Abstract
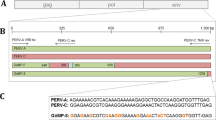
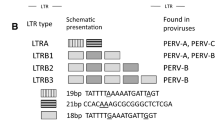
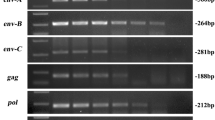
Porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERV) are widely distributed in the genomes of pigs. PERV-A and PERV-B are present in all pigs. They infect human cells in vitro and therefore represent a risk for xenotransplantation when pig cells, tissues or organs are used. PERV-C infects only pig cells and is not present in the genomes of all pigs. However, PERV-A/C recombinants infecting human cells and characterized by high replication titers were found in pigs. To select PERV-C-free animals that cannot generate such recombinants, PCR-based assays were developed (Kaulitz et al., J Virol Methods, 175:60, 2011). When screening for PERV-C in German wild boars (Sus scrofa scrofa), applying these methods, a new variant of PERV-C was identified. Whereas in all 125 wild boar only the new variant of PERV-C was found, different variants were present in some landrace pigs, and most importantly, some pigs were totally free of PERV-C.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilson CA (2008) Porcine endogenous retroviruses and xenotransplantation. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:3399–33412
Boeke JD, Stoye JP (1997) Retrotransposons, endogenous retroviruses and the evolution of retroelements. In: Coffin JM, Hughes SH, Varmus HE (eds) Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, pp 343–436
Herniou E, Martin J, Miller K, Cook J, Wilkinson M, Tristem M (1998) Retroviral diversity and distribution in vertebrates. J Virol 72:5955–5966
Stoye JP (2001) Endogenous retroviruses: still active after all these years? Curr Biol 11:R914–R916
Denner J (2010) Endogenous retroviruses. In: Kurth R, Bannert N (eds) Retroviruses: molecular biology, genomics and pathogenesis. Caister Academic Press, Norwich, pp 35–69
Akiyoshi DE, Denaro M, Zhu H, Greenstein JL, Banerjee P, Fishman JA (1998) Identification of a full-length cDNA for an endogenous retrovirus of miniature swine. J Virol 72:4503–4507
Takeuchi Y, Patience C, Magre S, Weiss RA, Banerjee PT, Le Tissier P, Stoye JP (1998) Host range and interference studies of three classes of pig endogenous retrovirus. J Virol 72:9986–9991
Le Tissier P, Stoye JP, Takeuchi Y, Patience C, Weiss RA (1997) Two sets of human-tropic pig retrovirus. Nature 389:681–682
Patience C, Switzer WM, Takeuchi Y, Griffiths DJ, Goward ME, Heneine W, Stoye JP, Weiss RA (2001) Multiple groups of novel retroviral genomes in pigs and related species. J Virol 75:2771–2775
Patience C, Takeuchi Y, Weiss RA (1997) Infection of human cells by an endogenous retrovirus of pigs. Nat Med 3:282–286
Wilson CA, Wong S, VanBrocklin M, Federspiel MJ (2000) Extended analysis of the in vitro tropism of porcine endogenous retrovirus. J Virol 74:49–56
Specke V, Tacke S, Boller K, Schwendemann J, Denner J (2001) Porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs): In vitro host range and attempts to establish small animal models. J Gen Virol 82:837–844
Specke V, Rubant S, Denner J (2001) Productive infection of human primary cells and cell lines with porcine endogenous retroviruses. Virology 285:177–180
Lieber MM, Sherr CJ, Benveniste RE, Todaro GJ (1975) Biologic and immunologic properties of porcine type C viruses. Virology 66:616–619
Niebert M, Tönjes RR (2005) Evolutionary spread and recombination of porcine endogenous retroviruses in the suiformes. J Virol 79:649–654
Wood JC, Quinn G, Suling KM, Oldmixon BA, Van Tine BA, Cina R, Arn S, Huang CA, Scobie L, Onions DE, Sachs DH, Schuurman HJ, Fishman JA, Patience C (2004) Identification of exogenous forms of human-tropic porcine endogenous retrovirus in miniature swine. J Virol 78:2494–2501
Bartosch B, Stefanidis D, Myers R, Weiss R, Patience C, Takeuchi Y (2004) Evidence and consequence of porcine endogenous retrovirus recombination. J Virol 78:13880–13890
Harrison I, Takeuchi Y, Bartosch B, Stoye JP (2004) Determinants of high titer in recombinant porcine endogenous retroviruses. J Virol 78(13871):13879
Oldmixon BA, Woods JC, Ericsson TA, Wilson CA, White-Scharf ME et al (2002) Porcine endogenous retrovirus transmission characteristics of an inbred herd of miniature swine. J Virol 76:3045–3048
