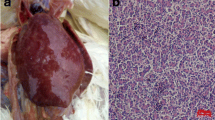
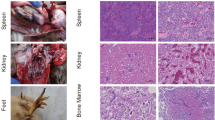
Abstract
Avian leukosis virus (ALV) causes high mortality associated with tumor formation and decreased fertility, and results in major economic losses in the poultry industry worldwide. Recently, a putative novel ALV subgroup virus named ALV-K was observed in Chinese local chickens. In this study, a novel ALV strain named GD14LZ was isolated from a Chinese local yellow broiler in 2014. The proviral genome was sequenced and phylogenetically analyzed. The replication ability and pathogenicity of this virus were also evaluated. The complete proviral genome sequence of GD14LZ was 7482 nt in length, with a genetic organization typical of replication-competent type C retroviruses lacking viral oncogenes. Sequence analysis showed that the gag, pol and gp37 genes of GD14LZ have high sequence similarity to those of other ALV strains (A–E subgroups), especially to those of ALV-E. The gp85 gene of the GD14LZ isolate showed a low sequence similarity to those other ALV strains (A–E subgroups) but showed high similarity to strains previously described as ALV-K. Phylogenetic analysis of gp85 also suggested that the GD14LZ isolate was related to ALV-K strains. Further study showed that this isolate replicated more slowly and was less pathogenic than other ALV strains. These results indicate that the GD14LZ isolate belongs to the novel subgroup ALV-K and probably arose by recombination of ALV-K with endogenous viruses with low replication and pathogenicity. This virus might have existed in local Chinese chickens for a long time.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Payne LN, Brown SR, Bumstead N, Howes K, Frazier JA, Thouless ME (1991) A novel subgroup of exogenous avian leukosis virus in chickens. J Gen Virol 72(Pt 4):801–807
Fadly AM (2003) Neoplastic diseases: leukosis/sarcomagroup. In: Diseases of poultry, 11th edn. Blackwell Publishing Co, Ames
Payne LN, Nair V (2012) The long view: 40 years of avian leukosis research. Avian Pathol 41:11–19
Zhang QC, Zhao DM, Guo HJ, Cui ZZ (2010) Isolation and identification of a subgroup A avian leukosis virus from imported meat-type grand-parent chickens. Virol Sin 25:130–136
Reinisova M, Plachy J, Kucerova D, Senigl F, Vinkler M, Hejnar J (2016) Genetic diversity of NHE1, receptor for subgroup J avian leukosis virus, in domestic chicken and wild anseriform species. PLoS One 11:e150589
Zhao DM, Zhang QC, Cui ZZ (2010) Isolation and identification of a subgroup B avian leukosis virus from chickens of Chinese native breed Luhua. Bing Du Xue Bao 26:53–57 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Ji J, Li H, Zhang H, Xie Q, Chang S, Shang H, Ma J, Bi Y (2012) Complete genome sequence of an avian leukosis virus isolate associated with hemangioma and myeloid leukosis in egg-type and meat-type chickens. J Virol 86:10907–10908
Li H, Xue C, Ji J, Chang S, Shang H, Zhang L, Ma J, Bi Y, Xie Q (2012) Complete genome sequence of a J subgroup avian leukosis virus isolated from local commercial broilers. J Virol 86:11937–11938
Chang SW, Hsu MF, Wang CH (2013) Gene detection, virus isolation, and sequence analysis of avian leukosis viruses in Taiwan country chickens. Avian Dis 57:172–177
Wang X, Zhao P, Cui ZZ (2012) Identification of a new subgroup of avian leukosis virus isolated from Chinese indigenous chicken breeds. Bing Du Xue Bao 28:609–614 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Cui N, Su S, Chen Z, Zhao X, Cui Z (2014) Genomic sequence analysis and biological characteristics of a rescued clone of avian leukosis virus strain JS11C1, isolated from indigenous chickens. J Gen Virol 95:2512–2522
Dong X, Zhao P, Xu B, Fan J, Meng F, Sun P, Ju S, Li Y, Chang S, Shi W, Cui Z (2015) Avian leukosis virus in indigenous chicken breeds, China. Emerg Microbes Infect 4:e76
Maas R, van Zoelen D, Oei H, Claassen I (2006) Replacement of primary chicken embryonic fibroblasts (CEF) by the DF-1 cell line for detection of avian leucosis viruses. Biologicals 34:177–181
Smith EJ, Fadly A, Okazaki W (1979) An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses. Avian Dis 23:698–707
Chen W, Liu Y, Li H, Chang S, Shu D, Zhang H, Chen F, Xie Q (2015) Intronic deletions of tva receptor gene decrease the susceptibility to infection by avian sarcoma and leukosis virus subgroup A. Sci Rep 5:9900
Himly M, Foster DN, Bottoli I, Iacovoni JS, Vogt PK (1998) The DF-1 chicken fibroblast cell line: transformation induced by diverse oncogenes and cell death resulting from infection by avian leukosis viruses. Virology 248:295–304
