Abstract
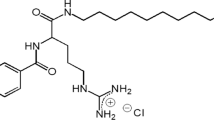
In this paper, we report on a catanionic vesicles-based strategy to reduce the cytotoxicity of the diacyl glycerol arginine-based synthetic surfactants 1,2-dimyristoyl-rac-glycero-3-O-(N α-acetyl-l-arginine) hydrochloride (1414RAc) and 1,2-dilauroyl-rac-glycero-3-O-(N α-acetyl-l-arginine) hydrochloride (1212RAc). The behavior of these surfactants was studied either as pure components or after their formulation as pseudo-tetra-chain catanionic mixtures with phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and as cationic mixtures with 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (DPPC) used as control. The antimicrobial activity of the negatively charged formulations against Acinetobacter baumannii was maintained with respect to the surfactant alone, while a significant improvement of the antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus was observed, together with a strong decrease of hemolytic activity. The influence of the net charge of the catanionic vesicles on membrane selectivity was studied using model membranes. The dynamics of surface tension changes induced by the addition of 1414RAc/PG aqueous dispersions into phospholipid monolayers composed of zwitterionic DPPC as model system for mammalian membranes and of negatively charged PG mimicking cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-positive bacteria was followed by tensiometry. Our results constitute a proof of principle that tuning formulation can reduce the cytotoxicity of many surfactants, opening their possible biological applications.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1212R:
-
1,2-Dilauroyl-glycero-3-O-l-arginine dihydrochloride
- 1212RAc:
-
1,2-Dilauroyl-rac-glycero-3-O-(N α-acetyl-l-arginine) hydrochloride
- 1414R:
-
1,2-Dimyristoyl-glycero-3-O-l-arginine dihydrochloride
- 1414RAc:
-
1,2-Dimyristoyl-rac-glycero-3-O-(N α-acetyl-l-arginine) hydrochloride
- DPPC:
-
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine
- HC50 :
-
Surfactant concentration inducing 50% of hemolysis
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentration
- PG:
-
Phosphatidylglycerol
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- OD:
-
Optical density
References
Benavides T, Mitjans M, Martinez V, Clapes P, Infante MR, Clothier RH, Vinardell MP (2004) Assessment of primary eye and skin irritants by in vitro cytotoxicity and phototoxicity models: an in vitro approach of new arginine-based surfactant-induced irritation. Toxicology 197:229–237. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2004.01.011
Bonincontro A, Spigone E, Pena MR, Letizia C, La Mesa C (2006) Lysozyme binding onto cat-anionic vesicles. J Colloid Interface Sci 304:342–347. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2006.09.046
Bonincontro A, Falivene M, La Mesa C, Risuleo G, Pena MR (2008) Dynamics of DNA adsorption on and release from SDS-DDAB cat-anionic vesicles: a multitechnique study. Langmuir 24:1973–1978. doi:10.1021/la701730h
Bramer T, Dew N, Edsman K (2007) Pharmaceutical applications for catanionic mixtures. J Pharm Pharmacol 59:1319–1334. doi:10.1211/jpp.59.10.0001
Brito RO, Marques EF, Silva SG, Vale ML, Gomes P, Araujo MJ, Rodriguez-Borges JE, Infante MR, Garcia MT, Ribosa I, Vinardell MP, Mitjans M (2009) Physicochemical and toxicological properties of novel amino acid-based amphiphiles and their spontaneously formed catanionic vesicles. Colloids Surf B 72:80–87. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.03.017
Burgo P, Aicart E, Junquera E (2007) Mixed vesicles and mixed micelles of the cationic–cationic surfactant system: didecyldimethylammonium bromide/dodecylethyldimethylammonium bromide/water. Colloids Surf A 292:165–172. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.06.019
Caria A, Khan A (1996) Phase behavior of catanionic surfactant mixtures: sodium bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate–didocyldimethylammonium bromide–water system. Langmuir 12:6282–6290. doi:10.1021/la960581z
