Abstract
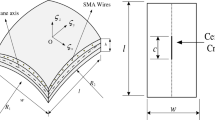
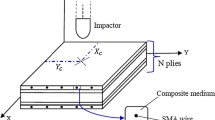
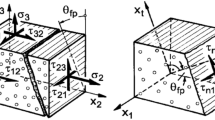
The damaged laminated composite structural strength and repair action due to functional material reinforcement is investigated mathematically in this research using a higher-order displacement field model. The effect of a crack on the frequency responses is predicted numerically using the finite element (FE) approach. The reduction in total structural strength due to the crack and elevated temperatures are computed using the proposed model. Further, the enhancement of parent structural strength/stiffness is achieved by reinforcing the shape memory alloy (SMA). Moreover, the damage repair and improved frequency are achieved through activated SMA under a temperature range. The numerical model efficacy is established by conducting the convergence and adequate comparison studies. The study of the cracked laminate is verified for different temperature ranges, with and without SMA fiber. Additionally, a few experimental frequencies of intact and damaged composite panels have been carried out for comparison to gain confidence in the proposed model. Finally, several numerical examples are solved by varying the important structural input parameters (material and geometry) and their influences discussed in detail.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leissa, A.W.: The free vibration of rectangular plates. J. Sound Vib. 31, 257–293 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-460X(73)80371-2
Liew, K.M., Hung, K.C., Lim, M.K.: A solution method for analysis of cracked plates under vibration. Eng. Fract. Mech. 48, 393–404 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7944(94)90130-9
Lee, H.P., Lim, S.P.: Vibration of cracked rectangular plates including transverse shear deformation and rotary inertia. Comput. Struct. 49, 715–718 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7949(93)90074-N
Brethee, K.F.: Free vibration analysis of clamped laminated composite plates with centeral crack. Anbar J. Eng. Sci. 9, 108–115 (2021)
Fujimoto, T., Wakata, K., Cao, F., Nisitani, H.: Vibration analysis of a cracked plate subjected to tension using a hybrid method of FEM and BFM. Mater. Sci. Forum. 440–441, 407–414 (2003). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.440-441.407
Guan-Liang, Q., Song-Nian, G., Jie-Sheng, J.: A finite element model of cracked plates and application to vibration problems. Comput. Struct. 39, 483–487 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7949(91)90056-R
Huang, C.S., Leissa, A.W.: Vibration analysis of rectangular plates with side cracks via the Ritz method. J. Sound Vib. 323, 974–988 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2009.01.018
Huang, C.S., Chan, C.W.: Vibration analyses of cracked plates by the ritz method with moving least-squares interpolation functions. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219455413500600
Asadigorji, H., Dardel, M.: Natural vibration analysis of rectangular plates with multiple all-over part- through cracks natural vibration analysis of rectangular plates with multiple all-over part through cracks. (2012)
Huang, C.S., Leissa, A.W., Chan, C.W.: Vibrations of rectangular plates with internal cracks or slits. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 53, 436–445 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2011.03.006
Rath, M.K., Sahu, S.K.: Vibration of woven fiber laminated composite plates in hygrothermal environment. JVC/Journal Vib. Control. 18, 1957–1970 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546311428638
Joshi, P.V., Jain, N.K., Ramtekkar, G.D.: Effect of thermal environment on free vibration of cracked rectangular plate: an analytical approach. Thin-Walled Struct. 91, 38–49 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2015.02.004
Xue, J., Wang, Y.: Free vibration analysis of a flat stiffened plate with side crack through the Ritz method. Arch. Appl. Mech. 89, 2089–2102 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-019-01565-6
Pushparaj, P., Suresha, B.: Free vibration analysis of laminated composite plates using finite element method. Polym. Polym. Compos. 24, 529–538 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/096739111602400712
Qu, G.M., Li, Y.Y., Cheng, L., Wang, B.: Vibration analysis of a piezoelectric composite plate with cracks. Compos. Struct. 72, 111–118 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2004.11.001
Damnjanović, E., Marjanović, M., Nefovska-Danilović, M.: Free vibration analysis of stiffened and cracked laminated composite plate assemblies using shear-deformable dynamic stiffness elements. Compos. Struct. 180, 723–740 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.08.038
Verma, A.K., Kumhar, V., Verma, M., Rastogi, V.: Vibration analysis of partially cracked symmetric laminated composite plates using Grey-Taguchi. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 12, 4529–4543 (2021)
Imran, M., Badshah, S., Khan, R.K.: Vibration analysis of cracked composite laminated plate: a review. Mehran Univ. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 38, 687–704 (2019)
Li, D.: Layerwise theories of laminated composite structures and their applications: a review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 28, 577–600 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-019-09392-2
Gayen, D., Tiwari, R., Chakraborty, D.: Static and dynamic analyses of cracked functionally graded structural components: a review. Compos. Part B Eng. 173, 106982 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106982