Dieckhoff B, Puhlmann J, Büscher K, Hafner-Marx A, Herbach N, Bannert N, Büttner M, Wanke R, Kurth R, Denner J (2007) Expression of porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs) in melanomas of Munich miniature swine (MMS) Troll. Vet Microbiol 123:53–68
Denner J (2008) Recombinant porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERV-A/C): a new risk for xenotransplantation? Arch Virol 153:1421–1426
Martin SI, Wilkinson R, Fishman JA (2006) Genomic presence of recombinant porcine endogenous retrovirus in transmitting miniature swine. Virol J 3:91–96
Denner J, Specke V, Thiesen U, Karlas A, Kurth R (2003) Genetic alterations of the long terminal repeat of an ecotropic porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV) during passage in human cells. Virology 314:125–133
Karlas A, Irgang M, Votteler J, Specke V, Ozel M, Kurth R, Denner J (2010) Characterisation of a human cell-adapted porcine endogenous retrovirus PERV-A/C. Ann Transplant 15:45–54
Scheef G, Fischer N, Krach U, Tönjes RR (2001) The number of a U3 repeat box acting as an enhancer in long terminal repeats of polytropic replication-competent porcine endogenous retroviruses dynamically fluctuates during serial virus passages in human cells. J Virol 75:6933–6940
Denner J, Schuurman H, Patience C (2009) The International Xenotransplantation Association consensus statement on conditions for undertaking clinical trials of porcine islet products in type 1 diabetes—Chapter 5: Strategies to prevent transmission of porcine endogenous retroviruses. Xenotransplantation 16:239–248
Dieckhoff B, Kessler B, Jobst D, Kues W, Petersen B, Pfeifer A, Kurth R, Niemann H, Wolf E, Denner J (2009) Distribution and expression of porcine endogenous retroviruses in multi-transgenic pigs generated for xenotransplantation. Xenotransplantation 16:64–73
Kaulitz D, Mihica D, Dorna J, Costa MR, Petersen B, Niemann H, Tönjes RR, Denner J (2011) Development of sensitive methods for detection of porcine endogenous retrovirus-C (PERV-C) in the genome of pigs. J Virol Methods 175:60–65
Mang R, Maas J, Chen X, Goudsmit J, van der Kuyl AC (2001) Identification of a novel type C porcine endogenous retrovirus: evidence that copy number of endogenous retroviruses increases during host inbreeding. J Gen Virol 32:1829–1834
Adlhoch C, Wolf A, Meisel H, Kaiser M, Ellerbrok H, Pauli G (2009) High HEV presence in four different wild boar populations in East and West Germany. Vet Microbiol 139:270–278
Adlhoch C, Kaiser M, Ellerbrok H, Pauli G (2010) High prevalence of porcine Hokovirus in German wild boar populations. Virol J 7:171
Preuss T, Fischer N, Boller K, Tonjes RR (2006) Isolation and characterization of an infectious replication-competent molecular clone of ecotropic porcine endogenous retrovirus class C. J Virol 80:10258–10261
Hector RD, Meikle S, Grant L, Wilkinson RA, Fishman JA, Scobie L (2007) Pre-screening of miniature swine may reduce the risk of transmitting human tropic recombinant porcine endogenous retroviruses. Xenotransplantation 14:222–226
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DE 729/4-3). We thank Kay-Martin Hanschmann, Paul Ehrlich Institute, Langen, Germany, for the probit analysis. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
705_2012_1490_MOESM1_ESM.ppt
Fig. S1. (A) Estimation of the efficiency of the duplex real-time PCR specific for the new variant (nv) of PERV-C. Dilution of a specific nv PERV-C amplicon (efficiency 107 %), and of a cyclophilin plasmid (efficiency 115 %). (B) Real-time PCR analysis of three different pigs for investigating the presence of PERV-C, PERV-C new variant and porcine cyclophilin. Primers and probes for PERV envC and the new variant of PERV envC were used. Notice that the residual low reactivity for PERV envC in pig 2 is due to the limited difference between the primers and the target. (PPT 1237 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaulitz, D., Mihica, D., Adlhoch, C. et al. Improved pig donor screening including newly identified variants of porcine endogenous retrovirus-C (PERV-C). Arch Virol 158, 341–348 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-012-1490-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-012-1490-9