Abstract
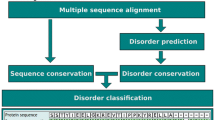
The association of structurally disordered proteins with a number of diseases has engendered enormous interest and therefore demands a prediction method that would facilitate their expeditious study at molecular level. The present study describes the development of a computational method for predicting disordered proteins using sequence and profile compositions as input features for the training of SVM models. First, we developed the amino acid and dipeptide compositions based SVM modules which yielded sensitivities of 75.6 and 73.2% along with Matthew’s Correlation Coefficient (MCC) values of 0.75 and 0.60, respectively. In addition, the use of predicted secondary structure content (coil, sheet and helices) in the form of composition values attained a sensitivity of 76.8% and MCC value of 0.77. Finally, the training of SVM models using evolutionary information hidden in the multiple sequence alignment profile improved the prediction performance by achieving a sensitivity value of 78% and MCC of 0.78. Furthermore, when evaluated on an independent dataset of partially disordered proteins, the same SVM module provided a correct prediction rate of 86.6%. Based on the above study, a web server (“DPROT”) was developed for the prediction of disordered proteins, which is available at http://www.imtech.res.in/raghava/dprot/.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhasin M, Raghava GPS (2004), ESLpred: SVM-based method for subcellular localization of eukaryotic proteins using dipeptide composition and PSI-BLAST. Nucleic Acids Res 32:414–419
Chou KC, Shen HB (2007a) MemType-2L: a web server for predicting membrane proteins and their types by incorporating evolution information through Pse-PSSM. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 360:339–345
Chou KC, Shen HB (2007b) Recent progresses in protein subcellular location prediction. Anal Biochem 370:1–16
Dosztanyi Z, Csizmok V, Tompa P, Simon I (2005) The pairwise energy content estimated from amino acid composition discriminates between folded and intrinsically unstructured proteins. J Mol Biol 347:827–839
Dunker AK, Obradovic Z (2001) The protein trinity-linking function and disorder. Nat Biotechnol 19:805–806
Dunker AK, Brown CJ, Obradovic Z (2002) Identification and functions of usefully disordered proteins. Adv Protein Chem 62:25–49
Fink AL (2005) Natively unfolded proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 15:35–41
Galzitskaya OV, Garbuzynskiy SO, Lobanov MY (2006) FoldUnfold: web server for the prediction of disordered regions in protein chain. Bioinformatics 22:2948–2949
Garg A, Bhasin M, Raghava GPS (2005a) Support vector machine-based method for subcellular localization of human proteins using amino acid compositions, their order, and similarity search. J Biol Chem 280:14427–14432
Garg A, Kaur H, Raghava GPS (2005b) Real value prediction of solvent accessibility in proteins using multiple sequence alignment and secondary structure. Proteins 61:318–325
Joachims T (1999) Making large-scale SVM learning particle. In: Scholkopf B, Burges C, Smola A (eds) Advances in kernel methods support vector learning. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 42–56
Jones DT (1999) Protein secondary structure prediction based on position specific scoring matrices. J Mol Biol 292:195–202
Jones DT, Ward JJ (2003) Prediction of disordered regions in proteins from position specific score matrices. Proteins 53:573–578
Kaur H, Raghava GPS (2002) BetaTPred: Prediction of beta turns in a protein using statistical algorithms. Bioinformatics 18:498–499
Kaur H, Raghava GPS (2003) A neural-network based method for prediction of gamma-turns in proteins from multiple sequence alignment. Protein Sci 2:923–929
Kaur H, Raghava GPS (2004a) Prediction of alpha-turns in proteins using PSI-BLAST profiles and secondary structure information. Proteins 55:83–90
Kaur H, Raghava GPS (2004b) A neural network method for prediction of β-turn types in proteins using evolutionary information. Bioinformatics 20:2751–2758
