Summary.
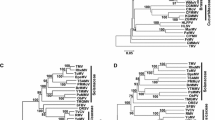
Molecular studies have been carried out on Tomato mild mottle virus (TMMV) and 2322 nucleotides of the aphid-transmitted virus have been sequenced. This translates to a 2187 nucleotide open reading frame and a 135 nucleotide untranslated region (UTR) followed by a poly A tail. The sequence is consistent with the NIb and coat protein regions of a member of the Potyviridae family of viruses. Sequence comparisons show this virus to have no close relationship with any previously sequenced aphid-transmitted virus; the highest identity was found with the whitefly-transmitted Ipomoviruses. The vector of transmission and the low level of sequence identity with other aphid-transmitted viruses suggest TMMV does not belong to any existing genus of the Potyviridae family.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received March 26, 2001 Accepted August 6, 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monger, W., Spence, N. & Foster, G. Molecular evidence that the aphid-transmitted Tomato mild mottle virus belongs to the Potyviridae family but not the Potyvirus genus. Arch. Virol. 146, 2435–2441 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050170013
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050170013