Schaefer-Klein J, Givol I, Barsov EV, Whitcomb JM, VanBrocklin M, Foster DN, Federspiel MJ, Hughes SH (1998) The EV-O-derived cell line DF-1 supports the efficient replication of avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses and vectors. Virology 248:305–311
Chesters PM, Smith LP, Nair V (2006) E (XSR) element contributes to the oncogenicity of Avian leukosis virus (subgroup J). J Gen Virol 87(Pt 9):2685–2692
Laimins LA, Tsichlis P, Khoury G (1984) Multiple enhancer domains in the 3’ terminus of the Prague strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res 12:6427–6442
Cullen BR, Raymond K, Ju G (1985) Functional analysis of the transcription control region located within the avian retroviral long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol 5:438–447
Zachow KR, Conklin KF (1992) CArG, CCAAT, and CCAAT-like protein binding sites in avian retrovirus long terminal repeat enhancers. J Virol 66:1959–1970
Barbosa T, Zavala G, Cheng S (2008) Molecular characterization of three recombinant isolates of avian leukosis virus obtained from contaminated Marek’s disease vaccines. Avian Dis 52:245–252
Ryden TA, Beemon K (1989) Avian retroviral long terminal repeats bind CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol 9:1155–1164
Ruddell A (1995) Transcription regulatory elements of the avian retroviral long terminal repeat. Virology 206:1–7
Zavala G, Cheng S (2006) Detection and characterization of avian leukosis virus in Marek’s disease vaccines. Avian Dis 50:209–215
Silva RF, Fadly AM, Taylor SP (2007) Development of a polymerase chain reaction to differentiate avian leukosis virus (ALV) subgroups: detection of an ALV contaminant in commercial Marek’s disease vaccines. Avian Dis 51:663–667
Cui Z, Du Y, Zhang Z, Silva RF (2003) Comparison of Chinese field strains of avian leukosis subgroup J viruses with prototype strain HPRS-103 and United States strains. Avian Dis 47:1321–1330
Summers BACJ (ed) (1995) Tumors of the central nervous system. In: Veterinary neuropathology. Mosby-Year Book, St Louis
Swayne DEFO (ed) Nervous system. In: Fletcher OJ, Abdul-Aziz T (eds) Avian histopathology, 3rd edn. American Association of Avian Pathologists, Jacksonville, pp 260–291
Iwata N, Ochiai K, Hayashi K, Ohashi K, Umemura T (2002) Avian retrovirus infection causes naturally occurring glioma: Isolation and transmission of a virus from so-called fowl glioma. Avian Pathol 31:193–199
Nakamura S, Ochiai K, Hatai H, Ochi A, Sunden Y, Umemura T (2011) Pathogenicity of avian leukosis viruses related to fowl glioma-inducing virus. Avian Pathol 40:499–505
Hatai H, Ochiai K, Nagakura K, Imanishi S, Ochi A, Kozakura R, Ono M, Goryo M, Ohashi K, Umemura T (2008) A recombinant avian leukosis virus associated with fowl glioma in layer chickens in Japan. Avian Pathol 37:127–137
Gowda S, Rao AS, Kim YW, Guntaka RV (1998) Identification of sequences in the long terminal repeat of avian sarcoma virus required for efficient transcription. Virology 162:243–247
Gao Y, Guan X, Liu Y, Li X, Yun B, Qi X, Wang Y, Gao H, Cui H, Liu C (2015) An avian leukosis virus subgroup J isolate with a Rous sarcoma virus-like 5’-LTR shows enhanced replication capability. J Gen Virol 96:150–158
Zavala G, Cheng S (2006) Experimental infection with avian leukosis virus isolated from Marek’s disease vaccines. Avian Dis 50:232–237
Ochi A, Ochiai K, Kobara A, Nakamura S, Hatai H, Handharyani E, Tiemann I, Tanaka IR, Toyoda T, Abe A (2012) Epidemiological study of fowl glioma-inducing virus in chickens in Asia and Germany. Avian Pathol 41:299–309
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. S2013030013313), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31472217), and the Guangdong Province Science and Technology Plan Project (Grant No. 2012B020306002, 2012B091100078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that have no competing interests.
Ethics statement
The animal experiment was carried out in accordance with the institutional and national guidelines for the use and care of laboratory animals. Use of animals in this study was approved by the South China Agricultural University Committee of Animal Experiments (approval ID: 201004152).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Lin, W., Chang, S. et al. Isolation, identification and evolution analysis of a novel subgroup of avian leukosis virus isolated from a local Chinese yellow broiler in South China. Arch Virol 161, 2717–2725 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-016-2965-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-016-2965-x