Abstract
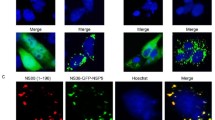
Nonstructural proteins of members of the family Reoviridae are believed to play significant roles in the virus replication cycle. Phylogenetic analyses indicate that the nonstructural protein NS80 of grass carp reovirus, encoded by a gene of Segment 4 (S4), is a primary determinant that is related to the formation of viroplasmic inclusion bodies (VIB), where viral replication and assembly are thought to occur. To understand the role of the NS80 protein in viral replication, an initial investigation of NS80 gene expression in both infected and transfected cells was conducted. Transmission electron microscopy results indicate that replication and assembly of GCRV occur within VIB-like structures in the perinuclear region of the cell cytoplasm. Furthermore, expression of the S4 gene in infected cells was detected with an NS80-specific antibody by western blot and immunofluorescence. Moreover, globular VIB-like structures were observed when expressing GFP-derived full-length NS80 (pEGFP-C1/NS80) and recombinants containing the C-terminal conserved region (pEGFP-C1/NS80335–724) in transfected Vero. No such structures were detected in cells transfected with an N-terminal recombinant (pEGFP-C1/NS801–334), suggesting that the NS80 C-terminal conserved region may be involved in the formation of inclusion structures. These data provide a foundation for further functional studies of NS80 related to viral inclusion formation in viral replication.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold MM, Murray KE, Nibert ML (2008) Formation of the factory matrix is an important, though not a sufficient function of nonstructural protein μNS during reovirus infection. Virology 375:412–423
Attoui H, Fang Q, Mohd JF, Cantaloube JF, Biagini P, Micco P, Lamballerie X (2002) Common evolutionary origin of aquareoviruses and orthoreoviruses revealed by genome characterization of golden shiner reovirus, grass carp reovirus, striped bass reovirus and golden ide reovirus (genus Aquareovirus, family Reoviridae). J Gen Virol 83:1941–1951
Attoui H, Jaafar FM, Belhouchet M, Biagini P, Cantaloube JF, de Micco P, de Lamballerie X (2005) Expansion of family Reoviridae to include nine-segmented dsRNA viruses: isolation and characterization of a new virus designated Aedes pseudoscutellaris reovirus assigned to a proposed genus Dinovernavirus. Virology 343:212–223
Broering TJ, Mccutcheon AM, Centonze V, Nibert ML (2000) Reovirus nonstructural protein μNS binds to core particles but does not inhibit their transcription and capping activities. J Virol 74(12):5516–5524
Broering TJ, Parker JSL, Joyce PL, Kim J, Nibert ML (2002) Mammalian reovirus nonstructural protein μNS forms large inclusions and colocalizes with reovirus microtubule-associated protein μ2 in transfected cells. J Virol 76:8285–8297
Broering TJ, Kim J, Miller CL, Piggott CDS, Dinoso JB, Nibert ML, Parker JSL (2004) Reovirus nonstructural protein μNS recruits viral core surface proteins and entering core particles to factory-like inclusions. J Virol 87(4):1882–1892
Broering TJ, Arnold MM, Miller CL, Hurt JA, Joyce PL, Nibert ML (2005) Carboxyl-proximal regions of reovirus nonstructural protein μNS necessary and sufficient for forming factory-like inclusions. J Virol 79:6194–6206
Brookes SM, Hyatt AD, Eaton BT (1993) Characterization of virus inclusion bodies in bluetongue virus-infected cells. J Gen Virol 74:525–530
Cheng LP, Fang Q, Shah S, Atanasov IC, Zhou ZH (2008) Subnanometer-resolution structures of the grass carp reovirus core and virion. J Mol Biol 382:213–222
Cheng LP, Zhu J, Hui WH, Zhang XK, Honig B, Fang Q, Zhou ZH (2010) Backbone model of an aquareovirus virion by cryo-electron microscopy and bioinformatics. J Mol Biol 397:852–863
Eichwald C, Rodriguez JF, Burrone OR (2004) Characterization of rotavirus NSP2/NSP5 interactions and the dynamics of viroplasm formation. J Gen Virol 85:625–634
Estes MK (2001) Rotaviruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE (eds) Fields virology, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1747–1786
Fan C, Zhang LL, Lei CF, Fang Q (2009) Expression and identification of inclusion forming-related domain of NS80 nonstructural protein of grass carp reovirus. Virol Sin 24:194–201
Fang Q, Ke L, Cai Y (1989) Growth characterization and high titre culture of GCHV. Virol Sin 3:314–339
