Abstract
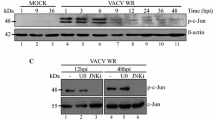
In this study, we describe the interaction between Araçatuba virus (ARAV), a naturally occurring Brazilian vaccinia virus isolated from an outbreak at a dairy farm, and the host cell’s signal transduction pathways. Even though ARAV infection led to phosphorylation of MAPKs MEK/ERK, JNK, and p38MAPK, genetic or pharmacological inhibition of these pathways had no impact on viral replication. We also provide evidence that ARAV stimulated the phosphorylation of Akt (PKB) at serine 473 (S473-P), a signaling event that is required for full activation of Akt during the infectious cycle. Furthermore, pharmacological inhibition of PI3K (LY294002) abrogated ARAV-induced Akt activation (S473-P) and affected early and late viral gene expression, which was followed by a decrease in virus yield (~1 log). Taken together, our data shed some light onto the biological differences between ARAV and vaccinia virus strain WR (VACV-WR), which could contribute, at least in part, to the low-virulence phenotype displayed by ARAV. Thus, while the requirement for the PI3K/Akt pathway for successful ARAV replication is also shared with VACV-WR and cowpox virus strain BR (CPXV-BR), ARAV showed a lower replicative capacity, as well as a smaller plaque-size phenotype after infection of A31 cells when compared to VACV-WR.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
McFadden G (2005) Poxvirus tropism. Nat Rev Microbiol 3(3):201–213
Morens DM, Folkers GK, Fauci AS (2004) The challenge of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Nature 430(6996):242–249
Condit RC, Moussatche N, Traktman P (2006) In a nutshell: structure and assembly of the vaccinia virion. Adv Virus Res 66:31–124
Trindade GS, Drumond BP, Guedes MIMC, Leite JA, Mota BEF, Campos MA, Fonseca FG, Nogueira ML, Lobato ZIP, Bonjardim CA, Ferreira PCP, Kroon EG (2007) Zoonotic vaccinia virus infection in Brazil: clinical description and implications for health professionals. J Clin Microbiol 45(4):1370–1372
Essbauer S, Pfeffer M, Meyer H (2010) Zoonotic Poxviruses. Vet Microbiol 140(3–4):229–236
Fonseca FG, Lanna MC, Campos MA, Kitajima EW, Peres JN, Golgher RR, Ferreira PC, Kroon EG (1998) Morphological and molecular characterization of the poxvirus BeAn 58058. Arch Virol 143(6):1171–1186
Damaso CR, Esposito JJ, Condit RC, Moussatché N (2000) An emergent poxvirus from humans and cattle in Rio de Janeiro State: Cantagalo virus may derive from Brazilian smallpox vaccine. Virology 277(2):439–449
de Souza Trindade G, Fonseca FG, Marques JT, Nogueira ML, Mendes LCN, Borges AS, Peiró JR, Pituco EM, Bonjardim CA, Ferreira PCP, Kroon EG (2003) Araçatuba virus: a vaccinialike virus associated with infection in humans and cattle. Emerg Infect Dis 9(2):155–160
Leite JA, Drumond BP, Trindade GS, Lobato ZIP, Fonseca FG, Santos JR, Madureira MC, Guedes MIMC, Ferreira JMS, Bonjardim CA, Ferreira PCP, Kroon EG (2005) Passatempo virus, a vaccinia virus strain, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis 11(12):1935–1938
Drumond BP, Leite JA, da Fonseca FG, Bonjardim CA, Ferreira PC, Kroon EG (2008) Brazilian Vaccinia virus strains are genetically divergent and differ from the Lister vaccine strain. Microbes Infect 10(2):185–197
Abrahão JS, Guedes MIM, Trindade GS, Fonseca FG, Campos RK, Mota BF, Lobato ZIP, Silva-Fernandez AT, Rodrigues GOL, Lima LS, Ferreira PCP, Bonjardim CA, Kroon EG (2009) One more piece in the VACV ecological puzzle: could peridomestic rodents be the link between wildlife and bovine Vaccinia outbreaks in Brazil? PLoS ONE 4(10):e7428
Medaglia ML, Pessoa LC, Sales ER, Freitas TR, Damaso CR (2009) Spread of cantagalo virus to northern of Brasil. Emerg Infect Dis 15(7):1142–1143
Ferreira JM, Drumond BP, Guedes MI, Pascoal-Xavier MA, Almeida-Leite CM, Arantes RM, Mota BE, Abrahão JS, Alves PA, Oliveira FM, Ferreira PC, Bonjardim CA, Lobato ZIP, Kroon EG (2008) Virulence in murine model shows the existence of two distinct populations of Brazilian Vaccinia virus strains. PLoS One 3(8):e3043
Pan H, Xie J, Ye F, Gao SJ (2006) Modulation of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection and replication by MEK/ERK, JNK, and p38 multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways during primary infection. J Virol 80(11):5371–5382
Rahaus M, Desloges N, Wolff MH (2006) Varicella-zoster virus influences the activities of components and targets of the ERK signaling pathway. J Gen Virol 87(Pt 4):749–758
Zapata HJ, Nakatsugawa M, Moffat JF (2007) Varicella-zoster virus infection of human fibroblast cells activates the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. J Virol 81(2):977–990
Lee CJ, Liao CL, Lin YL (2005) Flavivirus activates phosphatidyl- inositol 3-kinase signaling to block caspase-dependent apoptotic cell death at the early stage of virus infection. J Virol 79(13):8388–8399
He Y, Nakao H, Tan SL, Polyak SJ, Neddermann P, Vijaysri S, Jacobs BL, Katze MG (2002) Subversion of cell signaling pathways by hepatitis C virus nonstructural 5A protein via interaction with Grb2 and P85 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Virol 76(18):9207–9217
Wolf D, Witte V, Laffert B, Blume K, Stromer E, Trapp S, d’Aloja P, Schurmann A, Baur AS (2001) HIV-1 Nef associated PAK and PI3-kinases stimulate Akt-independent Bad-phosphorylation to induce anti-apoptotic signals. Nat Med 7(11):1217–1224
