Abstract
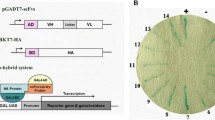
Influenza A viruses (IAV) are widespread in birds and domestic poultry, occasionally causing severe epidemics in humans and posing health threats. Hence, the need to develop a strategy for prophylaxis or therapy, such as a broadly neutralizing antibody against IAV, is urgent. In this study, single-chain variable fragment (scFv) phage display technology was used to select scFv fragments recognizing influenza envelope proteins. The Tomlinson I and J scFv phage display libraries were screened against the recombinant HA2 protein (rHA2) for three rounds. Only the third-round elution sample of the Tomlinson J library showed high binding affinity to rHA2, from which three clones (3JA18, 3JA62, and 3JA78) were chosen for preparative-scale production as soluble antibody by E. coli. The clone 3JA18 was selected for further tests due to its broad affinity for influenza H1N1, H3N2 and H5N1. Simulations of the scFv 3JA18-HA trimer complex revealed that the complementarity-determining region of the variable heavy chain (VH-CDR2) bound the stem region of HA. Neutralization assays using a peptide derived from VH-CDR2 also supported the simulation model. Both the selected antibody and its derived peptide were shown to suppress infection with H5N1 and H1N1 viruses, but not H3N2 viruses. The results also suggested that the scFvs selected from rHA2 could have neutralizing activity by interfering with the function of the HA stem region during virus entry into target cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peiris JS, de Jong MD, Guan Y (2007) Avian influenza virus (H5N1): a threat to human health. Clin Microbiol Rev 20(2):243–267. doi:10.1128/CMR.00037-06
Smith DJ, Lapedes AS, de Jong JC, Bestebroer TM, Rimmelzwaan GF, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA (2004) Mapping the antigenic and genetic evolution of influenza virus. Science 305(5682):371–376. doi:10.1126/science.1097211
Lynch GW, Selleck P, Church WB, Sullivan JS (2012) Seasoned adaptive antibody immunity for highly pathogenic pandemic influenza in humans. Immunol Cell Biol 90(2):149–158. doi:10.1038/icb.2011.38
Mei L, Song P, Tang Q, Shan K, Tobe RG, Selotlegeng L, Ali AH, Cheng Y, Xu L (2013) Changes in and shortcomings of control strategies, drug stockpiles, and vaccine development during outbreaks of avian influenza A H5N1, H1N1, and H7N9 among humans. Biosci Trends 7(2):64–76 (656 [pii])
Moscona A (2009) Global transmission of oseltamivir-resistant influenza. N Engl J Med 360(10):953–956. doi:10.1056/NEJMp0900648
Pielak RM, Schnell JR, Chou JJ (2009) Mechanism of drug inhibition and drug resistance of influenza A M2 channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(18):7379–7384. doi:10.1073/pnas.0902548106
Zhang H, Hale BG, Xu K, Sun B (2013) Viral and host factors required for avian H5N1 influenza A virus replication in mammalian cells. Viruses 5(6):1431–1446. doi:10.3390/v5061431
Skehel JJ, Wiley DC (2000) Receptor binding and membrane fusion in virus entry: the influenza hemagglutinin. Annu Rev Biochem 69:531–569. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.531
Vareckova E, Mucha V, Kostolansky F (2013) HA2 glycopolypeptide of influenza A virus and antiviral immunity. Acta Virol 57(2):247–256. doi:10.4149/av_2013_02_247
Whittle JRR, Zhang RJ, Khurana S, King LR, Manischewitz J, Golding H, Dormitzer PR, Haynes BF, Walter EB, Moody MA, Kepler TB, Liao HX, Harrison SC (2011) Broadly neutralizing human antibody that recognizes the receptor-binding pocket of influenza virus hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(34):14216–14221. doi:10.1073/pnas.1111497108
