Summary
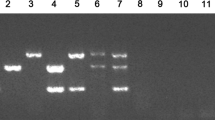
A nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was established to detect exogenous feline leukaemia virus (FeLV) proviral DNA in feline peripheral blood leukocytes (PBL). The assay detected a single copy of plasmid DNA of an infectious molecular clone of FeLV subgroup A in the sample by ethidium bromide staining in agarose gels. The utility of the nested PCR in the diagnosis of FeLV infections was compared with the detection of FeLV p27 antigen by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and virus isolation (VI). FeLV genomes were detected by PCR in all 4 samples that were positive by ELISA and VI but in none of 7 samples that were negative by the two methods. FeLV genomes were found by PCR in 13 of 39 samples from cats that were antigenaemic but from which no virus was isolated (‘discordant’ cats). These results demonstrated that a proportion of discordant cats harboured FeLV genome in their PBL.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received June 29, 1996 Accepted August 29, 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyazawa, T., Jarrett, O. Feline leukaemia virus proviral DNA detected by polymerase chain reaction in antigenaemic but non-viraemic (‘discordant’) cats. Arch. Virol. 142, 323–332 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050079
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050079