Summary
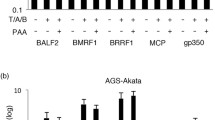
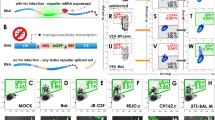
Studies of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection and pathogenesis are limited by the lack of recombinant EBV bearing a reporter gene. Currently such studies typically utilize cellular transformation and immortalization as indicators of virus infection which takes several weeks. To investigate the dependence on known cellular receptors for EBV infection, a novel enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) expressing virus, designated EBfaV-GFP, was used to infect a variety of different cell types. EBfaV-GFP infects B lymphoma-derived cell lines, lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) and primary B cells, as judged by expression of EGFP. Ability of clonal cells to be infected with EBfaV-GFP correlates with expression of the known EBV entry mediators CD21 and HLA-DR. EGFP-expressing LCLs were derived by infection of primary B cells with EBfaV-GFP. Cells of the Jurkat line, derived from T lymphocytes, could not be infected, and infected primary lymphocytes did not include appreciable numbers of CD2-positive cells, showing that EBV rarely infects T cells. Expression of EGFP by EBV provides the opportunity to rapidly visualize infection in living cells and better delineate populations of infected cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received October 22, 1998. Accepted January 25, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Speck, P., Longnecker, R. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection visualized by EGFP expression demonstrates dependence on known mediators of EBV entry. Arch. Virol. 144, 1123–1137 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050574
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050574