Denyer SP (1995) Mechanisms of action of antibacterial biocides. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 36:227–245
Epand RF, Infante MR, Flanagan TD, Epand RM (1998) Properties of lipoamino acids incorporated into membrane bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1373:67–75
Fogt A, Hägerstrand H, Isomaa B (1995) Effects of N,N′-bisdimethyl-1,2-ethanediamine dichloride, a double-chain surfactant, on membrane-related functions in human erythrocytes. Chem Biol Interact 94:147–155
Infante MR, Molinero J, Erra P, Julia R, Garcia-Dominguez JJ (1985) A comparative-study on surface-active and antimicrobial properties of some N α-lauroyl-l α, omega dibasic amino-acids derivatives. Fette Seifen Anstrichmittel 87:309–313
Kamenka N, Chorro M, Talmon Y, Zana R (1992) Study of mixed aggregates in aqueous-solutions of sodium dodecyl-sulfate and dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide. Colloids Surf 67:213–222
Lohner K, Sevcsik E, Pabst G (2008) Liposome-based biomembrane mimetic systems: implications for lipid–peptide interactions. Adv Planar Lipid Bilayers Liposomes 6:103–137. doi:10.1016/S1554-4516(07)06005-X
Lozano N, Perez L, Pons R, Luque-Ortega JR, Fernandez-Reyes M, Rivas L, Pinazo A (2008) Interaction studies of diacyl glycerol arginine-based surfactants with DPPC and DMPC monolayers, relation with antimicrobial activity. Colloids Surf A 319:196–203. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.07.015
Lozano N, Pinazo A, La Mesa C, Perez L, Andreozzi P, Pons R (2009) Catanionic vesicles formed with arginine-based surfactants and 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate monosodium salt. J Phys Chem B 113:6321–6327. doi:10.1021/jp810671p
Lozano N, Pinazo A, Perez L, Pons R (2010) Dynamic properties of cationic diacyl-glycerol-arginine-based surfactant/phospholipid mixtures at the air/water interface. Langmuir 26:2559–2566. doi:10.1021/la902850j
Marques EF, Brito RO, Wang YJ, Silva BFB (2006) Thermotropic phase behavior of triple-chained catanionic surfactants with varying headgroup chemistry. J Colloid Interface Sci 294:240–247. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2005.07.021
Marques EF, Brito RO, Silva SG, Rodriguez-Borges JE, Vale ML, Gomes P, Araujo MJ, Soderman O (2008) Spontaneous vesicle formation in catanionic mixtures of amino acid-based surfactants: chain length symmetry effects. Langmuir 24:11009–11017. doi:10.1021/la801518h
Marsh D (1996) Lateral pressure in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1286:183–223. doi:10.1016/S0304-4157(96)00009-3
Miyagishi S, Asakawa T, Nishida M (1989) Hydrophobicity and surface-activities of sodium salts of N-dodecanoyl amino-acids. J Colloid Interface Sci 131:68–73
Moran C, Infante MR, Clapes P (2001) Synthesis of glycero amino acid-based surfactants. Part 1. Enzymatic preparation of rac-1-O-(N α-acetyl-l-aminoacyl)glycerol derivatives. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans I, 2063-2070. doi:10.1039/b103132p
Moran C, Infante MR, Clapes P (2002) Synthesis of glycero amino acid-based surfactants. Part 2. Lipase-catalysed synthesis of 1-O-lauroyl-rac-glycero-3-O-(N α-acetyl-l-amino acid) and 1,2-di-O-lauroyl-rac-glycero-3-O-(N α-acetyl-l-amino acid) derivatives. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans I 1124–1134. doi:10.1039/hb200577h
Papanastasiou EA, Hua Q, Sandouk A, Son U, Christenson AJ, Van Hoek ML, Bishop BM (2009) Role of acetylation and charge in antimicrobial peptides based on human β-defensin-3. APMIS 117:492–499. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0463.2009.02460.x
Perez L, Torres JL, Manresa A, Solans C, Infante MR (1996) Synthesis, aggregation, and biological properties of a new class of gemini cationic amphiphilic compounds from arginine, bis(Args). Langmuir 12:5296–5301
