Abstract
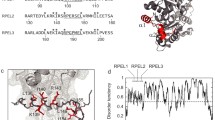
HS1 is a protein involved in erythroid proliferation and apoptotic cell death, containing several structurally significant motifs including a C-terminal SH3 domain. HPK1 is a member of the Ste20-related kinase family, which contains four proline-rich sequences and is constitutively associated with HS1 in hematopoietic cells. Recombinant fusion protein GST-SH3HS1 was expressed to assess the binding properties of 16 peptides derived from the HPK1 proline-rich regions. The binding affinities were determined by non-immobilized ligand interaction assay by circular dichroism. Our results revealed that the classical PxxPxK class II binding motif is not sufficient to induce the interaction with the GST-SH3HS1 domain, an event dependent on the presence of additional basic residue(s) located at the C-terminus of the PxxPxK motif: Lys−5 in P2 peptide and Lys−8 in P4c peptide. Lys replacement by Arg residues decreases the ligand binding affinity. The finding that both SH3HS1 domain and full-length HS1 protein bind to P2 peptide with similar affinity demonstrates that the whole protein sequence does not affect the interaction properties of the domain. In silico models of SH3HS1 as a complex with P2 or P4c highlight the domain residues that interact with the recognition determinants of the peptide ligand and that cooperate in the complex stabilization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anafi M, Kiefer F, Gish GD, Mbamalu G, Iscove NN, Pawson T (1997) SH2/SH3 adaptor proteins can link tyrosine kinases to a Ste20-related protein kinase, HPK1. J Biol Chem 272:27804–27811
Borin G, Calderan A, Ruzza P, Moroder L, Goehring W, Bovermann G, Wuensch E (1987) Synthesis of human [15-norleucine]little-gastrin-II and des-1-tryptophan-[12-norleucine]minigastrin-II. Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 368:1363–1372
Brunati AM, Donella-Deana A, James P, Quadroni M, Contri A, Marin O, Pinna LA (1999) Molecular features underlying the sequential phosphorylation of HS1 protein and its association with c-Fgr protein-tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 274:7557–7564
Brunati AM, Deana R, Folda A, Massimino ML, Marin O, Ledro S, Pinna LA, Donella-Deana AD (2005) Thrombin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of HS1 in human platelets is sequentially catalyzed by Syk and Lyn tyrosine kinases and associated with the cellular migration of the protein. J Biol Chem 280:21029–21035
Cohen GB, Ren RB, Baltimore D (1995) Modular binding domains in signal-transduction proteins. Cell 80:237–248
Feng SB, Chen JK, Yu HT, Simon JA, Schreiber SL (1994) 2 binding orientations for peptides to the Src SH3 domain—development of a general-model for SH3–ligand interactions. Science 266:1241–1247
Fukuda T, Kitamura D, Taniuchi I, Maekawa Y, Benhamou LE, Sarthou P, Watanabe T (1995) Restoration of surface Igm-mediated apoptosis in an anti-Igm-resistant variant of Wehi-231 lymphoma-cells by HS1, a protein-tyrosine kinase substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7302–7306
Hao JJ, Carey GB, Zhan X (2004) Syk-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation is required for the association of hematopoietic lineage cell-specific protein 1 with lipid rafts and B cell antigen receptor signalosome complex. J Biol Chem 279:33413–33420
Hashimoto S, Hirose M, Hashimoto A, Morishige M, Yamada A, Hosaka H, Akagi KI, Ogawa E, Oneyama C, Agatsuma T, Okada M, Kobayashi H, Wada H, Nakano H, Ikegami T, Nakagawa A, Sabe H (2006) Targeting AMAP1 and cortactin binding bearing an atypical src horology 3/proline interface for prevention of breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:7036–7041
Hata D, Nakamura T, Kawakami T, Kawakami Y, Herren B, Mayumi M (1994) Tyrosine phosphorylation of MB-1, B29, and HS1 proteins in human B-cells following receptor cross-linking. Immunol Lett 40:65–71
Hruby VJ, Sawyer TK, Yang YCS, Bregman MD, Hadley ME, Heward CB (1980) Synthesis and structure–function studies of melanocyte stimulating hormone analogs modified in the 2 and 4(7) positions: comparison of activities on frog skin melanophores and melanoma adenylate cyclase. J Med Chem 23:1432–1437
Hu MCT, Qiu WR, Wang XP, Meyer CF, Tan TH (1996) Human HPK1, a novel human hematopoietic progenitor kinase that activates the JNK/SAPK kinase cascade. Genes Dev 10:2251–2264
Kaneko T, Li L, Li SSC (2008) The SH3 domain—a family of versatile peptide- and protein-recognition module. Front Biosci 13:4938–4952
Karkkainen S, Hiipakka M, Wang JH, Kleino I, Vaha-Jaakkola M, Renkema GH, Liss M, Wagner R, Saksela K (2006) Identification of preferred protein interactions by phage-display of the human Src homology-3 proteome. EMBO Rep 7:186–191
Kiefer F, Tibbles LA, Anafi M, Janssen A, Zanke BW, Lassam N, Pawson T, Woodgett JR, Iscove NN (1996) HPK1, a hematopoietic protein kinase activating the SAPK/JNK pathway. EMBO J 15:7013–7025
Kim JM, Lee CD, Rath A, Davidson AR (2008) Recognition of non-canonical peptides by the yeast Fus1p SH3 domain: elucidation of a common mechanism for diverse SH3 domain specificities. J Mol Biol 377:889–901
