Summary
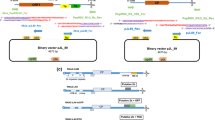
Leading from the success of inoculating plants with viral RNA transcribed in vitro from full length cDNA clones, attempts have been made to build cDNA clones which are directly infectious by inoculation. However, we and others have found that viral cDNA clones driven by the CaMV 35S promoter were able to infect some host plants yet not others, when manually inoculated onto leaves. Alternative methods including microprojectile bombardment have been used to deliver an infectious TMV construct into plant cells resulting in the infection of all TMV host plants tested. Lack of infection via manual inoculation may be due to unsuccessful delivery of a viable construct into the plant cell nucleus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received May 13, 1996 Accepted August 5, 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dagless, E.M., Shintaku, M.H., Nelson, R.S. et al. A CaMV 35S promoter driven cDNA clone of tobacco mosaic virus can infect host plant tissue despite being uninfectious when manually inoculated onto leaves. Arch. Virol. 142, 183–191 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050069
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050069