 72:310–317
Kosower EM, Kosower NS (1969) Lest I forget thee, glutathione. Nature 224:117–120
Kranich O, Hamprecht B, Dringen R (1996) Different preferences in the utilization of amino acids for glutathione synthesis in cultured neurons and astroglial cells derived from rat brain. Neurosci Lett 219:211–214
Kranich O, Dringen R, Sandberg M, Hamprecht B (1998) Utilization of cysteine and cysteine precursors for the synthesis of glutathione in astroglial cultures: preference for cystine. Glia 22:11–18
Lash LH, Jones DP (1985) Distribution of oxidized and reduced forms of glutathione and cysteine in rat plasma. Arch Biochem Biophys 240:583–592
Lauterburg BH, Adams JD, Mitchell JR (1984) Hepatic glutathione homeostasis in the rat: efflux accounts for glutathione turnover. Hepatology 4:586–590
Lei XG (2002) In vivo antioxidant role of glutathione peroxidase: evidence from knockout mice. Methods Enzymol 347:213–225
Lewerenz J, Maher P, Methner A (2011) Regulation of xCT expression and system xc-function in neuronal cells. Amino Acids (this issue)
Lin CI, Orlov I, Ruggiero AM et al (2001) Modulation of the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAC1 by the interacting protein GTRAP3-18. Nature 410:84–88
Liu Y, Vidensky S, Ruggiero AM et al (2008) Reticulon RTN2B regulates trafficking and function of neuronal glutamate transporter EAAC1. J Biol Chem 283:6561–6571
Maden M (2007) Retinoic acid in the development, regeneration and maintenance of the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:755–765
Maher P (2005) The effects of stress and aging on glutathione metabolism. Ageing Res Rev 4:288–314
Maier S, Reiterer V, Ruggiero AM et al (2009) GTRAP3-18 serves as a negative regulator of Rab1 in protein transport and neuronal differentiation. J Cell Mol Med 13:114–124
Mao WG, Li AP, Ye J et al (2004) Expressions of JWA protein and heat stress protein 70 induced by cell differentiation inducers combined with heat stress in K562 cells. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 22:60–63
Maragakis NJ, Rothstein JD (2004) Glutamate transporters: animal models to neurologic disease. Neurobiol Dis 15:461–473
Markovic J, Borras C, Ortega A et al (2007) Glutathione is recruited into the nucleus in early phases of cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 282:20416–20424
McBean G (2011) The transsulfuration pathway: a source of cysteine for glutathione in astrocytes. Amino Acids (this issue)
Meister A (1988) On the discovery of glutathione. Trends Biochem Sci 13:185–188
Nafia I, Re DB, Masmejean F et al (2008) Preferential vulnerability of mesencephalic dopamine neurons to glutamate transporter dysfunction. J Neurochem 105:484–496
Persson M, Rönnbäck L (2011) Microglial self defence mediated through GLT-1 and glutathione. Amino Acids (this issue)
Pines G, Danbolt NC, Bjoras M et al (1992) Cloning and expression of a rat brain l-glutamate transporter. Nature 360:464–467
Plaitakis A, Shashidharan P (2000) Glutamate transport and metabolism in dopaminergic neurons of substantia nigra: implications for the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 247(Suppl 2):II25–II35
Poot M, Teubert H, Rabinovitch PS, Kavanagh TJ (1995) De novo synthesis of glutathione is required for both entry into and progression through the cell cycle. J Cell Physiol 163:555–560
Pow DV (2001) Visualising the activity of the cystine-glutamate antiporter in glial cells using antibodies to aminoadipic acid, a selectively transported substrate. Glia 34:27–38
Qin S, Colin C, Hinners I et al (2006) System Xc- and apolipoprotein E expressed by microglia have opposite effects on the neurotoxicity of amyloid-beta peptide 1–40. J Neurosci 26:3345–3356
Radyuk SN, Rebrin I, Luchak JM et al (2009) The catalytic subunit of Drosophila glutamate-cysteine ligase is a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein. J Biol Chem 284:2266–2274
Ramassamy C, Averill D, Beffert U et al (2000) Oxidative insults are associated with apolipoprotein E genotype in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Neurobiol Dis 7:23–37
Rexhepaj R, Grahammer F, Volkl H et al (2006) Reduced intestinal and renal amino acid transport in PDK1 hypomorphic mice. FASEB J 20:2214–2222
Richman PG, Meister A (1975) Regulation of gamma-glutamyl-cysteine synthetase by nonallosteric feedback inhibition by glutathione. J Biol Chem 250:1422–1426