Kitamura D, Kaneko H, Miyagoe Y, Ariyasu T, Watanabe T (1989) Isolation and characterization of a novel human gene expressed specifically in the cells of hematopoietic lineage. Nucleic Acid Res 17:9367–9379
Knudsen BS, Zheng J, Feller SM, Mayer JP, Burrell SK, Cowburn D, Hanafusa H (1995) Affinity and specificity requirements for the first Src homology-3 domain of the crk proteins. EMBO J 14:2191–2198
Larson SM, Davidson AR (2000) The identification of conserved interactions within the SH3 domain by alignment of sequences and structures. Protein Sci 9:2170–2180
Lewitzky M, Harkiolaki M, Domart MC, Jones EY, Feller SM (2004) Mona/Gads SH3C binding to hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1) combines an atypical SH3 binding motif, R/KXXK, with a classical PXXP motif embedded in a polyproline type II (PPII) helix. J Biol Chem 279:28724–28732
Li SSC (2005) Specificity and versatility of SH3 and other proline-recognition domains: structural basis and implications for cellular signal transduction. Biochem J 390:641–653
Liu SK, Smith CA, Arnold R, Kiefer F, McGlade CJ (2000) The adaptor protein Gads (Grb2-related adaptor downstream of Shc) is implicated in coupling hemopoietic progenitor kinase-1 to the activated TCR. J Immunol 165:1417–1426
Marchiani A, Antolini A, Calderan A, Ruzza P (2010) Atypical SH3 domain binding motifs: features and properties. Curr Top Pept Protein Res (in press)
Mayer BJ (2001) SH3 domains: complexity in moderation. J Cell Sci 114:1253–1263
Nagata Y, Kiefer F, Watanabe T, Todokoro K (1999) Activation of hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 by erythropoietin. Blood 93:3347–3354
Rubini C, Ruzza P, Spaller MR, Siligardi G, Hussain R, Udugamasooriya DG, Bellanda M, Mammi S, Borgogno A, Calderan A, Cesaro L, Brunati AM, Donella-Deana A (2010) Recognition of lysine-rich peptide ligands by murine cortactin SH3 domain: CD, ITC and NMR studies. Biopolymers 94:298–306
Ruzza P, Siligardi G, Donella-Deana A, Calderan A, Hussain R, Rubini C, Cesaro L, Osler A, Guiotto A, Pinna LA, Borin G (2006) 4-Fluoroproline derivative peptides: effect on PPII conformation and SH3 affinity. J Pept Sci 12:462–471
Salvatella X, Peczuh MW, Gairi M, Jain RK, Sanchez-Quesada J, de Mendoza J, Hamilton AD, Giralt E (2000) Side chain elongation causes a change from enthalpy driven to entropy driven binding in the molecular recognition of tetraanionic peptides. Chem Commun: 1399–1400
Scielzo C, Ghia P, Conti A, Bachi A, Guida G, Geuna M, Alessio M, Caligaris-Cappio F (2005) HS1 protein is differentially expressed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patient subsets with good or poor prognoses. J Clin Invest 115:1644–1650
Siligardi G, Hussain R (1998) Biomolecules interactions and competitions by non-immobilised ligand interaction assay by circular dichroism. Enantiomer 3:77–86
Siligardi G, Hussain R, Donella-Deana A, Brunati A, Pinna LA, Ruzza P, Calderan A, Borin G (2002a) Binding interactions of derived HPK1 Pro-rich peptides to HS1-SH3 domain suggest a possible adapter function of HS1 protein. In: Benedetti E, Pedone C (eds) Peptides 2002. Ziino, Napoli, pp 886–887
Siligardi G, Panaretou B, Meyer P, Singh S, Woolfson DN, Piper PW, Pearl LH, Prodromou C (2002b) Regulation of Hsp90 ATPase activity by the co-chaperone Cdc37p/p50(cdc97). J Biol Chem 277:20151–20159
Steinauer R, White P (1995) Multi-gram synthesis of peptides containing C-terminal proline. In: Epton R (ed) Innovation and perspectives in solid phase synthesis 1994. Mayflower Worldwide Ltd, Kingswinford, pp 689–692
Takemoto Y, Sato M, Furuta M, Hashimoto Y (1996) Distinct binding patterns of HS1 to the Src SH2 and SH3 domains reflect possible mechanisms of recruitment and activation of downstream molecules. Int Immunol 8:1699–1705
Wang WF, Zhou GS, Hu MCT, Yao ZB, Tan TH (1997) Activation of the hematopoietic progenitor kinase-1 (HPK1)-dependent, stress-activated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)-activated kinase (TAK1), a kinase mediator of TGF beta signal transduction. J Biol Chem 272:22771–22775
Wellings DA, Atherton E (1997) Standard Fmoc protocols. In: Fields GB (ed) Solid-phase peptide synthesis. Academic Press, New York, pp 44–67
Yamanashi Y, Fukuda T, Nishizumi H, Inazu T, Higashi K, Kitamura D, Ishida T, Yamamura H, Watanabe T, Yamamoto T (1997) Role of tyrosine phosphorylation of HS1 in B cell antigen receptor-mediated apoptosis. J Exp Med 185:1387–1392
Zarrinpar A, Bhattacharyya RP, Lim WA (2003) Sci STKE 179:RE8
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by Italian National Research Council (Short-Term Mobility 2001), Italian Association for Cancer Research (grant to L.A.P.) and “Italian Cystic Fibrosis Research Foundation (Grant #4/2007)” with the contribution of Banca Popolare di Verona e Novara and “Fondazione Giorgio Zanotto”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors G. Siligardi and P. Ruzza contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siligardi, G., Ruzza, P., Hussain, R. et al. The SH3 domain of HS1 protein recognizes lysine-rich polyproline motifs. Amino Acids 42, 1361–1370 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0831-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0831-4