Ostachowicz, W., Krawczuk, M., Zak, A.: Natural frequencies of a multilayer composite plate with shape memory alloy wires. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 32, 71–83 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-874X(98)00076-6
Lau, K., Zhou, L., Tao, X.: Control of natural frequencies of a clamped–clamped composite beam with embedded shape memory alloy wires. Compos. Struct. 58, 39–47 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0263-8223(02)00042-9
Lau, K.: Vibration characteristics of SMA composite beams with different boundary conditions. Mater. Des. 23, 741–749 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-3069(02)00069-9
Barzegari, M.M., Dardel, M., Fathi, A., Pashaei, M.H.: Effect of shape memory alloy wires on natural frequency of plates. J. Mech. Eng. Autom. 2, 23–28 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5923/j.jmea.20120201.05
Barzegari, M.M., Dardel, M., Fathi, A.: Vibration analysis of a beam with embedded shape memory alloy wires. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 26, 536–550 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-9166(13)60048-8
Kheirikhah, M.M., Khosravi, P.: Buckling and free vibration analyses of composite sandwich plates reinforced by shape-memory alloy wires. J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 40, 515 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-018-1438-4
Zhang, R., Ni, Q.-Q., Masuda, A., Yamamura, T., Iwamoto, M.: Vibration characteristics of laminated composite plates with embedded shape memory alloys. Compos. Struct. 74, 389–398 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2005.04.019
Zhao, S., Teng, J., Wang, Z., Sun, X., Yang, B.: Investigation on the mechanical properties of SMA/GF/Epoxy hybrid composite laminates: flexural, impact, and interfacial shear performance. Materials (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11020246
Amabili, M.: A comparison of shell theories for large-amplitude vibrations of circular cylindrical shells: Lagrangian approach. J. Sound Vib. 264, 1091–1125 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-460X(02)01385-8
Panda, S.K., Singh, B.N.: Nonlinear finite element analysis of thermal post-buckling vibration of laminated composite shell panel embedded with SMA fibre. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 29, 47–57 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2013.01.007
Civalek, Ö.: Free vibration analysis of symmetrically laminated composite plates with first-order shear deformation theory (FSDT) by discrete singular convolution method. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 44, 725–731 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2008.04.001
Kamarian, S., Shakeri, M.: Natural Frequency Analysis of Composite Skew Plates with Embedded Shape Memory Alloys in Thermal Environment. AUT J. Mech. Eng. 1, 179–190 (2017)
Saeedi, A., Shokrieh, M.M.: Effect of shape memory alloy wires on the enhancement of fracture behavior of epoxy polymer. Polym. Test. 64, 221–228 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2017.10.009
Wang, E., Tian, Y., Wang, Z., Jiao, F., Guo, C., Jiang, F.: A study of shape memory alloy NiTi fiber/plate reinforced (SMAFR/SMAPR) Ti-Al laminated composites. J. Alloys Compd. 696, 1059–1066 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.062
Ali, O.M.M., Al-Kalali, R.H.M., Mubarak, E.M.M.: Vibrational analysis of composite beam embedded with Nitinol shape memory alloy wires. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 7, 143 (2018)
John, S., Hariri, M.: Effect of shape memory alloy actuation on the dynamic response of polymeric composite plates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 39, 769–776 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2008.02.005
Balasubramanian, M., Srimath, R., Vignesh, L., Rajesh, S.: Application of shape memory alloys in engineering - a review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2054/1/012078
Behera, A., Rajak, D.K., Kolahchi, R., Scutaru, M.-L., Pruncu, C.I.: Current global scenario of Sputter deposited NiTi smart systems. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 14582–14598 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.10.032
Taheri, M.N., Sabet, S.A., Kolahchi, R.: Experimental investigation of self-healing concrete after crack using nano-capsules including polymeric shell and nanoparticles core. Smart Struct. Syst. 25, 337–343 (2020)
Taherifar, R., Zareei, S.A., Bidgoli, M.R., Kolahchi, R.: Seismic analysis in pad concrete foundation reinforced by nanoparticles covered by smart layer utilizing plate higher order theory. Steel Compos. Struct. 37, 99–115 (2020)
Arbabi, A., Kolahchi, R., Bidgoli, M.R.: Experimental study for ZnO nanofibers effect on the smart and mechanical properties of concrete. Smart Struct. Syst. 25, 97–104 (2020). https://doi.org/10.12989/SSS.2020.25.1.097
Ghorbanpour Arani, A., Mortazavi, S.A., Kolahchi, R., Ghorbanpour Arani, A.H.: Vibration response of an elastically connected double-smart nanobeam-system based nano-electro-mechanical sensor. J. Solid Mech. 7, 121–130 (2015)
Xue, L., Dui, G., Liu, B., Zhang, J.: Theoretical analysis of a functionally graded shape memory alloy plate under graded temperature loading. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 23, 1181–1187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2015.1068398
Tobushi, H., Pieczyska, E., Ejiri, Y., Sakuragi, T.: Thermomechanical properties of shape-memory alloy and polymer and their composites. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 16, 236–247 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376490902746954
Panda, S.K., Singh, B.N.: Thermal post-buckling behaviour of laminated composite cylindrical/hyperboloid shallow shell panel using nonlinear finite element method. Compos. Struct. 91, 366–374 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2009.06.004