Perez L, Infante MR, Angelet M, Clapes P, Pinazo A (2004a) Glycerolipid arginine-based surfactants: synthesis and surface active properties. Prog Colloid Polym Sci 123:210–216. doi:10.1007/b11628
Perez L, Infante MR, Pons R, Moran MC, Vinardell P, Mitjans M, Pinazo A (2004b) A synthetic alternative to natural lecithins with antimicrobial properties. Colloids Surf B 35:235–242. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2004.03.014
Peypoux F, Laprevote O, Pagadoy M, Wallach J (2004) N-Acyl derivatives of Asn, new bacterial N-acyl d-amino acids with surfactant activity. Amino Acids 26:209–214. doi:10.1007/s00726-003-0056-2
Pinazo A, Perez L, Infante MR, Pons R (2004) Unconventional vesicle-to-ribbon transition behaviour of diacyl glycerol amino acid-based surfactants in extremely diluted systems induced by pH-concentration effects. Phys Chem Chem Phys 6:1475–1481. doi:10.1039/b313313n
Pinazo A, Angelet M, Pons R, Lozano M, Infante MR, Perez L (2009) Lysine–bisglycidol conjugates as novel cationic surfactants. Langmuir 25:7803–7814. doi:10.1021/la901675p
Pons R, Pinazo A, Lozano N, Rivas L, Fernandez-Reyes M, Luque-Ortega JR, Perez L, Infante MR, Moran C (2009) Formulaciones de lipoaminoácidos catiónicos con menor poder hemolítico basadas en la formación de pares cataniónicos. Spanish Pat. Appl. ES1641.261, November 13
Rideal E, Taylor FH (1957) On haemolysis by anionic detergents. Proc R Soc Lond B 146:225–241
Rideal E, Taylor FH (1958) On haemolysis and haemolytic acceleration. Proc R Soc Lond B 148:450–464
Russell AD (1995) Mechanisms of bacterial resistance to biocides. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 36:247–265
Sanson A, Egret-Chalier M, Bouloussa O, Maget-Dana R, Ptak M (1987) N-acyl aminoacids: amphiphilic properties and interactions with the lipid bilayers. In: Mittal KL, Bothorel P (eds) Surfactant in solution, vol 5, pp 793–805
Saugar JM, Rodriguez-Hernandez MJ, de la Torre BG, Pachon-Ibanez ME, Fernandez-Reyes M, Andreu D, Pachon J, Rivas L (2006) Activity of cecropin A-melittin hybrid peptides against colistin-resistant clinical strains of Acinetobacter baumannii: molecular basis for the differential mechanisms of action. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:1251–1256. doi:10.1128/AAC.50.4.1251-1256.2006
Valko EI, DuBois AS (1945) Correlation between antibacterial power and chemical structure of higher alkyl ammonium ions. J Bacteriol 50:481–490
Vieira DB, Carmona-Ribeiro AM (2006) Cationic lipids and surfactants as antifungal agents: mode of action. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:760–767. doi:10.1093/jac/dk1312
Vinardell MP, Benavides T, Mitjans M, Infante MR, Clapes P, Clothier R (2008) Comparative evaluation of cytotoxicity and phototoxicity of mono and diacyl glycerol amino acid-based surfactants. Food Chem Toxicol 46:3837–3841. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2008.10.007
Xia J, Xia Y, Nnanna IA (1995) Structure–function relationship of acyl amino acid surfactants: surface activity and antimicrobial properties. J Agric Food Chem 43:867–871
Acknowledgments
We thank the invaluable advice, suggestions, comments and critical reading of the manuscript by Dr. Luís Rivas and Dra. María Fernández-Reyes from the Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas (CIB-CSIC) of Madrid on biological experiments. Financial support from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (CTQ2007-604091/BQU and CTQ2009-14151-CO2-01) and Generalitat de Catalunya (2009SGR1331) is gratefully acknowledged. We are also grateful to Ms. Imma Carrera for technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lozano, N., Pérez, L., Pons, R. et al. Diacyl glycerol arginine-based surfactants: biological and physicochemical properties of catanionic formulations. Amino Acids 40, 721–729 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0710-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0710-4