Lu Z, Hu X, Li Y, Zheng L, Zhou Y, Jiang H, Ning T, Basang Z, Zhang C, Ke Y (2004) Human papillomavirus 16 E6 oncoprotein interferences with insulin signaling pathway by binding to tuberin. J Biol Chem 279(34):35664–35670
de Magalhães JC, Andrade AA, Silva PN, Sousa LP, Ropert C, Ferreira PC, Kroon EG, Gazzinelli RT, Bonjardim CA (2001) A mitogenic signal triggered at an early stage of vaccinia virus infection: implication of MEK/ERK and protein kinase A in virus multiplication. J Biol Chem 276(42):38353–38360
Andrade AA, Silva PNG, Pereira ACTC, Sousa LP, Ferreira PCP, Gazzinelli RT, Kroon EG, Ropert C, Bonjardim CA (2004) The vaccinia virus-stimulated mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is required for virus multiplication. Biochem J 381(Pt 2):437–446
Silva PN, Soares JA, Brasil BS, Nogueira SV, Andrade AA, de Magalhães JC, Bonjardim MB, Ferreira PC, Kroon EG, Bruna-Romero O, Bonjardim CA (2006) Differential role played by the MEK/ERK/EGR-1 pathway in orthopoxviruses vaccinia and cowpox biology. Biochem J 398(1):83–95
Soares JAP, Leite FGG, Andrade LG, Torres AA, Sousa LP, Barcelos LS, Teixeira MM, Ferreira PCP, Kroon EG, Souto-Padrón T, Bonjardim CA (2009) Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway early during vaccinia an cowpox virus infections is required for both host survival and viral replication. J Virol 83(13):6883–6899
Virolle T, Adamson ED, Baron V, Birle D, Mercola D, Mustelin T, de Belle I (2001) The Egr-1 transcription factor directly activates PTEN during irradiation-induced signalling. Nat Cell Biol 3(12):1124–1128
Davis RJ (2000) Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103(2):239–252
Tournier C, Hess P, Yang DD, Xu J, Turner TK, Nimnual A, Bar-Sagi D, Jones SN, Flavell RA, Davis RJ (2000) Requirement of JNK for stress-induced activation of the cytochrome c-mediated death pathway. Science 288(5467):870–874
Joklik WK (1962) The purification of four strains of poxvirus. Virology 18:9–18
Werden SJ, McFadden G (2008) The role of cell signaling in poxvirus tropism: the case of the M-T5 host range protein of myxoma virus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784(1):228–237
Johnston JB, McFadden G (2003) Poxvirus immunomodulatory strategies: current perspectives. J Virol 77(11):6093–6100
Cooray S (2004) The pivotal role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt signal transduction in virus survival. J Gen Virol 85(Pt 85):1065–1076
Trindade GS, Emerson GL, Carroll DS, Kroon EG, Damon IK (2007) Brazilian vaccinia virus and their origins. Emerg Infect Dis 13(7):965–972
Mathew EC, Sanderson CM, Hollinshead R, Smith GL (2001) A mutational analysis of the vaccinia virus B5R protein. J Gen Virol 82(Pt 5):1199–1213
Aldaz-Carroll L, Whitbeck JC, Ponce de Leon M, Lou H, Hirao L, Isaacs SN, Moss B, Eisenberg RJ, Cohen GH (2005) Epitope-mapping studies define two major neutralization sites on the Vaccinia virus extracellular enveloped virus glycoprotein B5R. J Virol 79(10):6260–6271
Saijo M, Ami Y, Suzaki Y, Nagata N, Iwata N, Hasegawa H, Ogata M, Fukushi S, Mizutani T, Sata T, Kurata T, Kurane I, Morikawa S (2006) LC16m8, a highly attenuated vaccinia virus vaccine lacking expression of the membrane protein B5R, protects monkeys from monkeypox. J Virol 80(11):5179–5188
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Angela S. Lopes, Ilda M. V. Gama, João R. dos Santos, and Andreza A. Carvalho for their secretarial and technical assistance. We also thank Dr. Bruno S.A.F. Brasil for critical reading of the manuscript. We are grateful to Dr. M. C. Sogayar (Department of Biochemistry, University of São Paulo, Brazil), who kindly provided us with the A31 cell line, and Dr. R. Davis (Howard Hughes Medical Institute, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, USA) for the WT and JNK1/2 double KO cells. WT and egr-1 KO cells were kindly provided by Dr. E. Adamson (The Burnham Institute, Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA, USA). The rabbit polyclonal antibodies against viral proteins CrmA/SPI-2 were a gift from Dr. D. Pickup (Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC, USA), and A17, D8, F18 and H3 were from Dr. B. Moss (NIAID, Bethesda, MD, USA). The rabbit polyclonal antibody against the viral A3 protein was from Dr. P. Traktman (Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA). This work was supported by Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), Coordenadoria de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Brazilian Ministry of Culture, Science, and Technology, and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). MHAF was a recipient and LCO is recipient of a pre-doctoral fellowship from CNPq. FLBM is recipient of an undergraduate fellowship from CNPq (PIBIC). CAB, EGK, GST and PCPF are recipients of research fellowships from CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Freitas, M.H.A., de Oliveira, L.C., Mügge, F.L.B. et al. The interplay between Araçatuba virus and host signaling pathways: role of PI3K/Akt in viral replication. Arch Virol 156, 1775–1785 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-011-1052-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-011-1052-6