Krause JC, Tsibane T, Tumpey TM, Huffman CJ, Basler CF, Crowe JE (2011) A broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibody that recognizes a conserved, novel epitope on the globular head of the influenza H1N1 virus hemagglutinin. J Virol 85(20):10905–10908. doi:10.1128/Jvi.00700-11
Ekiert DC, Kashyap AK, Steel J, Rubrum A, Bhabha G, Khayat R, Lee JH, Dillon MA, O’Neil RE, Faynboym AM, Horowitz M, Horowitz L, Ward AB, Palese P, Webby R, Lerner RA, Bhatt RR, Wilson IA (2012) Cross-neutralization of influenza A viruses mediated by a single antibody loop. Nature 489(7417):526. doi:10.1038/Nature11414
Prabhu N, Prabakaran M, Ho HT, Velumani S, Qiang J, Goutama M, Kwang J (2009) Monoclonal antibodies against the fusion peptide of hemagglutinin protect mice from lethal influenza A virus H5N1 infection. J Virol 83(6):2553–2562. doi:10.1128/JVI.02165-08
Throsby M, van den Brink E, Jongeneelen M, Poon LL, Alard P, Cornelissen L, Bakker A, Cox F, van Deventer E, Guan Y, Cinatl J, ter Meulen J, Lasters I, Carsetti R, Peiris M, de Kruif J, Goudsmit J (2008) Heterosubtypic neutralizing monoclonal antibodies cross-protective against H5N1 and H1N1 recovered from human IgM+ memory B cells. PLoS One 3(12):e3942. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003942
Sui J, Hwang WC, Perez S, Wei G, Aird D, Chen LM, Santelli E, Stec B, Cadwell G, Ali M, Wan H, Murakami A, Yammanuru A, Han T, Cox NJ, Bankston LA, Donis RO, Liddington RC, Marasco WA (2009) Structural and functional bases for broad-spectrum neutralization of avian and human influenza A viruses. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16(3):265–273. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1566
Corti D, Voss J, Gamblin SJ, Codoni G, Macagno A, Jarrossay D, Vachieri SG, Pinna D, Minola A, Vanzetta F, Silacci C, Fernandez-Rodriguez BM, Agatic G, Bianchi S, Giacchetto-Sasselli I, Calder L, Sallusto F, Collins P, Haire LF, Temperton N, Langedijk JP, Skehel JJ, Lanzavecchia A (2011) A neutralizing antibody selected from plasma cells that binds to group 1 and group 2 influenza A hemagglutinins. Science 333(6044):850–856. doi:10.1126/science.1205669
Schneemann A, Speir JA, Tan GS, Khayat R, Ekiert DC, Matsuoka Y, Wilson IA (2012) A virus-like particle that elicits cross-reactive antibodies to the conserved stem of influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Virol 86(21):11686–11697. doi:10.1128/JVI.01694-12
Ekiert DC, Bhabha G, Elsliger MA, Friesen RH, Jongeneelen M, Throsby M, Goudsmit J, Wilson IA (2009) Antibody recognition of a highly conserved influenza virus epitope. Science 324(5924):246–251. doi:10.1126/science.1171491
Burton DR, Poignard P, Stanfield RL, Wilson IA (2012) Broadly neutralizing antibodies present new prospects to counter highly antigenically diverse viruses. Science 337(6091):183–186. doi:10.1126/science.1225416
Brandenburg B, Koudstaal W, Goudsmit J, Klaren V, Tang C, Bujny MV, Korse HJWM, Kwaks T, Otterstrom JJ, Juraszek J, van Oijen AM, Vogels R, Friesen RHE (2013) Mechanisms of hemagglutinin targeted influenza virus neutralization. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080034
Carmen S, Jermutus L (2002) Concepts in antibody phage display. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 1(2):189–203
Pansri P, Jaruseranee N, Rangnoi K, Kristensen P, Yamabhai M (2009) A compact phage display human scFv library for selection of antibodies to a wide variety of antigens. BMC Biotechnol 9:6. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-9-6