Kumar M, Bhasin M, Natt NK, Raghava GPS (2005) BhairPred: prediction of b-hairpins in a protein from multiple alignment information using ANN and SVM techniques. Nucleic Acids Res 33:154–159
Lata S, Sharma BK, Raghava GPS (2007) Analysis and prediction of antibacterial peptides. BMC Bioinformatics 8:263
Linding R, Jensen LJ, Diella F, Bork P, Gibson TJ, Russell RB (2003a) Protein disorder prediction: implications for structural proteomics. Structure 11:1453–1459
Linding R, Russell RB, Neduva V, Gibson TJ (2003b) GlobPlot: exploring protein sequences for globularity and disorder. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3701–3708
Radivojac P, Obradovic Z, Smith DK, Zhu G, Vucetic S, Brown CJ, Lawson JD, Dunker AK. (2004) Protein flexibility and intrinsic disorder. Protein Sci 13:71–80
Rashid M, Saha S, Raghava GPS (2007) Support vector machine-based method for predicting subcellular localization of mycobacterial proteins using evolutionary information and motifs. BMC Bioinformatics 8:337
Romero P, Obradovic Z, Dunker AK (1999) Folding minimal sequences: the lower bound for sequence complexity of globular proteins. FEBS Lett 462:363–367
Romero P, Obradovic Z, Li X, Garner EC, Brown CJ, Dunker AK (2001) Sequence complexity of disordered protein. Proteins 42:38–48
Shen HB, Chou KC (2007a) EzyPred: a top-down approach for predicting enzyme functional classes and subclasses. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 364:53–59
Shen HB, Chou KC (2007b) Nuc-PLoc: a new web-server for predicting protein subnuclear localization by fusing PseAA composition and PsePSSM. Protein Eng Des Sel 20:561–567
Shimizu K, Muraoka Y, Hirose S, Tomii K, Noguchi T (2007) Predicting mostly disordered proteins by using structure-unknown protein data. BMC Bioinformatics 8:78
Sussman JL, Prilusky J, Felder CE, Zeev-Ben-Mordehai T, Rydberg EH, Man O, Beckmann JS, Silman I (2005) Fold index: a simple tool to predict whether a given protein sequence is intrinsically unfolded. Bioinformatics 21:3435–3438
Vihinen M, Torkkila E, Riikonen P (1994) Accuracy of protein flexibility predictions. Proteins 19:141–149
Vucetic S, Obradovic Z, Vacic V, Radivojac P, Peng K, Iakoucheva LM, Cortese MS, Lawson JD, Brown CJ, Sikes JG, Newton CD, Dunker AK (2005) DisProt: a database of protein disorder. Bioinformatics 21:137–140
Ward JJ, McGuffin LJ, Bryson K, Buxton BF, Jones DT (2004) The DISOPRED server for the prediction of protein disorder. Bioinformatics 20:2138–2139
Weinreb PH, Zhen W, Poon AW, Conway KA, Lansbury PT Jr (1996) NACP, a protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and learning, is natively unfolded. Biochemistry 35:13709–13715
Wright PE, Dyson HJ (1999) Intrinsically unstructured proteins: re-assessing the protein structure-function paradigm. J Mol Biol 293:321–331
Xie D, Li A, Wang M, Fan Z Feng H (2005) LOCSVMPSI: a web server for subcellular localization of eukaryotic proteins using SVM and profile of PSI-BLAST. Nucleic Acids Res 33:105–110
Xie Q, Arnold GE, Romero P, Obradovic Z, Garner E, Dunker AK (1998) The sequence attribute method for determining relationships between sequence and protein disorder. Genome Inform 9:193–200
Yang ZR, Thomson R, McNeil P, Esnouf RM (2005) RONN: the bio-basis function neural network technique applied to the detection of natively disordered regions in proteins. Bioinformatics 21:3369–3376
Yip YL, Scheib H, Diemand AV, Gattiker A, Famiglietti LM, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A (2004) The Swiss-Prot variant page and the ModSNP database: a resource for sequence and structure information on human protein variants. Hum Mutat 23:464–470
Zhi-Qiang Ye, Zhao SQ, Gao G, Liu XQ, Langlois RE, Lu H, Wei L (2007) Finding new structural and sequence attributes to predict possible disease association of single amino acid polymorphism (SAP). Bioinformatics 23:1444–1450
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India for financial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sethi, D., Garg, A. & Raghava, G.P.S. DPROT: prediction of disordered proteins using evolutionary information. Amino Acids 35, 599–605 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0085-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0085-y