Abstract
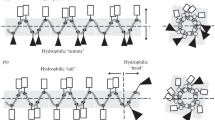
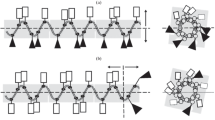
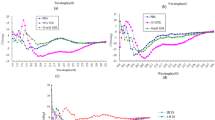
Four variants of the highly hemolytic antimicrobial peptide Pin2 were chemically synthesized with the aim to investigate the role of the proline residue in this peptide, by replacing it with the motif glycine-valine-glycine [GVG], which was found to confer low hemolytic activity in a spider antimicrobial peptide. The proline residue in position 14 of Pin2 was substituted by [V], [GV], [VG] and [GVG]. Only the peptide variant with the proline substituted for [GVG] was less hemolytic compared to that of all other variants. The peptide variant [GVG] kept its antimicrobial activity in Muller–Hilton agar diffusion assays, whereas the other three variants were less effective. However, all Pin2 antimicrobial peptide variants, were active when challenged against a Gram-positive bacteria in Muller–Hilton broth assays suggesting that chemical properties of the antimicrobial peptides such as hydrophobicity is an important indication for antimicrobial activity in semi-solid environments.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
Circular dichroism
- OD:
-
Optical density
- Oxki2:
-
Oxypinin 2
- Pin2:
-
Pandinin 2
- TFA:
-
Trifluoroacetic acid
- TFE:
-
Trifluoroethanol
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentration
References
Amiche M, Seon AA, Wroblewski H, Nicolas P (2000) Isolation of dermatoxin from frog skin, an antibacterial peptide encoded by a novel member of the dermaseptin genes family. Eur J Biochem 267:4583–4592
Andreu D, Rivas L (1998) Animal antimicrobial peptides: an overview. Biopolymers 47:415–433
Batista CVF, Rosendo da Silva L, Sebben A, Scaloni A, Ferrara L, Paiva GR, Olamendi-Portugal T, Possani LD, Bloch C Jr (1999) Antimicrobial peptides from the Brazilian frog Phyllomedusa distincta. Peptides 20:679–686
Bazzo R, Tappin MJ, Pastore A, Harvey TS, Carver JA, Campbell ID (1988) The structure of melittin. A 1H-NMR study in methanol. Eur J Biochem 173:139–146
Bohm G, Muhr R, Jaenicke R (1992) Quantitative analysis of protein far UV circular dichroism spectra by neural networks. Protein Eng 5:191–195
Bywater RP, Thomas D, Vriend G (2001) A sequence and structural study of transmembrane helices. J Comput Aided Mol Des 15:533–552
Chandrapati S, O’Sullivan DJ (1998) Procedure for quantifiable assessment of nutritional parameters influencing Nisin production by Lactococcus lactis subsp lactis. J Biotechnol 63:229–233
Cordes FS, Bright JN, Sansom MSP (2002) Proline-induced distortions of transmembrane helices. J Mol Biol 323:951–960
Corzo G, Escoubas P, Villegas E, Barnham KJ, He W, Norton RS, Nakajima T (2001) Characterization of unique amphipathic antimicrobial peptides from venom of the scorpion Pandinus imperator. Biochem J 359:35–45
Corzo G, Villegas E, Gomez-Lagunas F, Possani LD, Belokoneva OS, Nakajima T (2002) Oxyopinins, large amphipathic peptides isolated from the venom of the wolf spider Oxyopes kitabensis with cytolytic properties and positive insecticidal cooperativity with spider neurotoxins. J Biol Chem 277:23627–23637
Dathe M, Kaduk C, Tachikawa E, Melzig MF, Wenschuh H, Bienert M (1998) Proline at position 14 of alamethicin is essential for hemolytic activity, catecholamine secretion from chromaffin cells and enhanced metabolic activity in endothelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1370:175–183
Dempsey CE, Bazzo R, Harvey TS, Syperek I, Boheim G, Campbell ID (1991) Contribution of proline-14 to the structure and actions of melittin. FEBS Lett 281:240–244
Holak TA, Engstrom A, Kraulis PJ, Lindeberg G, Bennich H, Jones TA, Gronenborn AM, Clore GM (1988) The solution conformation of the antibacterial peptide cecropin A: a nuclear magnetic resonance and dynamical simulated annealing study. Biochemistry 27:7620–7629
Iwai H, Nakajima Y, Natori S, Arata Y, Shimada I (1993) Solution conformation of an antibacterial peptide, sarcotoxin IA, as determined by 1H-NMR. Eur J Biochem 217:639–644
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Mor A, Nguyen VH, Delfour A, Migliore-Samour D, Nicolas P (1991) Isolation, amino acid sequence, and synthesis of dermaseptin, a novel antimicrobial peptide of amphibian skin. Biochemistry 30:8824–8830
Oren Z, Shai Y (1997) Selective lysis of bacteria but not mammalian cells by diastereomers of melittin: structure–function study. Biochemistry 36:1826–1835
Orivel J, Redeker V, Le Caer JP, Krier F, Revol-Junelles AM, Longeon A, Chaffotte A, Dejean A, Rossier J (2001) Ponericins, new antibacterial and insecticidal peptides from the venom of the ant Pachycondyla goeldii. J Biol Chem 276:17823–17829
Sansom MSP (1992) Proline residues in transmembrane helices of channel and transport proteins: a molecular modelling study. Protein Eng 5:53–60
Shin SY, Kang JH, Lee DG, Jang SY, Seo MY (1999) Influences of hinge region of a synthetic antimicrobial peptide, cecropin A(1–13)-melittin(1–13) hybrid on antibiotic activity. Bull Korean Chem Soc 20:1078–1084
Thennarasu S, Nagaraj R (1996) Specific antimicrobial and hemolytic activities of 18-residue peptides derived from the amino terminal region of the toxin pardaxin. Protein Eng 9:1219–1224
Wong H, Bowie JH, Carver JA (1997) The solution structure and activity of caerin 1.1, an antimicrobial peptide from the Australian green tree frog, Litoria splendida. Eur J Biochem 247:545–557
Zidovetzki R, Rost B, Armstrong DL, Pecht I (2003) Transmembrane domains in the functions of Fc receptors. Biophys Chem 1000:555–575
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from CONACyT 83962/2007 to E.V., and CONACyT 49773/24968 to G.C. The mass spectrometry determination conducted by Dr. Fernando Zamudio is greatly acknowledged. The authors also acknowledge QBP Ma. Rocio Patiño Maya from Instituto de Química–UNAM for CD spectra data acquisition. Alexis Rodriguez is recipient of a PhD scholarship (#199738) from CONACyT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, A., Villegas, E., Satake, H. et al. Amino acid substitutions in an alpha-helical antimicrobial arachnid peptide affect its chemical properties and biological activity towards pathogenic bacteria but improves its therapeutic index. Amino Acids 40, 61–68 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0449-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0449-y