Kierny MR, Cunningham TD, Kay BK (2012) Detection of biomarkers using recombinant antibodies coupled to nanostructured platforms. Nano Rev. doi:10.3402/nano.v3i0.17240
Li ZJ, Cho CH (2012) Peptides as targeting probes against tumor vasculature for diagnosis and drug delivery. J Transl Med. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-10-S1-S1
Eisenhardt SU, Schwarz M, Bassler N, Peter K (2007) Subtractive single-chain antibody (scFv) phage-display: tailoring phage-display for high specificity against function-specific conformations of cell membrane molecules. Nat Protoc 2(12):3063–3073. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.455
Ueberberg S, Schneider S (2010) Phage library-screening: a powerful approach for generation of targeting-agents specific for normal pancreatic islet-cells and islet-cell carcinoma in vivo. Regul Pept 160(1–3):1–8. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2009.11.017
Poungpair O, Chaicumpa W, Kulkeaw K, Maneewatch S, Thueng-in K, Srimanote P, Tongtawe P, Songserm T, Lekcharoensuk P, Tapchaisri P (2009) Human single chain monoclonal antibody that recognizes matrix protein of heterologous influenza A virus subtypes. J Virol Methods 159(1):105–111. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.03.010
Yodsheewan R, Maneewatch S, Srimanote P, Thueng-In K, Songserm T, Dong-Din-On F, Bangphoomi K, Sookrung N, Choowongkomon K, Chaicumpa W (2013) Human monoclonal ScFv specific to NS1 protein inhibits replication of influenza viruses across types and subtypes. Antiviral Res 100(1):226–237. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.07.019
Zhang X, Qi X, Zhang Q, Zeng X, Shi Z, Jin Q, Zhan F, Xu Y, Liu Z, Feng Z, Jiao Y (2013) Human 4F5 single-chain Fv antibody recognizing a conserved HA1 epitope has broad neutralizing potency against H5N1 influenza A viruses of different clades. Antiviral Res 99(2):91–99. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.05.001
de Wildt RM, Mundy CR, Gorick BD, Tomlinson IM (2000) Antibody arrays for high-throughput screening of antibody-antigen interactions. Nat Biotechnol 18(9):989–994. doi:10.1038/79494
Lin SC, Jan JT, Dionne B, Butler M, Huang MH, Wu CY, Wong CH, Wu SC (2013) Different immunity elicited by recombinant H5N1 hemagglutinin proteins containing pauci-mannose, high-mannose, or complex type N-glycans. PLoS One 8(6):e66719. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066719
Wu CY, Yeh YC, Yang YC, Chou C, Liu MT, Wu HS, Chan JT, Hsiao PW (2010) Mammalian expression of virus-like particles for advanced mimicry of authentic influenza virus. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/Journal.Pone.0009784
Lin Y, Wu C, Li T, Hsiao P, Chang D (2014) A rapid and sensitive early diagnosis of influenza virus subtype via surface enhanced raman scattering. J Biosens Bioelectron 5(150):2
Imai M, Watanabe T, Hatta M, Das SC, Ozawa M, Shinya K, Zhong G, Hanson A, Katsura H, Watanabe S, Li C, Kawakami E, Yamada S, Kiso M, Suzuki Y, Maher EA, Neumann G, Kawaoka Y (2012) Experimental adaptation of an influenza H5 HA confers respiratory droplet transmission to a reassortant H5 HA/H1N1 virus in ferrets. Nature 486(7403):420–428. doi:10.1038/nature10831
Chang DK, Cheng SF, Deo Trivedi V, Yang SH (2000) The amino-terminal region of the fusion peptide of influenza virus hemagglutinin HA2 inserts into sodium dodecyl sulfate micelle with residues 16-18 at the aqueous boundary at acidic pH. Oligomerization and the conformational flexibility. J Biol Chem 275(25):19150–19158. doi:10.1074/jbc.M907148199
Chen J, Skehel JJ, Wiley DC (1998) A polar octapeptide fused to the N-terminal fusion peptide solubilizes the influenza virus HA2 subunit ectodomain. Biochemistry 37(39):13643–13649. doi:10.1021/bi981098l
Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhang C, Liu Y, Liu X (2012) Isolation of single chain variable fragment (scFv) specific for Cry1C toxin from human single fold scFv libraries. Toxicon 60(7):1290–1297. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2012.08.014
Nefkens I, Garcia JM, Ling CS, Lagarde N, Nicholls J, Tang DJ, Peiris M, Buchy P, Altmeyer R (2007) Hemagglutinin pseudotyped lentiviral particles: characterization of a new method for avian H5N1 influenza sero-diagnosis. J Clin Virol 39(1):27–33. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2007.02.005
Wu J, Zeng XQ, Zhang HB, Ni HZ, Pei L, Zou LR, Liang LJ, Zhang X, Lin JY, Ke CW (2014) Novel phage display-derived H5N1-specific scFvs with potential use in rapid avian flu diagnosis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(5):704–713. doi:10.4014/jmb.1311.11107
Dreyfus C, Laursen NS, Kwaks T, Zuijdgeest D, Khayat R, Ekiert DC, Lee JH, Metlagel Z, Bujny MV, Jongeneelen M, van der Vlugt R, Lamrani M, Korse HJ, Geelen E, Sahin O, Sieuwerts M, Brakenhoff JP, Vogels R, Li OT, Poon LL, Peiris M, Koudstaal W, Ward AB, Wilson IA, Goudsmit J, Friesen RH (2012) Highly conserved protective epitopes on influenza B viruses. Science 337(6100):1343–1348. doi:10.1126/science.1222908
Tharakaraman K, Subramanian V, Cain D, Sasisekharan V, Sasisekharan R (2014) Broadly neutralizing influenza hemagglutinin stem-specific antibody CR8020 targets residues that are prone to escape due to host selection pressure. Cell Host Microbe 15(5):644–651. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2014.04.009
Ekiert DC, Friesen RH, Bhabha G, Kwaks T, Jongeneelen M, Yu W, Ophorst C, Cox F, Korse HJ, Brandenburg B, Vogels R, Brakenhoff JP, Kompier R, Koldijk MH, Cornelissen LA, Poon LL, Peiris M, Koudstaal W, Wilson IA, Goudsmit J (2011) A highly conserved neutralizing epitope on group 2 influenza A viruses. Science 333(6044):843–850. doi:10.1126/science.1204839
Russell RJ, Kerry PS, Stevens DJ, Steinhauer DA, Martin SR, Gamblin SJ, Skehel JJ (2008) Structure of influenza hemagglutinin in complex with an inhibitor of membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(46):17736–17741. doi:10.1073/pnas.0807142105
Fleishman SJ, Whitehead TA, Ekiert DC, Dreyfus C, Corn JE, Strauch EM, Wilson IA, Baker D (2011) Computational design of proteins targeting the conserved stem region of influenza hemagglutinin. Science 332(6031):816–821. doi:10.1126/science.1202617
Nabel GJ, Fauci AS (2010) Induction of unnatural immunity: prospects for a broadly protective universal influenza vaccine. Nature medicine 16(12):1389–1391. doi:10.1038/nm1210-1389
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (grant number 99-2113-M-001-024-MY3 and 102-2113-M-001-008-MY2). We thank Dr. Jia-Tsrong Jan and Hsiu-Hwa Ma (Genomics Research Center, Academia Sinica) for providing us with influenza viruses. We thank Dr. Hsien-Ming Lee (Institute of Chemistry, Academia Sinica) for providing the microscopy system. We also thank Dr. Han-Chung Wu and Dr. Ruei-Min Lu (Institute of Cellular and Organismic Biology, Academia Sinica) for discussion on the experimental design of the scFv technique.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, TW., Cheng, SF., Tseng, YT. et al. Development of single-chain variable fragments (scFv) against influenza virus targeting hemagglutinin subunit 2 (HA2). Arch Virol 161, 19–31 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2625-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2625-6