Mehar, K., Panda, S.K., Dehengia, A., Kar, V.R.: Vibration analysis of functionally graded carbon nanotube reinforced composite plate in thermal environment. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 18, 151–173 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/1099636215613324
Mehar, K., Mishra, P.K., Panda, S.K.: Numerical investigation of thermal frequency responses of graded hybrid smart nanocomposite (CNT-SMA-Epoxy) structure. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 28, 2242–2254 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2020.1725193
Cook RD, Malkus DS, Plesha ME, W.R.: Concepts and Applications of Finite Element Analysis. John Willy and Sons Pvt-Singapore (2003)
Reddy, J.N.: Mechanics of Laminated Composite Plates and Shells. CRC Press (2003)
Dewangan, H.C., Panda, S.K.: Numerical transient responses of cut-out borne composite panel and experimental validity. Proc. Inst Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 235, 1521–1536 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954410020977344
Dewangan, H.C., Sharma, N., Panda, S.K.: Numerical nonlinear static analysis of Cutout-Borne multilayered structures and experimental validation. AIAA J. 60, 985–997 (2022). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J060643
Bachene, M., Tiberkak, R., Rechak, S.: Vibration analysis of cracked plates using the extended finite element method. Arch. Appl. Mech. 79, 249–262 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-008-0224-7
Duan, B., Tawfik, M., Goek, S.N., Ro, J.-J., Mei, C.: Vibration of laminated composite plates embedded with shape memory alloy at elevated temperatures. Smart Struct. Mater. 2000 Ind. Commer. Appl. Smart Struct. Technol. 3991, 366–376 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.388179
Cross, W.B., Anthony, H.K., Frederick, J.S.: Nitinol characterization study. NASA, Langley Research Center (1969)
Mahabadi, R.K., Shakeri, M., Daneshpazhooh, M.: Free vibration of laminated composite plate with shape memory alloy fibers. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 13, 314–330 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1590/1679-78252162
Acknowledgements
SERB India supports this research work under Teachers Associateship for Research Excellence (TARE) scheme. The authors are thankful to TARE (SERB India) for their constant support. File no TAR/2020/000168 dated 19th Dec 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Individual terms of matrix [B]:
[B]1,1 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [B]1,3 = \(1/R_{x}\), [B]2,2 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [B]2,3 = \(1/R_{y}\), [B]3,1 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [B]3,2 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [B]3,3 = \(2/R_{xy}\), [B]4,1 = \(- 1/R_{x}\), [B]4,3 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [B]4,4 = 1, [B]5,2 = \(- 1/R_{y}\), [B]5,3 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [B]5,5 = 1, [B]6,4 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [B]7,5 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [B]8,4 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [B]8,5 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [B]9,4 = \(- 1/R_{x}\), [B]9,6 = 2, [B]10,5 = \(- 1/R_{y}\), [B]10,7 = 2, [B]11,6 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [B]12,7 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [B]13,6 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [B]13,7 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [B]14,6 = \(- 1/R_{x}\), [B]14,8 = 2, [B]15,7 = \(- 1/R_{y}\), [B]15,9 = 2, [B]16,8 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [B]17,9 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [B]18,8 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [B]18,9 = \(\partial /\partial x\),[B]19,8 = \(- 1/R_{x}\), [B]20,9 = \(- 1/R_{y}\).
Individual terms of matrix [BG]:
[BG]1,1 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [BG]1,3 = \(1/R_{x}\), [BG]2,1 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [BG]3,2 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [BG]4,2 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [BG]4,3 = \(1/R_{y}\), [BG]5,1 = \(- 1/R_{x}\), [BG]5,3 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [BG]6,2 = \(- 1/R_{y}\), [BG]6,3 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [BG]7,4 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [BG]8,4 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [BG]9,5 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [BG]10,5 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [BG]11,4 = \(- 1/R_{x}\), [BG]12,5 = \(- 1/R_{y}\), [BG]13,6 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [BG]14,6 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [BG]15,7 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [BG]16,7 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [BG]17,6 = \(- 1/R_{x}\), [BG]18,7 = \(- 1/R_{y}\), [BG]19,8 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [BG]20,8 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [BG]21,9 = \(\partial /\partial x\), [BG]22,9 = \(\partial /\partial y\), [BG]23,8 = \(- 1/R_{x}\), [BG]24,9 = \(- 1/R_{y}\).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erukala, K.K., Mishra, P.K., Dewangan, H.C. et al. Damaged composite structural strength enhancement under elevated thermal environment using shape memory alloy fiber. Acta Mech 233, 3133–3155 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03272-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-022-03272-w