Fang Q, Attoui H, Cantaloube JF, Biagini P, Zhu Z, de Micco P, de Lamballerie X (2000) Sequence of genome segments 1, 2, and 3 of the grass carp reovirus (genus Aquareovirus, family Reoviridae). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 274:762–766
Fang Q, Seng EK, Ding QQ, Zhang LL (2008) Characterization of infectious particles of grass carp reovirus by treatment with proteases. Arch Virol 153:675–682
Fang Q, Sanket S, Liang YY, Zhou ZH (2005) 3D reconstruction and capsid protein characterization of grass carp reovirus. Sci China Ser C Life Sci 48:593–600
Kar AK, Bhattacharya B, Roy P (2007) Bluetongue virus RNA binding protein NS2 is a modulator of viral replication and assembly. BMC Mol Biol 8:4
Ke L, Fang Q, Cai Y (1990) Characteristics of a new isolation of hemorrhagic virus of grass carp. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 14:153–159 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Kobayashi T, Ooms LS, Chappell JD, Dermody TS (2009) Identification of functional domains in reovirus replication proteins μNS and μ2. J Virol 83:2892–2906
Mertens PPC, Attoui H, Duncan R, Dermody TS (2005) Reoviridae. In: Fauquet CM, Mayo MA, Maniloff J, Desselberger U, Ball LA (eds) Virus taxonomy. Eighth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Elsevier, London, pp 447–454
Miller CL, Arnold MM, Broering TJ, Hastings CE, Nibert ML (2010) Localization of mammalian orthoreovirus proteins to cytoplasmic factory-like structures via nonoverlapping regions of μNS. J Virol 84:867–882
Miller DJ, Schwartz MD, Ahlquist P (2001) Flock house virus RNA replicates on outer mitochondrial membranes in Drosophila cells. J Virol 75:11664–11676
Mohd Jaafar F, Fang Q, Attoui H (2008) Complete characterisation of the American grass carp reovirus genome (genus Aquareovirus: family Reoviridae) reveals an evolutionary link between aquareoviruses and coltiviruses. Virology 373:310–321
Nibert ML, Schiff LA, Fields BN (2001) Reoviruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds) Field virology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1679–1728
Parker JSL, Broering TJ, Kim J, Higgins DE, Nibert ML (2002) Reovirus core protein μ2 determines the filamentous morphology of viral inclusion bodies by interacting with and stabilizing microtubules. J Virol 76:4483–4496
Rangel AAC, Rockemann DD, Hetrick FM, Samal SK (1999) Identification of grass carp hemorrhage virus as a new genogroup of aquareovirus. J Gen Virol 80:2399–2402
Roizman B, Knipe DM (2001) Herpes simplex viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE (eds) Fields virology, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 2399–2460
Silvestri LS, Taraporewala ZF, Patton JT (2004) Rotavirus replication: plus-sense templates for double-stranded RNA synthesis are made in viroplasms. J Virol 78:7763–7774
Touris-Otero F, Cortez-San Martín M, Martínez-Costas J, Benavente J (2004) Avian reovirus morphogenesis occurs within viral factories and begins with the selective recruitment of σNS and λA to μNS inclusions. J Mol Biol 341:361–374
Touris-Otero F, Martinez-Costas J, Vakharia VN, Benavente J (2004) Avian reovirus nonstructural protein μNS forms viroplasm-like inclusions and recruits protein σNS to these structures. Virology 319:94–106
Wei T, Shimizu T, Hagiwara K, Kikuchi A, Moriyasu Y, Suzuki N, Chen H, Omura T (2006) Pns12 protein of rice dwarf virus is essential for formation of viroplasms and nucleation of viral-assembly complexes. J Gen Virol 87:429–438
Zhang LL, Lei CF, Fan C, Fang (2009) Expression of outer capsid protein VP5 of grass carp reovirus in E. coli and analysis of its immunogenicity. Virol Sin 24:545–551
Zhang Y, Guo D, Geng H, Liu M, Hu Q, Wang J, Tong G, Kong X, Liu N, Liu C (2007) Characterization of M-class genome segments of muscovy duck reovirus S14. Virus Res 125:42–53
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Simon Rayner for critical reading of the manuscript, and Ms. Xiaoyun Sun for assistance in experiments. This work was partly supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2009CB118701) and the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (30871940).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, C., Shao, L. & Fang, Q. Characterization of the nonstructural protein NS80 of grass carp reovirus. Arch Virol 155, 1755–1763 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-010-0753-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-010-0753-6