Rothstein JD, Martin L, Levey AI et al (1994) Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron 13:713–725
Ruggiero AM, Liu Y, Vidensky S et al (2008) The endoplasmic reticulum exit of glutamate transporter is regulated by the inducible mammalian Yip6b/GTRAP3-18 protein. J Biol Chem 283:6175–6183
Sagara JI, Miura K, Bannai S (1993) Maintenance of neuronal glutathione by glial cells. J Neurochem 61:1672–1676
Sagara J, Makino N, Bannai S (1996) Glutathione efflux from cultured astrocytes. J Neurochem 66:1876–1881
Sato H, Tamba M, Ishii T, Bannai S (1999) Cloning and expression of a plasma membrane cystine/glutamate exchange transporter composed of two distinct proteins. J Biol Chem 274:11455–11458
Schniepp R, Kohler K, Ladewig T et al (2004) Retinal colocalization and in vitro interaction of the glutamate transporter EAAT3 and the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase SGK1 [correction]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:1442–1449
Seelig GF, Simondsen RP, Meister A (1984) Reversible dissociation of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase into two subunits. J Biol Chem 259:9345–9347
Shanker G, Allen JW, Mutkus LA, Aschner M (2001) The uptake of cysteine in cultured primary astrocytes and neurons. Brain Res 902:156–163
Sheldon AL, Gonzalez MI, Robinson MB (2006) A carboxyl-terminal determinant of the neuronal glutamate transporter, EAAC1, is required for platelet-derived growth factor-dependent trafficking. J Biol Chem 281:4876–4886
Sian J, Dexter DT, Lees AJ et al (1994) Alterations in glutathione levels in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders affecting basal ganglia. Ann Neurol 36:348–355
Sims NR, Nilsson M, Muyderman H (2004) Mitochondrial glutathione: a modulator of brain cell death. J Bioenerg Biomembr 36:329–333
Soboll S, Grundel S, Harris J et al (1995) The content of glutathione and glutathione S-transferases and the glutathione peroxidase activity in rat liver nuclei determined by a non-aqueous technique of cell fractionation. Biochem J 311(Pt 3):889–894
Storck T, Schulte S, Hofmann K, Stoffel W (1992) Structure, expression, and functional analysis of a Na(+)-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10955–10959
Voehringer DW (1999) BCL-2 and glutathione: alterations in cellular redox state that regulate apoptosis sensitivity. Free Radic Biol Med 27:945–950
Voehringer DW, McConkey DJ, McDonnell TJ et al (1998) Bcl-2 expression causes redistribution of glutathione to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2956–2960
Wang XF, Cynader MS (2000) Astrocytes provide cysteine to neurons by releasing glutathione. J Neurochem 74:1434–1442
Wang NP, Zhou JW, Li AP et al (2003) The mechanism of JWA gene involved in oxidative stress of cells. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 21:212–215
Watabe M, Aoyama K, Nakaki T (2007) Regulation of glutathione synthesis via interaction between glutamate transport-associated protein 3-18 (GTRAP3-18) and excitatory amino acid carrier-1 (EAAC1) at plasma membrane. Mol Pharmacol 72:1103–1110
Watabe M, Aoyama K, Nakaki T (2008) A dominant role of GTRAP3–18 in neuronal glutathione synthesis. J Neurosci 28:9404–9413
Winterbourn CC, Metodiewa D (1994) The reaction of superoxide with reduced glutathione. Arch Biochem Biophys 314:284–290
Xia P, Pei G, Schwarz W (2006) Regulation of the glutamate transporter EAAC1 by expression and activation of delta-opioid receptor. Eur J Neurosci 24:87–93
Yamada K, Watanabe M, Shibata T et al (1996) EAAT4 is a post-synaptic glutamate transporter at Purkinje cell synapses. Neuroreport 7:2013–2017
Yernool D, Boudker O, Jin Y, Gouaux E (2004) Structure of a glutamate transporter homologue from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Nature 431:811–818
Zerangue N, Kavanaugh MP (1996) Interaction of l-cysteine with a human excitatory amino acid transporter. J Physiol 493(Pt 2):419–423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoyama, K., Watabe, M. & Nakaki, T. Modulation of neuronal glutathione synthesis by EAAC1 and its interacting protein GTRAP3-18. Amino Acids 42, 163–169 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0861-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0861-y