Abstract
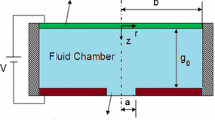
In this paper, the fluid flow and the diaphragm deflection are studied in the pneumatically actuated diaphragm microvalve by performing finite element and analytical fluid-structure interaction simulations. The results of these approaches are compared and their validity is discussed. An analytical relation is obtained for the critical diaphragm deflection which leads to unstable response of the microvalve. This relation shows that the critical deflection is only a function of the microvalve geometry, namely its inlet height and outlet radius. The phenomenon of the diaphragm deflection jump is justified in the microvalve behavior. The effect of different fluid flow and diaphragm parameters on the microvalve response is investigated that can be used to improve the microvalve design.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oh K.W., Ahn C.H.: A review of microvalves. J. Micromech. Microeng. 16, R13–R39 (2006)
Luharuka R., LeBlanc S., Bintoro J.S., Berthelot Y.H., Hesketh P.J.: Simulated and experimental dynamic response characterization of an electromagnetic microvalve. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 143, 399–408 (2008)
Takao H., Miyamura K., Ebi H., Ashiki M., Sawada K., Ishida M.: A MEMS microvalve with PDMS diaphragm and two-chamber configuration of thermo-pneumatic actuator for integrated blood test system on silicon. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 119, 468–475 (2005)
Pelesko J.A., Bernstein D.H.: Modeling MEMS and NEMS. Chapman & Hall/CRC, London (2003)
Yoo J.C., Choi Y.J., Kang C.J., Kim Y.S.: A novel polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic system including thermopneumatic-actuated micropump and Paraffin-actuated microvalve. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 139, 216–220 (2007)
Kim J.H., Na K.H., Kang C.J., Jeon D., Kim Y.S.: A disposable thermopneumatic-actuated microvalve stacked with PDMS layers and ITO-coated glass. Microelectron. Eng. 73(74), 864–869 (2004)
Li H.Q., Roberts D.C., Steyn J.L., Turner K.T., Yaglioglu O., Hagood N.W., Spearing S.M., Schmidt M.A.: Fabrication of a high frequency piezoelectric microvalve. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 111, 51–56 (2004)
Roberts D.C., Li H., Steyn J.L., Yaglioglu O., Spearing S.M., Schmidt M.A., Hagood N.W.: A Piezoelectric Microvalve for Compact High-Frequency, High-Differential Pressure Hydraulic Micropumping Systems. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2, 81–92 (2003)
Kim H., In C., Yoon G., Kim J.: A slim type microvalve driven by PZT films. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 121, 162–171 (2005)
Yoshida K., Tanaka S., Hagihara Y., Tomonari S., Esashi M.: Normally closed electrostatic microvalve with pressure balance mechanism for portable fuel cell application part I: design and simulation. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 157, 299–306 (2010)
Tanaka K.Y.S, Hagihara Y., Tomonari S., Esashi M.: Normally closed electrostatic microvalve with pressure balance mechanism for portable fuel cell application. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 157, 290–298 (2010)
Gong Q., Zhou Z., Yang Y., Wang X.: Design, optimization, and simulation on microelectromagnetic pump. Sens. Actuators A 83, 200–207 (2000)
Bintoro J.S., Hesketh P.J., Berthelot Y.H.: CMOS compatible bistable electromagnetic microvalve on a single wafer. Microelectron. J. 36, 667–672 (2005)
Vieider, C., Ohman, O., Elderstig, H.: A pneumatically actuated micro valve with silicone rubber membrane The 8th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors and Actuators, and Eurosensors IX, Sweden, 284–286(1995)
Yang F., Kao I.: Analysis of fluid flow and deflection for pressure-balanced MEMS diaphragm valves. Sens. Actuators 79, 13–21 (2000)
Wachutka, G.: Coupled-field modeling of microdevices and microsystems. In: Proceeding of the International Conference on Simulation of Semiconductor Processes and Devices, SISPAD 2002, Germany, 9–14 (2002)
Huff, M.A., Schmidt M.A.: Fabrication packaging and testing of a wafer-bonded microvalve. In: Proceedings IEEE Solid State Sensor and Actuator Workshop, Hilton Head Island, SC, 194–197 (1992)
Timoshenko S.: Theory of Plates and Shells. McGraw-Hill, NY (1989)
Wang C.M., Reddy J.N., Lee K.H.: Shear deformable beams and plates, relationships with classical solutions. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2000)
White F.M.: Fluid Mechanics, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, NY (2002)
Wang C.Y.: Axisymmetrically supported heavy circular plate. Thin-Walled Structures 42, 1709–1718 (2004)
Zhang Q., Hisada T.: Analysis of fluid-structure interaction problems with structural buckling and large domain changes by ALE finite element method. Comput. Method. Appl. Mech. Eng. 190, 6341–6357 (2001)
Afrasiab, H., Movahhedy, M.R., Assempour A.: Fluid–structure interaction analysis in microfluidic devices: A dimensionless finite element approach. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids. doi:10.1002/fld.2592 (2011)
Donea J., Huerta A.: Finite Element Methods for Flow Problems. Wiley, Chichester (2003)
Belytschko T., Liu W.K., Moran B.: Nonlinear finite element for continua and structures. Wiley, NY (2000)
Horn, J., Turek, S.: Proposal for Numerical Benchmarking of Fluid-Structure Interaction between an Elastic Object and Laminar Incompressible Flow. In: Bungartz, H.J., Schafer, M. Fluid-Structure Interaction: Modelling, Simulation, Optimisation LNCSE., Springer, Berlin (2006)
Stein K., Tezduyar T.E., Benney R.: Mesh moving techniques for fluid-structure interactions with large displacements. J. Appl. Mech. 70, 59–63 (2003)
Cavallo P.A., Hosangadi A., Lee R.A., Dash S.M.: Dynamic unstructured grid methodology with application to aero/propulsive flowfields. AIAA Paper 97, 2310 (1997)
Farhat C., Degand C., Koobus B., Lesoinne M.: Torsional springs for two dimensional dynamic unstructured fluid meshes. Comput. Method. Appl. Mech. Engrg. 163, 231–245 (1998)
Gao X.W., Chen P.C., Tang L.: Deforming mesh for computational aeroelasticity using a nonlinear elastic boundary element method. AIAA J. 40, 1512–1517 (2002)
Johnson A.A., Tezduyar T.E.: Advanced mesh generation and update methods for 3D flow simulations. Comput. Mech. 23, 130–143 (1999)
Yoseph P.Z.B., Mereu S., Chippada S., Kalro V.J.: Automatic monitoring of element shape quality in 2-D and 3-D computational mesh dynamics. Comput. Mech. 27, 378–395 (2001)
Nielsen E.J., Anderson W.K.: Recent improvements in aerodynamic design optimization on unstructured meshes. AIAA J. 40, 1155–1163 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afrasiab, H., Movahhedy, M.R. & Assempour, A. Finite element and analytical fluid-structure interaction analysis of the pneumatically actuated diaphragm microvalves. Acta Mech 222, 175 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-011-0508-9
Received:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-011-0508-9