Abstract
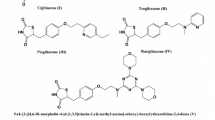
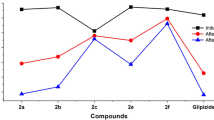
Sulfonylurea drugs are widely used for the therapy of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. These drugs improve glucose and lipid levels by stimulating insulin secretion by the pancreatic β-cell comprising two generations with the second one more potent than the first. Glibenclamide is a well-known and potent second-generation sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic drug which is most widely used in type II diabetes. In this research, five new analogs were synthesized by exchanging the lipophilic phenyl and urea moieties in the first and the end of the molecule with chlorobenzamide and hydrophilic and antidiabetic aminobenzothiazole substituents. Their glucose and lipid-lowering activities were evaluated and compared to the standard drug. Results showed that all of the new compounds exhibited better activities. In addition, in particular aminomethylbenzothiazoles derivatives could have exerted prominent hypoglycemic and a noticeable hypolipidemic effects superior to glibenclamide.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakrabarti R, Vikramadithyan RK, Mullangi R, Sharma VM, Jagadheshan H, Rao YN, Sairam P, Rajagopalan R (2002) J Ethnopharmacol 81:343
Satoh J, Takahashi K, Takizawa Y, Ishihara H, Hirai M, Katagiri H, Hinokio Y, Suzuki S, Tsuji I, Oka Y (2005) Diabetes Res Clin Pract 70:291
Jawale DV, Pratap UR, Rahuja N, Srivastava AK, Mane RA (2012) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:436
McClenaghan NH, Ball AJ, Flatt PR (2001) Biochem Pharmacol 61:527
Pill J, Kühnle HF (1999) Metabolism 48:34
Ahmadi A, Khalili M, Farsadrooh M, Ghiasi M, Nahri-Niknafs B (2013) Drug Res 63:614
Ahmadi A, Khalili M, Khatami K, Farsadrooh M, Nahri-Niknafs B (2014) Mini Rev Med Chem 14:208
Velingkar VS, Dandekar VD, Murugananthan K (2009) Inter J Pharm Pharm Sci 1:149
Schneider S, Ueberberg S, Korobeynikov A, Schechinger W, Schwanstecher C, Schwanstecher M, Klein HH, Schirrmacher E (2007) Regul Pept 139:1
Zaman MK, Arayne MS, Sultana N, Farooq A (2006) Pak J Pharm Sci 19:114
Mariappan G, Prabhat P, Sutharson L, Banerjee J, Patangia U, Nath S (2012) J Korean Chem Soc 56:251
Patel SS, Shah RS, Goyal RK (2009) Indian J Exp Biol 47:564
Latha RC, Daisy P (2011) Chem Biol Interact 189:112
Tyagi S, Kumar S, Kumar A, Singla M (2010) Int J Pharm World Res 1:1
Rathish IG, Javed K, Bano S, Ahmad S, Alam MS, Pillai KK (2009) Eur J Med Chem 44:2673
Meyer M, Chudziak F, Schwanstecher C, Schwanstecher M, Panten U (1999) Br J Pharmacol 128:27
Proks P, Reimann F, Green N, Gribble F, Ashcroft F (2002) Diabetes 51:S368
Calderone V, Rapposelli S, Martelli A, Digiacomo M, Testai L, Torri S, Marchetti P, Breschi MC, Balsamo A (2009) Bioorg Med Chem 17:5426
Meltzer-Mats E, Babai-Shani G, Pasternak L, Uritsky N, Getter T, Viskind O, Eckel J, Cerasi E, Senderowitz H, Sasson S, Gruzman A (2013) J Med Chem 56:5335
Devaki K, Beulah U, Akila G, Narmadha R, Gopalakrishnan VK (2011) J Basic Clin Pharm 2:167
Acknowledgments
This work was a research project at Karaj Branch, Islamic Azad University, Iran and the authors would like to express their gratitude to them. They thank Fariba Ansari for her assistance with the pharmacological tests. They appreciate Mojtaba Chaichi, EFL educator at Safir English Language Academy, for proofreading the initial draft of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadi, A., Khalili, M., Ghaderi, P. et al. Synthesis and blood glucose and lipid-lowering effects of benzothiazole-substituted benzenesulfonylurea derivatives. Monatsh Chem 146, 2059–2065 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-015-1471-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-015-1471-2